Abstract
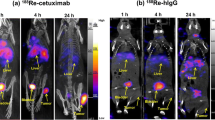
To assess the preclinical potential of technetium-99m labelled conjugated para-isothiocyanato-benzyl diethylene triamine penta-acetic acid cetuximab (99mTc-p-SCN-Bzl-DTPA cetuximab) for imaging EGFR in HNSCC mice and rabbits xenografts. Cetuximab, a chimeric monoclonal antibody targeting EGFR, was conjugated with p-SCN-Bzl-DTPA followed by labelling with 99mTc. The labelled conjugate was evaluated for in vitro stability in L−cysteine at 37 °C. The 99mTc-p-SCN-Bzl-DTPA cetuximab was also investigated for immunoreactivity, internationalization kinetics, dose escalation (up to 300 µg) and biodistribution in HNSCC mice xenograft. The suitability of labelled moiety as a specific EGFR radio-tracer was assessed in HNSCC rabbit xenograft. 99mTc-p-SCN-Bzl-DTPA cetuximab exhibited more than 98% radiochemical purity at room temperature. In excess L−cysteine, it showed a stable behaviour at 37 °C up to 4 h p.l. The labelled conjugate was internalized in vitro in FaDu tumor cells up to 19.55%. Significantly higher uptake in tumor (at 10 µg; 34.75 ± 0.38% ID/g: pi) was seen in HNSCC mice xenograft with dose escalation assay from 1 to 300 µg/mouse. Blocking of EGFR with excess cetuximab consequently decreased the uptake of tumor up to 6.80 ± 1.25%. SPECT images of rabbit xenograft confirmed increase in tumor to background ratio after 4 h pi and validated its potential in preclinical trial as a specific FaDu tumor tracer. Our in vitro and in vivo preclinical findings indicate that the 99mTc-p-SCN-Bzl-DTPA cetuximab prepared at optimal dose of cetuximab could become a useful tool for EGFR imaging in HNSCC using SPECT.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chong CR, Janne PA (2013) The quest to overcome resistance to EGFR-targeted therapies in cancer. Nat Med 19:1389–1400
Scaltriti M, Baselga J (2006) The epidermal growth factor receptor pathway: a model for targeted therapy. Clin Cancer Res 12:5268–5272
Nicholson RI, Gee JM, Harper ME (2001) EGFR and cancer prognosis. Eur J Cancer 37:S9–S15
Schlomm T, Kirstein P, Iwers L et al (2007) Clinical significance of epidermal growth factor receptor protein overexpression and gene copy number gains in prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13:6579–6584
Parra HS, Cavina R, Latteri F et al (2004) Analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor expression as a predictive factor for response to gefitinib (‘Iressa’, ZD1839) in non-small-cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 91:208–212
Zlobec I, Vuong T, Hayashi S et al (2007) A simple and reproducible scoring system for EGFR in colorectal cancer: application to prognosis and prediction of response to preoperative brachytherapy. Br J Cancer 96:793–800
Garousi J, Andersson KG, Mitran B et al (2016) PET imaging of epidermal growth factor receptor expression in tumours using 89Zr-labelled ZEGFR:2377 affibody molecules. Int J Oncol 48:1325–1332
Menke-van der Houven van Oordt CW, Gootjes EC, Huisman MC et al. 89Zr-cetuximab PET imaging in patients with advanced colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 2015;6:30384–30393
Nayak TK, Regino CA, Wong KJ et al (2010) PET imaging of HER1-expressing xenografts in mice with 86Y-CHX-A’’-DTPA-cetuximab. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 37:1368–1376
Eiblmaier M, Meyer LA, Watson MA, Fracasso PM, Pike LJ, Anderson CJ (2008) Correlating EGFR expression with receptor-binding properties and internalization of 64Cu-DOTA-cetuximab in 5 cervical cancer cell lines. J Nucl Med 49:1472–1479
Yun M, Kim DY, Lee JJ et al (2017) A high-affinity repebody for molecular imaging of EGFRexpressing malignant tumors. Theranostics 7:2620–2633
Hwang DE, Ryou JH, Oh JR, Han JW, Park TK, Kim HS (2016) Anti-human VEGF repebody effectively suppresses choroidal neovascularization and vascular leakage. PLoS ONE 11:e0152522
Lee JJ, Choi HJ, Yun M et al (2015) Enzymatic prenylation and oxime ligation for the synthesis of stable and homogeneous protein-drug conjugates for targeted therapy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 54:12020–12024
Lee JJ, Kim HJ, Yang C-S et al (2014) A high-affinity protein binder that blocks the IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway effectively suppresses non–small cell lung cancer. Mol Ther 22:1254-
Kim JY, Park H, Lee JC et al (2009) A simple Cu-64 production and its application of Cu-64 ATSM. Appl Radiat Isot 67:1190–1194
Cai W, Chen K, Mohamedali KA et al (2006) PET of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor expression. J Nucl Med 47:2048–2056
Yang CH, Chou HC, Fu YN et al (2015) EGFR over-expression in non-small cell lung cancers harboring EGFR mutations is associated with marked down-regulation of CD82. Biochim Biophys Acta 1852:1540–1549
Cross DA, Ashton SE, Ghiorghiu S et al (2014) AZD9291, an irreversible EGFR TKI, overcomes T790M-mediated resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Discov 4:1046–1061
Petrulli JR, Sullivan JM, Zheng MQ et al (2013) Quantitative analysis of [11C]-erlotinib PET demonstrates specific binding for activating mutations of the EGFR kinase domain. Neoplasia 15:1347–1353
Cooper MS, Ma MT, Sunassee K et al (2012) Comparison of 64Cu-complexing bifunctional chelators for radioimmunoconjugation: labeling efficiency, specific activity, and in vitro/in vivo stability. Bioconjug Chem 23:1029–1039
Schechter NR, Wendt RE, Yang DJ et al (2004) Radiation dosimetry of 99mTc-labeled C225 in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. J Nucl Med 45:1683–1687
Wen X, Wu QP, Ke S et al (2001) Conjugation with (111)InDTPA-poly(ethylene glycol) improves imaging of anti-EGF receptor antibody C225. J Nucl Med 42:1530–1537
Li WP, Meyer LA, Capretto DA et al (2008) Receptor-binding, biodistribution, and metabolism studies of 64Cu-DOTA-cetuximab, a PET-imaging agent for epidermal growth-factor receptor-positive tumors. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 23:158–171
Perk LR, Visser GW, Vosjan MJ et al (2005) (89)Zr as a PET surrogate radioisotope for scouting biodistribution of the therapeutic radiometals (90)Y and (177)Lu in tumor-bearing nude mice after coupling to the internalizing antibody cetuximab. J Nucl Med 46:1898–1906
Nayak TK, Regino CA, Wong KJ et al (2010) PET imaging of HER1-expressing xenografts in mice with 86Y-CHX-A″- DTPA-cetuximab. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 37:1368–1376
Shah SQ, Gul-E-Raana, Uddin G (2018) Imaging prostate cancer (PCa) with [99mTc(CO)3finasteride dithiocarbamate. J Labelled Comp Radiopharm 61:550–556
Brady ED, Chong HS, Milenic DE, Brechbiel MW (2004) Development of a spectroscopic assay for bifunctional ligand-protein conjugates based on copper. Nucl Med Boil 31:795–802
Shah SQ, Mahmood S (2018) Evaluation of 99mTc-labeled bevacizumab-N-HYNIC conjugate in human ovarian tumor xenografts. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 33:96–102
Koenig JA, Kaur R, Dodgeon I, Edwardson JM, Humphrey PP (1998) Fates of endocytosed somatostatin sst2 receptors and associated agonists. Biochem J 336:291–298
Cai W, Chen K, He L, Cao Q, Koong A, Chen X (2007) Quantitative PET of EGFR expression in xenograft-bearing mice using 64Cu-labeled cetuximab, a chimeric anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 34:850–858
Niu G, Sun X, Cao Q et al (2010) Cetuximab-based immunotherapy and radioimmunotherapy of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 16:2095–2105
Goldenberg A, Masui H, Divgi C et al (1989) Imaging of human tumor xenografts with an indium-111-labeled anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody. J Natl Cancer Inst 81:1616–1625
Niu G, Li Z, Xie J, Le QT, Chen X (2009) PET of EGFR antibody distribution in head andneck squamous cell carcinoma models. J Nucl Med 50:1116–1123
Kareem H, Sandstrom K, Elia R et al (2010) Blocking EGFR in the liver improves the tumor-to-liver uptake ratio of radiolabeled EGF. Tumor Biol 31:79–87
Divgi CR, Welt S, Kris M et al (1991) Phase I and imaging trial of indium 111-labeledanti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody 225 in patients withsquamous cell lung carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 83:97–104
Milenic DE, Wong KJ, Baidoo KE et al (2008) Cetuximab: preclinical evaluation of a monoclonal antibody targeting EGFR for radioimmunodiagnostic and radioimmunotherapeutic applications. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 23:619–631
Acknowledgements
We thank the Higher Education Commission (HEC), Islamabad, Pakistan for providing all sorts of financial assistance under National Research Program for Universities. The instant study is part of the HEC funded research grant No. 3122.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GR performed conjugation of cetuximab with p-SCN-Bzl-DTPA, labeling with radionuclide, in vitro studies and biodistribution in animal model mice. SQS performed the imaging studies using rabbit xenograft. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
No human was involved in this study. Experiments on mice and rabbits models were executed in compliance with Nuclear Medicine Research Laboratory (NMRL) and approval of ethics committee at Institute of Chemical Sciences (ICS), University of Peshawar.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shah, S.Q., Gul-e-Raana Synthesis and preclinical investigation of 99mTc-p-SCN-Bzl-DTPA-cetuximab for targeting EGFR using head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) xenografts. Mol Biol Rep 46, 1675–1682 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-019-04616-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-019-04616-x