Abstract
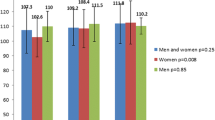
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) is a nuclear hormone receptor that regulates a number of genes involved in lipid and carbohydrate metabolism. The aim of this study was to investigate the association of C1431T and Pro12Ala polymorphisms of PPARγ gene and their haplotypes and diplotypes with risk of metabolic syndrome (MetS) in an Iranian population. A total of 340 unrelated Iranian subjects, including 175 MetS patients and 165 normal controls were enrolled. Each group was then divided into two subgroups according to the genotype (Pro/Pro and Pro/Ala + Ala/Ala for Pro12Ala, CC and CT + TT for C1431T). Genotypes were determined using a TaqMan method. Anthropometric indices, fasting plasma glucose and fasting lipid profile were measured by routine methods. A significant difference in the frequencies of the C1431T genotypes was observed between MetS and control subjects (P = 0.014), whereas no association was found for the Pro12Ala. The T allele carriers had a significantly increased risk of MetS compared to the CC genotype (P = 0.016) even after correction for multiple-testing and adjustment for age, sex and genotype. The T allele may therefore be considered as a risk factor for MetS (P = 0.003). Analysis of combined groups showed that X/Ala-CC and Pro/Pro-X/T diplotypes were associated with a higher body weight, waist circumference and waist to hip ratio among the individuals with MetS. Moreover the Ala-T haplotype was weakly associated with a higher level of triglyceride and lower level of HDL, suggesting the possibility of an interaction between Ala and T alleles. This study suggests that the PPARγ C1431T polymorphism is related to an increased risk of MetS in an Iranian population and interacts with the Pro12Ala polymorphism, further increasing the risk of MetS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Denke MA, Pasternak RC (2001) Defining and treating the metabolic syndrome: a primer from the adult treatment panel III. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med 3:251–253
Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ (2005) The metabolic syndrome. Lancet 365:1415–1428
Bruce KD, Hanson MA (2010) The developmental origins, mechanisms, and implications of metabolic syndrome. J Nutr 140:648–652
Gotoda T (2004) Genetic susceptibility to metabolic syndrome. Nihon Rinsho 62:1037–1044
Monda KL, North KE, Hunt SC, Rao DC, Province MA et al (2010) The genetics of obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 10:86–108
Kristiansson K, Perola M, Tikkanen E, Kettunen J, Surakka I et al (2012) Genome-wide screen for metabolic syndrome susceptibility Loci reveals strong lipid gene contribution but no evidence for common genetic basis for clustering of metabolic syndrome traits. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 5:242–249
Desvergne B, Wahli W (1999) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: nuclear control of metabolism. Endocr Rev 20:649–688
Fajas L, Debril MB, Auwerx J (2001) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma: from adipogenesis to carcinogenesis. J Mol Endocrinol 27:1–9
Meirhaeghe A, Amouyel P (2004) Impact of genetic variation of PPARgamma in humans. Mol Genet Metab 83:93–102
Yen CJ, Beamer BA, Negri C, Silver K, Brown KA et al (1997) Molecular scanning of the human peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma (hPPAR gamma) gene in diabetic Caucasians: identification of a Pro12Ala PPAR gamma 2 missense mutation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 241:270–274
Altshuler D, Hirschhorn JN, Klannemark M, Lindgren CM, Vohl MC et al (2000) The common PPARgamma Pro12Ala polymorphism is associated with decreased risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet 26:76–80
Huguenin GV, Rosa G (2010) The Ala allele in the PPAR-gamma2 gene is associated with reduced risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Caucasians and improved insulin sensitivity in overweight subjects. Br J Nutr 104:488–497
Doney AS, Fischer B, Cecil JE, Boylan K, McGuigan FE et al (2004) Association of the Pro12Ala and C1431T variants of PPARG and their haplotypes with susceptibility to Type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 47:555–558
Meshkani R, Taghikhani M, Larijani B, Bahrami Y, Khatami S et al (2007) Pro12Ala polymorphism of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma2 (PPARgamma-2) gene is associated with greater insulin sensitivity and decreased risk of type 2 diabetes in an Iranian population. Clin Chem Lab Med 45:477–482
Masud S, Ye S (2003) Effect of the peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-gamma gene Pro12Ala variant on body mass index: a meta-analysis. J Med Genet 40:773–780
Deeb SS, Fajas L, Nemoto M, Pihlajamaki J, Mykkanen L et al (1998) A Pro12Ala substitution in PPARgamma2 associated with decreased receptor activity, lower body mass index and improved insulin sensitivity. Nat Genet 20:284–287
Ostgren CJ, Lindblad U, Melander O, Melander A, Groop L et al (2003) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gammaPro12Ala polymorphism and the association with blood pressure in type 2 diabetes: skaraborg hypertension and diabetes project. J Hypertens 21:1657–1662
Tai ES, Corella D, Deurenberg-Yap M, Adiconis X, Chew SK et al (2004) Differential effects of the C1431T and Pro12Ala PPARgamma gene variants on plasma lipids and diabetes risk in an Asian population. J Lipid Res 45:674–685
Zhou X, Chen J, Xu W (2012) Association between C1431T polymorphism in peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma gene and coronary artery disease in Chinese Han population. Mol Biol Rep 39:1863–1868
Wang XL, Oosterhof J, Duarte N (1999) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma C161–>T polymorphism and coronary artery disease. Cardiovasc Res 44:588–594
Rhee EJ, Oh KW, Lee WY, Kim SY, Oh ES et al (2006) Effects of two common polymorphisms of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma gene on metabolic syndrome. Arch Med Res 37:86–94
Shi H, Yu X, Li Q, Ye X, Gao Y et al (2012) Association between PPAR-gamma and RXR-alpha gene polymorphism and metabolic syndrome risk: a case-control study of a Chinese Han population. Arch Med Res 43:233–242
Dongxia L, Qi H, Lisong L, Jincheng G (2008) Association of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptorgamma gene Pro12Ala and C161T polymorphisms with metabolic syndrome. Circ J 72:551–557
Doney A, Fischer B, Frew D, Cumming A, Flavell DM et al (2002) Haplotype analysis of the PPARgamma Pro12Ala and C1431T variants reveals opposing associations with body weight. BMC Genet 3:21
Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, Donato KA, Eckel RH et al (2005) Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: an American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation 112:2735–2752
Gaunt TR, Rodriguez S, Day IN (2007) Cubic exact solutions for the estimation of pairwise haplotype frequencies: implications for linkage disequilibrium analyses and a web tool ‘CubeX’. BMC Bioinformatics 8:428
Mirzaei H, Akrami SM, Golmohammadi T, Doosti M, Heshmat R et al (2009) Polymorphism of Pro12Ala in the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma2 gene in Iranian diabetic and obese subjects. Metab Syndr Relat Disord 7:453–458
Namvaran F, Azarpira N, Rahimi-Moghaddam P, Dabbaghmanesh MH (2011) Polymorphism of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) Pro12Ala in the Iranian population: relation with insulin resistance and response to treatment with pioglitazone in type 2 diabetes. Eur J Pharmacol 671:1–6
Meirhaeghe A, Cottel D, Amouyel P, Dallongeville J (2005) Association between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma haplotypes and the metabolic syndrome in French men and women. Diabetes 54:3043–3048
Gurnell M (2003) PPARgamma and metabolism: insights from the study of human genetic variants. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 59:267–277
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all the study participants for their cooperation. This work was supported by Research Project No. 467, as a PhD thesis, financed by the Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases Research Center, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Hassan Rooki and Majid Ghayour-Mobarhan have contributed equally to this study
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rooki, H., Haerian, Ms., Azimzadeh, P. et al. Associations between C1431T and Pro12Ala variants of PPARγ gene and their haplotypes with susceptibility to metabolic syndrome in an Iranian population. Mol Biol Rep 41, 3127–3133 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3172-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3172-z