Abstract
Background
Aberrant expression of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) is associated with the progression of human cancers, including gastric cancer (GC). The function of lncRNA DLGAP1-AS2, as a promising oncogene, has been identified in several human cancers. Therefore, this study was aimed to explore the association of DLGAP1-AS2 with gastric tumorigenesis, as well.
Methods and results
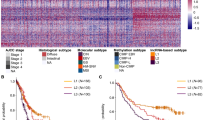
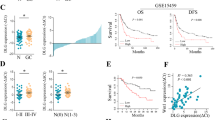
The expression level of DLGAP1-AS2 was initially pre-evaluated in GC datasets from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO). Moreover, qRT-PCR experiment was performed on 25 GC and 25 adjacent normal tissue samples. The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data were also analyzed for further validation. Consistent with data obtained from GEO datasets, qRT-PCR results revealed that DLGAP1-AS2 was significantly (p < 0.0032) upregulated in GC specimens compared to normal samples, which was additionally confirmed using TCGA analysis (p < 0.0001). DLGAP1-AS2 expression level was also correlated with age (p = 0.0008), lymphatic and vascular invasion (p = 0.0415) in internal samples as well as poor survival of GC patients (p = 0.00074) in GEO datasets. Also, Gene Ontology analysis illustrated that DLGAP1-AS2 may be involved in the cellular process, including hippo signaling, regulated by YAP1, as its valid downstream target, in GC samples. Moreover, ROC curve analysis showed the high accuracy of the DLGAP1-AS2 expression pattern as a diagnostic biomarker for GC.
Conclusion
Our findings indicated that DLGAP1-AS2 might display oncogenic properties through gastric tumorigenesis and could be suggested as a therapeutic, diagnostic, and prognostic target.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated in this study are available in the manuscript. This manuscript is published as a preprint with https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-529611/v1
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Necula L, Matei L, Dragu D, Neagu AI, Mambet C, Nedeianu S, Chivu-Economescu M (2019) Recent advances in gastric cancer early diagnosis. World J Gastroenterol 25(17):2029–2044. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i17.2029
Thrift AP, El-Serag HB (2020) Burden of gastric cancer. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 18(3):534–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.045
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68(6):394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: Cancer J Clin 68(6):394–424
Sitarz R, Skierucha M, Mielko J, Offerhaus GJA, Maciejewski R, Polkowski WP (2018) Gastric cancer: epidemiology, prevention, classification, and treatment. Cancer Manag Res 10:239–248. https://doi.org/10.2147/cmar.s149619
Cuzzuol BR, Vieira ES, Araújo GRL, Apolonio JS, de Carvalho LS, da Silva Junior RT, de Melo FF (2020) Gastric cancer: a brief review, from risk factors to treatment. Arch Gastroenterol Res 1(2):34–39
Marin J, Al-Abdulla R, Lozano E, Briz O, Bujanda L, Banales M, Macias R (2016) Mechanisms of resistance to chemotherapy in gastric cancer. ACAMC 16(3):318–334
Shi WJ, Gao JB (2016) Molecular mechanisms of chemoresistance in gastric cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol 8(9):673–681. https://doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v8.i9.673
Amini M, Ghorban K, Mokhtarzadeh A, Dadmanesh M, Baradaran B (2020) CD40 DNA hypermethylation in primary gastric tumors; as a novel diagnostic biomarker. Life Sci 254:117774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117774
Padmanabhan N, Ushijima T, Tan P (2017) How to stomach an epigenetic insult: the gastric cancer epigenome. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 14(8):467
Nasrollahzadeh-Khakiani M, Emadi-Baygi M, Schulz WA, Nikpour P (2016) Long noncoding RNAs in gastric cancer carcinogenesis and metastasis. Brief Funct Genom 16(3):129–145. https://doi.org/10.1093/bfgp/elw011
Li H, Yu B, Li J, Su L, Yan M, Zhu Z, Liu B (2014) Overexpression of lncRNA H19 enhances carcinogenesis and metastasis of gastric cancer. Oncotarget 5(8):2318
Li T, Mo X, Fu L, Xiao B, Guo J (2016) Molecular mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs on gastric cancer. Oncotarget 7(8):8601–8612. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.6926
Tan H, Zhang S, Zhang J, Zhu L, Chen Y, Yang H, Liu B (2020) Long non-coding RNAs in gastric cancer: New emerging biological functions and therapeutic implications. Theranostics 10(19):8880
Xiao N, Hu Y, Juan L (2020) Comprehensive analysis of differentially expressed lncRNAs in gastric cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:557
Foroughi K, Amini M, Atashi A, Mahmoodzadeh H, Hamann U, Manoochehri M (2018) Tissue-specific down-regulation of the long non-coding RNAs PCAT18 and LINC01133 in gastric cancer development. Int J Mol Sci 19(12):3881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123881
Yang F, Bi J, Xue X, Zheng L, Zhi K, Hua J, Fang G (2012) Up-regulated long non-coding RNA H19 contributes to proliferation of gastric cancer cells. Febs j 279(17):3159–3165. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08694.x
Yang F, Xue X, Bi J, Zheng L, Zhi K, Gu Y, Fang G (2013) Long noncoding RNA CCAT1, which could be activated by c-Myc, promotes the progression of gastric carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 139(3):437–445. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1324-x
Yang F, Xue X, Zheng L, Bi J, Zhou Y, Zhi K, Fang G (2014) Long non-coding RNA GHET1 promotes gastric carcinoma cell proliferation by increasing c-Myc mRNA stability. FEBS J 281(3):802–813. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.12625
Zhang EB, Han L, Yin DD, Kong R, De W, Chen J (2014) c-Myc-induced, long, noncoding H19 affects cell proliferation and predicts a poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. Med Oncol 31(5):914. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0914-7
Zhuang M, Gao W, Xu J, Wang P, Shu Y (2014) The long non-coding RNA H19-derived miR-675 modulates human gastric cancer cell proliferation by targeting tumor suppressor RUNX1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 448(3):315–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.12.126
Li J, Xu Q, Wang W, Sun S (2019) MIR100HG: a credible prognostic biomarker and an oncogenic lncRNA in gastric cancer. Biosci Reps. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20190171
Liu H, Wu N, Zhang Z, Zhong X, Zhang H, Guo H, Liu Y (2019) Long non-coding RNA LINC00941 as a potential biomarker promotes the proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer. Front Genet 10:5
Yang Z, Guo X, Li G, Shi Y, Li L (2016) Long noncoding RNAs as potential biomarkers in gastric cancer: opportunities and challenges. Cancer Lett 371(1):62–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2015.11.011
Chen K, Zhang Z, Yu A, Li J, Liu J, Zhang X (2020) lncRNA DLGAP1-AS2 knockdown inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion by regulating miR-154-5p methylation. BioMed Res Int 200:1–6
Liu Z, Pan L, Yan X, Duan X (2020) The long noncoding RNA DLGAP1-AS2 facilitates cholangiocarcinoma progression via miR-505 and GALNT10. FEBS Open Bio. https://doi.org/10.1002/2211-5463.13061
Miao W, Li N, Gu B, Yi G, Su Z, Cheng H (2020) LncRNA DLGAP1-AS2 modulates glioma development by up-regulating YAP1 expression. J Biochem 167(4):411–418
Matsuoka T, Yashiro M (2018) Biomarkers of gastric cancer: current topics and future perspective. World J Gastroenterol 24(26):2818–2832. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i26.2818
Fang XY, Pan HF, Leng RX, Ye DQ (2015) Long noncoding RNAs: novel insights into gastric cancer. Cancer Lett 356(2):357–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2014.11.005
Ma Z, Liu X, Paul ME, Chen M, Zheng P, Chen H (2021) Comparative investigation of early-onset gastric cancer. Oncol Lett 21(5):1–6
Hu X, Xin Y, Xiao Y, Zhao J (2014) Overexpression of YAP1 is correlated with progression, metastasis and poor prognosis in patients with gastric carcinoma. Pathol Oncol Res 20(4):805–811. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-014-9757-y
Kang W, Tong JH, Chan AW, Lee TL, Lung RW, Leung PP, To KF (2011) Yes-associated protein 1 exhibits oncogenic property in gastric cancer and its nuclear accumulation associates with poor prognosis. Clin Cancer Res 17(8):2130–2139. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-10-2467
Liu J, Zhao X, Wang K, Zhang X, Yu Y, Lv Y, Li J (2019) A novel YAP1/SLC35B4 regulatory axis contributes to proliferation and progression of gastric carcinoma. Cell Death Dis 10(6):452. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1674-2
Sun D, Li X, He Y, Li W, Wang Y, Wang H, Xin Y (2016) YAP1 enhances cell proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget 7(49):81062–81076. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.13188
Yu L, Gao C, Feng B, Wang L, Tian X, Wang H, Ma D (2017) Distinct prognostic values of YAP1 in gastric cancer. Tumour Biol. https://doi.org/10.1177/1010428317695926
Kang W, Cheng AS, Yu J, To KF (2016) Emerging role of Hippo pathway in gastric and other gastrointestinal cancers. World J Gastroenterol 22(3):1279
Funding
The authors are grateful for supports from the Immunology Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
R.S and M.Am performed the majority of experiments and data analysis. S.A contributed to carrying out the experiments and interpreted the results; M.AM and H.B helped with project design; M.M.M and N.B wrote the manuscript. B.B and A.J contributed to designing the project; M.As helped with sample preparation. A.M revised the manuscript, designed and conducted the project.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the ethical committee of Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran.
Consent to participate
All of the patients who participated in the study had given written informed consent.
Consent for publication
Patients signed informed consent regarding publishing their data.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soltani, R., Amini, M., Mazaheri Moghaddam, M. et al. LncRNA DLGAP1-AS2 overexpression associates with gastric tumorigenesis: a promising diagnostic and therapeutic target. Mol Biol Rep 49, 6817–6826 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-07038-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-07038-w