Abstract
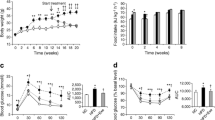
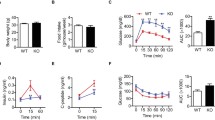
Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) is one member of the silent information regulator 2 (Sir2)-like family of proteins involved in glucose homeostasis in mammals. It has been reported that SIRT1 modulates endocrine signaling of glucose and fat homeostasis by regulating transcription factors such as forkhead transcription factor 3a (FOXO3a), glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) and PPARγ coactivator (PGC-1α). However, it is still not clear how SIRT1 is involved in the development of insulin resistance. To determine the location and expression of SIRT1 and its target proteins in rats and analyze the interactions and functions of these proteins in insulin resistance. Forty-eight male Sprague–Dawley rats were randomly divided into four regimen groups: normal control (NC), calorie restriction (CR), high-fat (HFa), and high-fructose (HFr). Animals were fed for 12 weeks and blood samples collected from tail veins at weeks 2, 4, 6, 8 and 12 after fasting for 16 h. Baseline metabolic parameters such as fasting blood sugar, insulin, cholesterol and triglycerides were analyzed. A glucose tolerance test was carried out at the end of the study. Visceral fat, consisting of epididymis and perirenal fat, was isolated and weighed. The pancreas from each animal was also immediately removed. Immunohistochemical staining was performed to detect the locations of SIRT1, FOXO3a, GLUT4, PPARγ and PGC-1α in the β-cell of the rat pancreas. Expression in the pancreas was analyzed by western blotting. Blood biochemical analysis indicated that the HFa and HFr groups were insulin-resistant. Immunohistochemical staining showed that GLUT4 was a nuclear protein. SIRT1, FOXO3a, PPARγ and PGC-1α were present in both the nucleus and the cytoplasm of β-cells of pancreatic islets. The expression of SIRT1, GLUT4 and PGC-1α increased significantly in response to CR, but decreased in the HFr and HFa groups. FOXO3a was similar in the CR and the NC groups, whereas it declined in the HFa and HFr groups. PPARγ was elevated in the HFa group, but dropped in the CR and HFr groups. These data suggest that SIRT1 and its regulators are involved in the development of insulin resistance.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Simmons RK, Unwin N, Griffin SJ (2009) International Diabetes Federation: an update of the evidence concerning the prevention of type 2 diabetes. Diabet Res Clin Pract 87(2):143–149
Gallwitz B (2009) Implications of postprandial glucose and weight control in people with type 2 diabetes: understanding and implementing the International Diabetes Federation guidelines. Diabet Care 32(Suppl 2):S322–S325
Alberti KG, Zimmet P, Shaw J (2006) Metabolic syndrome—a new world-wide definition. A consensus statement from the International Diabetes Federation. Diabet Med 23:469–480
Masoro EJ (2000) Caloric restriction and aging: an update. Exp Gerontol 35:299–305
Lee M, Aronne LJ (2007) Weight management for type 2 diabetes mellitus: global cardiovascular risk reduction. Am J Cardiol 99:68B–79B
Anderson RM, Bitterman KJ, Wood JG, Medvedik O, Sinclair DA (2003) Nicotinamide and PNC1 govern lifespan extension by calorie restriction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature 423:181–185
Imai S, Armstrong CM, Kaeberlein M, Guarente L (2000) Transcriptional silencing and longevity protein Sir2 is an NAD-dependent histone deacetylase. Nature 403:795–800
Blander G, Guarente L (2004) The Sir2 family of protein deacetylases. Annu Rev Biochem 73:417–435
Tsuchiya M, Dang N, Kerr EO, Hu D, Steffen KK, Oakes JA, Kennedy BK, Kaeberlein M (2006) Sirtuin-independent effects of nicotinamide on lifespan extension from calorie restriction in yeast. Aging Cell 5:505–514
Michishita E, Park JY, Burneskis JM, Barrett JC, Horikawa I (2005) Evolutionarily conserved and nonconserved cellular localizations and functions of human SIRT proteins. Mol Biol Cell 16:4623–4635
Tissenbaum HA, Guarente L (2001) Increased dosage of a Sir-2 gene extends lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 410:227–230
Rodgers JT, Lerin C, Haas W, Gygi SP, Spiegelman BM, Puigserver P (2005) Nutrient control of glucose homeostasis through a complex of PGC-1alpha and SIRT1. Nature 434:113–118
Liang F, Kume S, Koya D (2009) SIRT1 and insulin resistance. Nat Rev Endocrinol 5(7):367–373
Picard F, Kurtev M, Chung N, Topark-Ngarm A, Senawong T, Machado De Oliveira R, Leid M, McBurney MW, Guarente L (2004) SIRT1 promotes fat mobilization in white adipocytes by repressing PPAR-gamma. Nature 429:771–776
Rutanen J, Yaluri N, Modi S, Pihlajamaki J, Vanttinen M, Itkonen P, Kainulainen S, Yamamoto H, Lagouge M, Sinclair DA (2010) SIRT1 expression may be associated with energy expenditure and insulin sensitivity. Diabetes 59(4):829–835
Chen Y-R, Fang S-R, Fu Y-C, Zhou X-H, Xu M-Y, Xu W-C (2010) Calorie restriction on insulin resistance and expression of SIRT1 and SIRT4 in rats. Biochem Cell Biol 88(4):715–722
Stark AH, Timar B, Madar Z (2000) Adaptation of Sprague–Dawley rats to long-term feeding of high fat or high fructose diets. Eur J Nutr 39:229–234
D’Angelo G, Elmarakby AA, Pollock DM, Stepp DW (2005) Fructose feeding increases insulin resistance but not blood pressure in Sprague–Dawley rats. Hypertension 46:806–811
Picard F, Wanatabe M, Schoonjans K, Lydon J, O’Malley BW, Auwerx J (2002) Progesterone receptor knockout mice have an improved glucose homeostasis secondary to beta -cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:15644–15648
Xiong S, Salazar G, Patrushev N, Alexander RW (2011) Wayne FoxO1 mediates an autofeedback loop regulating SIRT1 expression. J Biol Chem 286(7):5289–5299
Brunet A, Sweeney LB, Sturgill JF, Chua KF, Greer PL, Lin Y, Tran H, Ross SE, Mostoslavsky R, Cohen HY, Hu LS, Cheng HL, Jedrychowski MP, Gygi SP, Sinclair DA, Alt FW, Greenberg ME (2004) Stress-dependent regulation of FOXO transcription factors by the SIRT1 deacetylase. Science 303:2011–2015
Ehses JA, Ellingsgaard H, Boni-Schnetzler M, Donath MY (2009) Pancreatic islet inflammation in type 2 diabetes: from alpha and beta cell compensation to dysfunction. Arch Physiol Biochem 115:240–247
Bogan JS, Hendon N, McKee AE, Tsao TS, Lodish HF (2003) Functional cloning of TUG as a regulator of GLUT4 glucose transporter trafficking. Nature 425:727–733
Derlacz RA, Hyc K, Usarek M, Jagielski AK, Drozak J, Jarzyna R (2008) PPAR-gamma-independent inhibitory effect of rosiglitazone on glucose synthesis in primary cultured rabbit kidney-cortex tubules. Biochem Cell Biol 86:396–404
Housley MP, Udeshi ND, Rodgers JT, Shabanowitz J, Puigserver P, Hunt DF, Hart GW (2009) A PGC-1alpha-O-GlcNAc transferase complex regulates FoxO transcription factor activity in response to glucose. J Biol Chem 284:5148–5157
Wang X, Qu F, Chen Z, Liang T, Qu A (2009) Labeling and imaging of GLUT4 in live L6 cells with quantum dots. Biochem Cell Biol 87:687–694
Livingstone C, Dominiczak AF, Campbell IW, Gould GW (1995) Insulin resistance, hypertension and the insulin-responsive glucose transporter, GLUT4. Clin Sci (Lond) 89:109–116
Tsao TS, Burcelin R, Katz EB, Huang L, Charron MJ (1996) Enhanced insulin action due to targeted GLUT4 overexpression exclusively in muscle. Diabetes 45:28–36
Picard F, Auwerx J (2002) PPAR(gamma) and glucose homeostasis. Annu Rev Nutr 22:167–197
Nemoto S, Fergusson MM, Finkel T (2005) SIRT1 functionally interacts with the metabolic regulator and transcriptional coactivator PGC-1{alpha}. J Biol Chem 280:16456–16460
Jager S, Handschin C, St-Pierre J, Spiegelman BM (2007) AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) action in skeletal muscle via direct phosphorylation of PGC-1alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:12017–12022
Lagouge M, Argmann C, Gerhart-Hines Z, Meziane H, Lerin C, Daussin F, Messadeq N, Milne J, Lambert P, Elliott P, Geny B, Laakso M, Puigserver P, Auwerx J (2006) Resveratrol improves mitochondrial function and protects against metabolic disease by activating SIRT1 and PGC-1alpha. Cell 127:1109–1122
Puigserver P, Rhee J, Donovan J, Walkey CJ, Yoon JC, Oriente F, Kitamura Y, Altomonte J, Dong H, Accili D, Spiegelman BM (2003) Insulin-regulated hepatic gluconeogenesis through FOXO1-PGC-1alpha interaction. Nature 423:550–555
Engel N, Mahlknecht U (2008) Aging and anti-aging: unexpected side effects of everyday medication through sirtuin1 modulation. Int J Mol Med 21:223–232
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Project No. 10151503102000017 and S2012010009336) and the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province (Project No. 2011B031800322).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, YR., Lai, Yl., Lin, Sd. et al. SIRT1 interacts with metabolic transcriptional factors in the pancreas of insulin-resistant and calorie-restricted rats. Mol Biol Rep 40, 3373–3380 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-2412-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-2412-3