Abstract
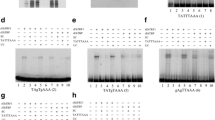
Entamoeba histolytica is a human pathogen, which can survive using haemoglobin (Hb) as only iron supply. Two probable haemophores (Ehhmbp26 and Ehhmbp45) are involved in iron acquisition in this parasite. However, mechanisms related to their transcriptional regulation have not been studied yet. In the present work, transcriptional profiles of both genes were evaluated in trophozoites cultures grown with different iron sources. ehhmbp26 gene was repressed totally by free iron, whereas ehhmbp45 gene showed clearly detectable mRNA levels. Expression profiles for both genes were significantly increased under iron privation condition. Interestingly, ehhmbp26 transcript was highly expressed by Holo-transferrin presence. This induction appears to be independent of direct contact between these proteins, because, in vitro assays evidenced that Ehhmbp26 protein was unable to bind this metalloprotein. Besides, in silico analysis of promoter nucleotide sequences of ehhmbp26 and ehhmbp45 genes revealed some distinctive core promoter elements described in E. histolytica and T-rich regions. Taking altogether these data suggest in E. histolytica dissimilar transcriptional mechanisms involved on iron acquisition control the expression of these genes, and they are unlike to those previously described for instance: in bacteria. Our findings evidenced this pathogen regulates the expression of ehhmbp26 and ehhmbp45 genes depending on the available iron supply, always ensuring the success of its infective process.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marquis JF, Gros P (2007) Intracellular Leishmania: your iron or mine? Trends Microbiol 15:93–95
Perkins-Balding D, Ratliff-Griffin M, Stojiljkovic I (2004) Iron transport systems in Neisseria meningitidis. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 68:154–171
Wilson ME, Britigan BE (1998) Iron acquisition by parasitic protozoa. Parasitol Today 14:348–353
Steverding D (2000) The transferrin receptor of Trypanosoma brucei. Parasitol Int 48:191–198
Tsai CD, Liu HW, Tai JH (2002) Characterization of an iron-responsive promoter in the protozoan pathogen Trichomonas vaginalis. J Biol Chem 277:5153–5162
Dey I, Keller K, Belley A, Chadee K (2003) Identification and characterization of a cyclooxygenase-like enzyme from Entamoeba histolytica. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:13561–13566
Reyes-Lopez M, Serrano-Luna JJ, Negrete-Abascal E, Leon-Sicairos N, Guerrero-Barrera AL, De la GM (2001) Entamoeba histolytica: transferrin binding proteins. Exp Parasitol 99:132–140
Cruz-Castaneda A, Olivares-Trejo JJ (2008) Ehhmbp45 is a novel hemoglobin-binding protein identified in Entamoeba histolytica. FEBS Lett 582:2806–2810
Cruz-Castaneda A, Hernandez-Sanchez J, Olivares-Trejo JJ (2009) Cloning and identification of a gene coding for a 26-kDa hemoglobin-binding protein from Entamoeba histolytica. Biochimie 91:383–389
Cruz-Castaneda A, Lopez-Casamichana M, Olivares-Trejo JJ (2011) Entamoeba histolytica secretes two haem-binding proteins to scavenge haem. Biochem J 434:105–111
Diamond LS, Harlow DR, Cunnick CC (1978) A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 72:431–432
Rossi MS, Fetherston JD, Letoffe S, Carniel E, Perry RD, Ghigo JM (2001) Identification and characterization of the hemophore-dependent heme acquisition system of Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun 69:6707–6717
Leon-Sicairos N, Reyes-Lopez M, Canizalez-Roman A, Bermudez-Cruz RM, Serrano-Luna J, Arroyo R, De la GM (2005) Human hololactoferrin: endocytosis and use as an iron source by the parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Microbiology 151:3859–3871
Lopez-Soto F, Leon-Sicairos N, Reyes-Lopez M, Serrano-Luna J, Ordaz-Pichardo C, Pina-Vazquez C, Ortiz-Estrada G, De la GM (2009) Use and endocytosis of iron-containing proteins by Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites. Infect Genet Evol 9:1038–1050
Flores-Soto E, zuara-Liceaga E, Lopez-Camarillo C, Orozco E (2005) The Entamoeba histolytica Ehcp112 gene has a distal and weak promoter. Exp Parasitol 110:286–291
Hackney JA, Ehrenkaufer GM, Singh U (2007) Identification of putative transcriptional regulatory networks in Entamoeba histolytica using Bayesian inference. Nucleic Acids Res 35:2141–2152
Perez DG, Gomez C, Lopez-Bayghen E, Tannich E, Orozco E (1998) Transcriptional analysis of the EhPgp5 promoter of Entamoeba histolytica multidrug-resistant mutant. J Biol Chem 273:7285–7292
Purdy JE, Pho LT, Mann BJ, Petri WA Jr (1996) Upstream regulatory elements controlling expression of the Entamoeba histolytica lectin. Mol Biochem Parasitol 78:91–103
Smith JM, Meerovitch E (1982) Specificity of iron requirements of Entamoeba histolytica in vitro. Arch Invest Med (Mex) 13(3):63–69
Buss H, Lioutas C, Dobinsky S, Nickel R, Tannich E (1995) Analysis of the 170-kDa lectin gene promoter of Entamoeba histolytica. Mol Biochem Parasitol 72:1–10
Singh U, Rogers JB, Mann BJ, Petri WA Jr (1997) Transcription initiation is controlled by three core promoter elements in the hgl5 gene of the protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:8812–8817
Romero-Diaz M, Gomez C, Lopez-Reyes I, Martinez MB, Orozco E, Rodriguez MA (2007) Structural and functional analysis of the Entamoeba histolytica EhrabB gene promoter. BMC Mol Biol 8:82
Gomez C, Perez DG, Lopez-Bayghen E, Orozco E (1998) Transcriptional analysis of the EhPgp1 promoter of Entamoeba histolytica multidrug-resistant mutant. J Biol Chem 273:7277–7284
Singh U, Rogers JB (1998) The novel core promoter element GAAC in the hgl5 gene of Entamoeba histolytica is able to direct a transcription start site independent of TATA or initiator regions. J Biol Chem 273:21663–21668
Singh U, Gilchrist CA, Schaenman JM, Rogers JB, Hockensmith JW, Mann BJ, Petri WA (2002) Context-dependent roles of the Entamoeba histolytica core promoter element GAAC in transcriptional activation and protein complex assembly. Mol Biochem Parasitol 120:107–116
Iyer LM, Anantharaman V, Wolf MY, Aravind L (2008) Comparative genomics of transcription factors and chromatin proteins in parasitic protists and other eukaryotes. Int J Parasitol 38:1–31
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACyT), México and Instituto de Ciencia y Tecnología del Distrito Federal (ICyT-DF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sánchez-Cruz, C., López-Casamichana, M., Cruz-Castañeda, A. et al. Transferrin regulates mRNA levels of a gene involved in iron utilization in Entamoeba histolytica . Mol Biol Rep 39, 4545–4551 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-1244-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-1244-x