Abstract
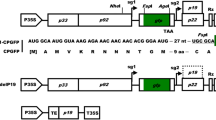
Plants are becoming an interesting alternative system for the heterologous production of pharmaceutical proteins, providing a more scalable, cost-effective, and biologically safer option than the current expression systems. The development of plant virus expression vectors has allowed rapid and high-level transient expression of recombinant genes, and, in turn, provided an attractive plant-based production platform. Here we report the development of vectors based on the tobamovirus Pepper mild mottle virus (PMMoV) to be used in transient expression of foreign genes. In this PMMoV vector, a middle part of the viral coat protein gene was replaced by the green fluorescent protein (GFP) gene, and this recombinant genome was assembled in a binary vector suitable for plant agroinoculation. The accumulation of GFP was evaluated by observation of green fluorescent signals under UV light and by western blotting. Furthermore, by using this vector, the multiepitope gene for chikungunya virus was successfully expressed and confirmed by western blotting. This PMMoV-based vector represents an alternative system for a high-level production of heterologous protein in plants.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yusibov V, Streatfield SJ, Kushnir N (2011) Clinical development of plant-produced recombinant pharmaceuticals: vaccines, antibodies, and beyond. Hum Vaccin 7:313–321
Paul M, Ma JK-C (2011) Plant-made pharmaceuticals: leading products and production platforms. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 58:58–67
Baulcombe DC, Chapman S, Santa Cruz S (1995) Jellyfish green fluorescent protein as a reporter for virus infections. Plant J 7:1045–1053
Burch-Smith TM, Anderson JC, Martin GB, Dinesh-Kumar SP (2004) Applications and advantages of virus-induced gene silencing for gene function studies in plants. Plant J 39:734–746
Escobar NM, Haupt S, Thow G, Boevink P, Chapman S, Oparka K (2003) High-throughput viral expression of cDNA-green fluorescent protein fusions reveals novel subcellular addresses and identifies unique proteins that interact with plasmodesmata. Plant Cell 15:1507–1523
Liu Y, Schiff M, Dinesh-Kumar SP (2002) Virus-induced gene silencing in tomato. Plant J 31:777–786
Lico C, Chen Q, Santi L (2008) Viral vectors for production of recombinant proteins in plants. J Cell Physiol 216:366–377
Dawson WO, Lewandowski DJ, Hilf ME, Bubrick P, Raffo AJ, Shaw JJ, Grantham GL, Desjardins PR (1989) A tobacco mosaic virus-hybrid expresses and loses an added gene. Virology 172:285–292
Donson J, Kearney CM, Hilf ME, Dawson WO (1991) Systemic expression of a bacterial gene by a tobacco mosaic virus-based vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:7204–7208
Azhakanandam K, Weissinger SM, Nicholson JS, Qu R, Weissinger AK (2007) Amplicon-plus targeting technology (APTT) for rapid production of a highly unstable vaccine protein in tobacco plants. Plant Mol Biol 63:393–404
Lindbo JA (2007) TRBO: a high-efficiency tobacco mosaic virus RNA-based overexpression vector. Plant Physiol 145:1232–1240
Voinnet O, Rivas S, Mestre P, Baulcombe D (2003) An enhanced transient expression system in plants based on suppression of gene silencing by the p19 protein of tomato bushy stunt virus. Plant J 33:949–956
Lindbo JA (2007) High-efficiency protein expression in plants from agroinfection-compatible tobacco mosaic virus expression vectors. BMC Biotechnol 7:52
Rhee SJ, Jang YJ, Lee GP (2016) Identification of the subgenomic promoter of the coat protein gene of cucumber fruit mottle mosaic virus and development of a heterologous expression vector. Arch Virol 161:1527–1538
Liu Z, Kearney CM (2010) A tobamovirus expression vector for agroinfection of legumes and Nicotiana. J Biotechnol 147:151–159
Mlotshwa S, Verver J, Sithole-Niang I, Prins M, Van Kammen AB, Wellink J (2002) Transgenic plants expressing HC-Pro show enhanced virus sensitivity while silencing of the transgene results in resistance. Virus Genes 25:45–57
Gleba Y, Klimyuk V, Marillonnet S (2007) Viral vectors for the expression of proteins in plants. Curr Opin Biotech 18:134–141
Mallory AC, Parks G, Endres MW, Baulcombe D, Bowman LH, Pruss GJ, Vance VB (2002) The amplicon-plus system for high-level expression of transgenes in plants. Nat Biotechnol 20:622–625
Pogue GP, Lindbo JA, Garger SJ, Fitzmaurice WP (2002) Making an ally from an enemy: plant virology and the new agriculture. Annu Rev Phytopathol 40:45–74
Alonso E, García-Luque I, de la Cruz A, Wicke B, Avila-Rincón MJ, Serra MT, Castresana C, Díaz-Ruíz JR (1991) Nucleotide sequence of the genomic RNA of pepper mild mottle virus, a resistance-breaking tobamovirus in pepper. J Gen Virol 72:2875–2884
Eiras M, Chaves ALR, Moreira SR, Araujo J, De, Colariccio A (2004) Caracterização de um Isolado do Pepper mild mottle virus que não Quebra a Resistência do Gene L3 em Capsicum sp. Fitopatol Brasil 29:670–675
Dawson W, Lehto KM (1990) Regulation of tobamovirus gene expression. In Maramorosch K, Murphy FA, Shatkin AJ (eds) Advances in virus research, vol 38. Elsevier, New York, pp 307–342
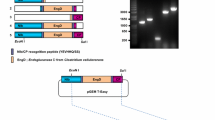
Junqueira BRT, Nicolini C, Lucinda N, Orílio AF, Nagata T (2014) A simplified approach to construct infectious cDNA clones of a tobamovirus in a binary vector. J Virol Methods 198:32–36
Gibson DG, Young L, Chuang R-Y, Venter JC, Hutchison CA, Smith HO (2009) Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases. Nat Methods 6:343–345
Man M, Epel BL (2004) Characterization of regulatory elements within the coat protein (CP) coding region of Tobacco mosaic virus affecting subgenomic transcription and green flourescent protein expression from the CP subgenomic RNA promoter. J Gen Virol 85:1727–1738
Kam Y-W, Lum F-M, Teo T-H, Lee WWL, Simarmata D, Harjanto S, Chua C-L, Chan Y-F, Wee J-K, Chow A, Lin RTP, Leo Y-S, Le Grand R, Sam I-C, Tong J-C, Roques P, Wiesmüller KH, Rénia L, Rötzschke O, Ng LFP (2012) Early neutralizing IgG response to Chikungunya virus in infected patients targets a dominant linear epitope on the E2 glycoprotein. EMBO Mol Med 4:330–343
Blawid R, Nagata T (2015) Construction of an infectious clone of a plant RNA virus in a binary vector using one-step Gibson assembly. J Virol Methods 222:11–15
Marillonnet S, Giritch A, Gils M, Kandzia R, Klimyuk V, Gleba Y (2004) In planta engineering of viral RNA replicons: efficient assembly by recombination of DNA modules delivered by Agrobacterium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:6852–6857
Musiychuk K, Stephenson N, Bi H, Farrance CE, Orozovic G, Brodelius M, Brodelius P, Horsey A, Ugulava N, Shamloul A-M, Mett V, Rabindram S, Streatfield SJ, Yusibov V (2007) A launch vector for the production of vaccine antigens in plants. Influenza Other Resp 1:19–25
Kumagai MH, Donson J, della-Cioppa G, Grill LK (2000) Rapid, high-level expression of glycosylated rice alpha-amylase in transfected plants by an RNA viral vector. Gene 245:169–174
Kubota K, Tsuda S, Tamai A, Meshi T (2003) Tomato mosaic virus replication protein suppresses virus-targetted posttranscriptional gene silencing. J Virol 77:11016–11026
Vogler H, Akbergenov R, Shivaprasad PV, Dang V, Fasler M, Kwon M-O, Zhanybekova S, Hohn T, Heinlein M (2007) Modification of small RNAs associated with suppression of RNA silencing by tobamovirus replicase protein. J Virol 81:10379–10388
Souza AC, Vasques RM, Inoue-Nagata AK, Lacorte C, Maldaner FR, Noronha EF, Nagata T (2013) Expression and assembly of Norwalk virus-like particles in plants using a viral RNA silencing suppressor gene. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:9021–9027
Mallory AC, Ely L, Smith TH, Marathe R, Anandalakshmi R, Fagard M, Vaucheret H, Pruss G, Bowman L, Vance BV (2001) HC-Pro suppression of transgene silencing eliminates the small RNAs but not transgene methylation or the mobile signal. Plant Cell 13:571–583
Funding
This study was funded by the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development, CNPq (Grant Number 401755/2013-4).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vasques, R.M., Lacorte, C., da Luz, L.L. et al. Development of a new tobamovirus-based viral vector for protein expression in plants. Mol Biol Rep 46, 97–103 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-018-4449-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-018-4449-4