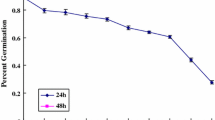
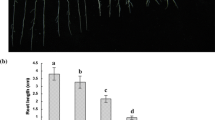
Abstract
Trichloroethylene (TCE) is a widespread and persistent environmental contaminant. Plants are able to take up a range of harmful organic compounds, including some of the most abundant environmental pollutants like TCE. In this study, complementary DNA microarrays were constructed to have a better view of transcript expression in Arabidopsis thaliana during TCE-induced stress. The microarray analysis demonstrated the complexity of gene expression patterns resulting from TCE. A total of 1,020 transcripts were differentially up-regulated by TCE. Those genes might specifically contribute to the TCE transformation, conjugation, and compartmentation in plant. This study provides informative preliminary data for more in-depth analyses of TCE tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dekant W, Schulz A, Metzler M, Henschler D (1986) Absorption, elimination, and metabolism of trichloroethylene: a quantitative comparison between mice and rats. Xenobiotica 16:143
Johnson PD, Goldberg SJ, May MZ, Dawson BV (2003) Threshold of trichloroethylene contamination in maternal drinking waters affecting fetal heart development in the rat. Environ Health Perspect 111:289–292
Maltoni C, Lefemine G, Cotti G, Perino G (1988) Long-term carcinogenicity bioassays on trichloroethylene administered by inhalation to Sprague-Dawley rats and Swiss and B6C3F1 mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci 534:316–342
NTP (National Toxicology Program) (1990) Carcinogenesis studies of trichloroethylene in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice. NTP Technical Report
ATSDR (1997) US Department of Health and Human Services, Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Toxicologic profile for trichloroethylene
Schroll R, Bierling B, Cao G, Dorfler U, Lahaniati M, Langenbach T, Scheunert I, Winkler R (1994) Uptake pathways of organic chemicals from soil by agricultural plants. Chemosphere 28:297–303
Anderson TA, Walton BT (1995) Comparative fate of 14C TCE in the root zone of plants from a former solvent disposal site. Environ Toxicol Chem 14:2041–2047
Susarla S, Medina VF, McCutcheon SC (2002) Phytoremediation: an ecological solution to organic chemical contamination. Ecol Eng 18:647–658
Aken BV, Correa PA, Chnoor JL (2010) Phytoremediation of polychlorinated biphenyls: new trends and promises. Environ Sci Technol 44:2767–2776
Shang TQ, Doty SL, Wilson AM, Howald WN, Gordon MP (2001) Trichloroethylene oxidative metabolism in plants: the trichloroethanol pathway. Phytochemistry 58:1055–1065
Narayanan M, Davis LC, Erickson LE (1995) Fate of volatile chlorinated organic compounds in a laboratory chamber with alfalfa plants. Environ Sci Technol 29:2437–2444
Newman LA, Strand SE, Choe N, Duffy J, Ekuan G, Ruszaj M, Shurtleff BB, Wilmoth J, Heilman P, Gordon MP (1997) Uptake and biotransformation of trichloroethylene by hybrid poplars. Environ Sci Technol 31:1062–1067
Orchard BJ, Doucette WJ, Chard JK, Bugbee B (2000) Uptake of TCE by hybrid poplar trees grown hydroponically in flow through plant growth chambers. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:895–903
Schuchardt J, Beule D, Malik A, Wolski E, Eickhoff H, Lehrach H, Herzel H (2000) Normalization strategies for cDNA microarrays. Nucleic Acids Res 28:E47
Deyholos M, Galbraith DW (2001) High-density microarrays for gene expression analysis. Cytometry 43:229–238
Ensley BD (1991) Biochemical diversity of trichloroethylene metabolism. Annu Rev Microbiol 45:283–299
Lash LH, Fisher JW, Lipscomb JC, Parker JC (2000) Metabolism of trichloroethylene. Environ Health Perspect 108:177–200
Sandermann H (1994) Higher plant metabolism of xenobiotics: the ‘green liver’ concept. Pharmacogenetics 4:225–241
Sandermann H (1992) Plant metabolism of xenobiotics. Trends Biochem Sci 17:82–84
Ishikawa T (1992) The ATP-dependent glutathione S-conjugate export pump. Trends Biochem Sci 17:463–469
Ishikawa T, Li ZS, Lu YP, Rea PA (1997) The GS-X pump in plant, yeast, and animal cells: structure, function, and gene expression. Biosci Rep 17:189–207
Rea PA, Li ZS, Lu YP, Drozdowicz YM, Martinoia E (1998) From vacuolar GS-X pumps to multispecific ABC transporters. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49:727–760
Coleman J, Blake-Kalff M, Davies E (1997) Detoxification of xenobiotics by plants: chemical modification and vacuolar compartmentation. Trends Plant Sci 2:144–151
Schaffner A, Messner B, Langebartels C, Sandermann H (2002) Genes and enzymes for in-planta phytoremediation of air, water and soil. Acta Biotechnol 22:141–151
Komives T, Gullner G (2005) Phase I xenobiotic metabolic systems in plants Z. Naturforsch 60:179–185
Chapple C (1998) Molecular-genetic analysis of plant cytochrome P450–dependent monooxygenases. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49:311–343
Wojtaszek P (1997) Oxidative burst: an early plant response to pathogen infection. Biochem J 322:681–692
Ryter SW, Kim HP, Hoetzel A, Park JW, Nakahira K, Wang X, Choi AM (2007) Mechanisms of cell death in oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal 9:49–89
Yu L, Wan F, Dutta S, Welsh S, Liu ZH, Freundt E, Baehrecke EH, Lenardo M (2006) Autophagic programmed cell death by selective catalase degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:4952–4957
Marrs K (1996) The functions and regulation of glutathione S-transferases in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 47:127–158
Berhane K, Widersten M, Engstrom A, Kozarich JW, Mannervik B (1994) Detoxication of base propenals and other α, β-unsaturated aldehyde products of radical reactions and lipid peroxidation by human glutathione transferases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:1480–1484
Hvorup RN, Winnen B, Chang AB, Jiang Y, Zhou XF, Saier MH (2003) The multidrug/oligosaccharidyl-lipid/polysaccharide (MOP) exporter superfamily. Eur J Biochem 270:799–813
Yazaki K (2005) Transporters of secondary metabolites. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8:301–307
Omote H, Hiasa M, Matsumoto T, Otsuka M, Moriyama Y (2006) The MATE proteins as fundamental transporters of metabolic and xenobiotic organic cations. Trends Pharmaco Sci 27:587–593
Vincent A, Chantal V, Catherine C, Jean-Claude K (2000) Lipid transfer proteins are encoded by a small multigene family in Arabidiosis thaliana. Plant Sci 157:1–12
Jean-Claude K (1997) Lipid-transfer proteins: a puzzling family of plant proteins. Trends Plant Sci 2:66–70
Martinez M, Rubio-Somoza I, Carbonero P, Diaz I (2003) A cathepsin B-like cysteine protease gene from Hordeum vulgare (gene CatB) induced by GA in aleurone cells is under circadian control in leaves. J Exp Bot 384:951–959
Pinheiro C, Kehr J, Ricardo CP (2005) Effect of water stress on lupin stem protein analysed by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Planta 221:716–728
Aharoni A, Vorst O (2002) DNA microarrays for functional plant genomics. Plant Mol Biol 48:99–118
Schena M, Shalon D, Davis RW, Brown PO (1995) Quantitative monitoring of gene expression patterns with a complementary DNA microarray. Science 270(5235):467–470
Cui GH, Huang LQ, Tang XJ, Zhao JX (2011) Candidate genes involved in tanshinone biosynthesis in hairy roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza revealed by cDNA microarray. Mol Biol Rep 38:2471–2478
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by Hi-tech Research and Development Program (863) of China (2008AA10Z401) and Shanghai Natural Science Foundation (11ZR1432600).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, B., Peng, RH., Xiong, AS. et al. Analysis of gene expression profile of Arabidopsis genes under trichloroethylene stresses with the use of a full-length cDNA microarray. Mol Biol Rep 39, 3799–3806 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-1157-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-1157-8