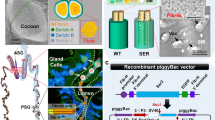
Abstract
A targeting vector consisting of a fusion gene of the green fluorescent protein (GFP) gene gfp and the antimicrobial peptide cecropin gene cec flanked by pieces of the 5′ and 3′ sequences of the fibroin L chain gene fib-L of the silkworm (Bombyx mori) and a negative selection DsRed marker gene driven by the baculovirus immediate early gene 1 (i.e.-1) promoter, was used to target the silkworm genome in order to explore the possibility of improving the performance of silk. A transgenic silkworm with a green fluorescent cocoon was obtained and PCR analysis of its genome confirmed that the target genes had been integrated into the silkworm genome correctly. Furthermore, in the posterior silk glands of the G6 generation transformation silkworm, a band representing the fusion protein Fib-L-GFP-Cec with a molecular mass of 68.7 kDa was detected by western blotting with an antibody against GFP. An investigation of the number of bacteria attached to a cocoon showed the transgenic silkworm cocoon possessed antibacterial properties. These results suggested the performance of silk can be improved by modifying the fibroin gene.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao Y, Wang BC (2009) Biodegradation of silk biomaterials. Int J Mol Sci 10(4):1514–1524
Gosline JM, Demont ME, Denny MW (1986) The structure and properties of spider silk. Endeavour 10:37–43
Lewis RV (2006) Spider silk: ancient ideas for new biomaterials. Chem Rev 106(9):3762-3744
Inoue S, Tanaka K, Arisaka F, Kimura S, Ohtomo K, Mizuno S (2000) Silk fibroin of Bombyx mori is secreted, assembling a high molecular mass elementary unit consisting of H-chain, L-chain, and P25, with a 6:6:1 molar ratio. J Biol Chem 275:40517–40528
Tamura T, Thibert C, Royer C, Kanda T, Abraham E, Kamba M, Komoto N, Thomas JL, Mauchamp B, Chavancy G, Shirk P, Fraser M, Prudhomme JC, Couble P (2000) Germline transformation of the silkworm Bombyx mori L. using a piggyBac transposon-derived vector. Nat Biotechnol 18(1):81–84
Kim A, Pyykko I (2011) Size matters: versatile use of piggyBac transposons as a genetic manipulation tool. Mol Cell Biochem 354(1–2):301–309
Daubnerová I, Roller L, Zitnan D (2009) Transgenesis approaches for functional analysis of peptidergic cells in the silkworm Bombyx mori. Gen Comp Endocrinol 162(1):36–42
Royer C, Jalabert A, Da Rocha M, Grenier AM, Mauchamp B, Couble P, Chavancy G (2005) Biosynthesis and cocoon-export of a recombinant globular protein in transgenic silkworms. Transgenic Res 14(4):463–472
Zhao A, Zhao T, Zhang Y, Xia Q, Lu C, Zhou Z, Xiang Z, Nakagaki M (2010) New and highly efficient expression systems for expressing selectively foreign protein in the silk glands of transgenic silkworm. Transgenic Res 19:29–44
Kojima K, Kuwana Y, Sezutsu H, Kobayashi I, Uchino K, Tamura T, Tamada Y (2007) A new method for the modification of fibroin heavy chain protein in the transgenic silkworm. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71(12):2943–2951
Teulé F, Miao YG, Sohn BH, Kim YS, Hull JJ, Fraser MJ Jr, Lewis RV, Jarvis DL (2012) Silkworms transformed with chimeric silkworm/spider silk genes spin composite silk fibers with improved mechanical properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(3):923–928
Tamura T, Thibert C, Royer C, Kanda T, Abraham E, Kamba M, Komoto N, Thomas JL, Mauchamp B, Chavancy G, Shirk P, Fraser M, Prudhomme JC, Couble P (2000) Germline transformation of the silkworm Bombyx mori L. using a piggyBac transposon-derived vector. Nat Biotechnol 18:81–84
Hammer RE, Pursel VG, Rexroad CE Jr, Wall RJ, Bolt DJ, Ebert KM, Palmiter RD, Brinster RL (1985) Production of transgenic rabbits, sheep and pigs by microinjection. Nature 315(6021):680–683
Suraokar M, Bradley A (2000) Targeting sheep. Nature 405:1004–1005
Yamao M, Katayama N, Nakazawa H, Yamakawa M, Hayashi Y, Hara S, Kamei K, Mori H (1999) Gene targeting in the silkworm by use of a baculovirus. Genes Dev 13(5):511–516
Mori H (2002) Transgenic insects expressing green fluorescent protein-silk fibroin light chain fusion protein in transgenic silkworms. Methods Mol Biol 183:235–244
Wu X, Cao C (2004) Targeting of human aFGF gene into silkworm, Bombyx mori L. through homologous recombination. J Zhejiang Univ Sci 5:644–650
Zhang F, Zhao Y, Lu CD (1999) Fluorescent transgenic silkworm. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 31:119–123
Zhao Y, Chen X, Peng W, Dong L, Huang JT, Lu CD (2001) Use of homologous recombination to change heart heavy chain gene of silk fibroin protein. J Biochem Biophys 33(1):112–116
Li Y, Cao G, Chen H, Jia H, Xue R, Gong C (2010) Expression of the hGM-CSF in the silk glands of gene-targeted silkworm. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 391:1427–1431
Cao G, Zhang Y, Xue R, Zhu Y, Wei Y, Zheng X, Gong C (2012) Alternative splicing, expression patterns and promoter characters of vasa-like gene from the silkworm Bombyx mori. Mol Biol Rep 39(5):5967–5976
Zhao Y, Li X, Cao G, Xue R, Gong C (2009) Expression of hIGF-I in the silk glands of transgenic silkworms and in transformed silkworm cells. Sci China Ser C Life Sci 52(12):1131–1139
Guo XY, Zhou ZY, Feng LC, Wang L, Lu C, Xiang ZH (2001) The sperm mediated method is used to import the exogenous gene into silkworm. Prog Biochem Biophys 28(3):423–425
Cao G, Xue R, Shen W, He Z (2006) The research of hGM-CSF gene transgenic silkworm based on piggyBac. Sci Seric 32(3):324–327
Takasu Y, Kobayashi I, Beumer K, Uchino K, Sezutsu H, Sajwan S, Carroll D, Tamura T, Zurovec M (2010) Targeted mutagenesis in the silkworm Bombyx mori using zinc finger nuclease mRNA injection. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 40(10):759–765
Ma S, Zhang S, Wang F, Liu Y, Liu Y, Xu H, Liu C, Lin Y, Zhao P, Xia Q (2012) Highly efficient and specific genome editing in silkworm using custom TALENs. PLoS ONE 7(9):e45035
Wei C, Liu J, Yu Z (2013) TALEN or Cas9-Rapid, Efficient and Specific Choices for Genome Modifications. J Gen Genomics 40:281–289
Liu C, Zhao P, Cheng T, Cha X, Xia Q, Xiang Z (2005) A new transcription pattern analysis of silkworm Fhx/P25 gene. Prog Biochem Biophy 32(8):740–746
Wang S, Lu C (2006) Fibroin heavy chain promoter cloned fragment leakage expression in silkworm vivo and cultured insect cells. Sericulture 4:491–493
Liu Y, Yu L, Guo X, Guo T, Wang S, Lu C (2006) Analysis of tissue-specific region in sericin 1 gene promoter of Bombyx mori. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 342(1):273–279
Pan X, Cao G, Xue R, Gong C (2009) Fibroin heavy chain promoter-driven DsRed instantaneous secretory expression. Biol Eng 25(5):761–766
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge financial support by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, 2012CB114600), the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (20113201130002) and a Project funded by the Priority Academic Program of Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Zhen Li, Yue Jiang, Guangli Cao, Jingzhi Li, Renyu Xue, Chengliang Gong contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Jiang, Y., Cao, G. et al. Construction of transgenic silkworm spinning antibacterial silk with fluorescence. Mol Biol Rep 42, 19–25 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3735-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3735-z