Abstract
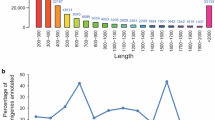
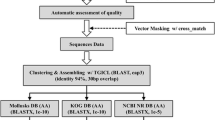
Sika deer is one of the best-known and highly valued animals of China. Despite its economic, cultural, and biological importance, there has not been a large-scale sequencing project for Sika deer to date. With the ultimate goal of sequencing the complete genome of this organism, we first established a bone marrow cDNA library for Sika deer and generated a total of 2,025 reads. After processing the sequences, 2,017 high-quality expressed sequence tags (ESTs) were obtained. These ESTs were assembled into 1,157 unigenes, including 238 contigs and 919 singletons. Comparative analyses indicated that 888 (76.75%) of the unigenes had significant matches to sequences in the non-redundant protein database, In addition to highly expressed genes, such as stearoyl-CoA desaturase, cytochrome c oxidase, adipocyte-type fatty acid-binding protein, adiponectin and thymosin beta-4, we also obtained vascular endothelial growth factor-A and heparin-binding growth-associated molecule, both of which are of great importance for angiogenesis research. There were 244 (21.09%) unigenes with no significant match to any sequence in current protein or nucleotide databases, and these sequences may represent genes with unknown function in Sika deer. Open reading frame analysis of the sequences was performed using the getorf program. In addition, the sequences were functionally classified using the gene ontology hierarchy, clusters of orthologous groups of proteins and Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes databases. Analysis of ESTs described in this paper provides an important resource for the transcriptome exploration of Sika deer, and will also facilitate further studies on functional genomics, gene discovery and genome annotation of Sika deer.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ESTs:
-
Expressed sequence tags
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- GO:
-
Gene ontology
- COGs:
-
Clusters of orthologous groups of proteins
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes
References
Lü X, Wei F, Li M, Yang G, Liu H (2006) Genetic diversity among Chinese Sika deer (Cervus nippon) populations and relationships between Chinese and Japanese Sika deer. Chin Sci Bull 51:433–440
Wei Z, Yang Y, Chen Y, Yu Y (2003) Partial cDNA sequence cloning of two housekeeping genes from Sika deer. J Jilin Univ (Medicine Edition) 29:713–718
Wang Y, Yang C, Liu G, Jiang J, Wu J (2006) Generation and analysis of expressed sequence tags from a cDNA library of Tamarix androssowii. Plant Sci 170:28–36
Akao T, Sano M, Yamada O, Akeno T, Fujii K, Goto K, Ohashi-Kunihiro S, Takase K, Yasukawa-Watanabe M, Yamaguchi K, Kurihara Y, Maruyama J, Juvvadi PR, Tanaka A, Hata Y, Koyama Y, Yamaguchi S, Kitamoto N, Gomi K, Abe K, Takeuchi M, Kobayashi T, Horiuchi H, Kitamoto K, Kashiwagi Y, Machida M, Akita O (2007) Analysis of expressed sequence tags from the fungus Aspergillus oryzae cultured under different conditions. DNA Res 14:47–57
Hwang DM, Fung YW, Wang RX, Laurenssen CM, Ng SH, Lam WY, Tsui KW, Fung KP, Waye M, Lee CY (1995) Analysis of expressed sequence tags from a fetal human heart cDNA library. Genomics 30:293–298
Nelson PS, Ng WL, Schummer M, True LD, Liu AY, Bumgarner RE, Ferguson C, Dimak A, Hood L (1998) An expressed-sequence-tag database of the human prostate: sequence analysis of 1168 cDNA clones. Genomics 47:12–25
Ewing B, Green P (2000) Analysis of expressed sequence tags indicates 35,000 human genes. Nat Genet 25:232–234
da Mota AF, Sonstegard TS, Van Tassell CP, Shade LL, Matukumalli LK, Wood DL, Capuco AV, Brito MA, Connor EE, Martinez ML, Coutinho LL (2004) Characterization of open reading frame-expressed sequence tags generated from Bos indicus and B. taurus mammary gland cDNA libraries. Anim Genet 35:213–219
Lee SH, Park EW, Cho YM, Lee JW, Kim HY, Lee JH, Oh SJ, Cheong IC, Yoon DH (2006) Confirming single nucleotide polymorphisms from expressed sequence tag datasets derived from three cattle cDNA libraries. J Biochem Mol Biol 39:183–188
Lim D, Lee SH, Cho YM, Yoon D, Shin Y, Kim KW, Park HS, Kim H (2010) Transcript profiling of expressed sequence tags from intramuscular fat, longissimus dorsi muscle and liver in Korean cattle (Hanwoo). BMB Rep 43:115–121
Oishi M, Gohma H, Lejukole HY, Taniguchi Y, Yamada T, Suzuki K, Shinkai H, Uenishi H, Yasue H, Sasaki Y (2004) Generation of a total of 6483 expressed sequence tags from 60 day-old bovine whole fetus and fetal placenta. Anim Biotechnol 15:1–8
Li J, Zhang W (2009) Expression sequence tag and QTL/MAS of goat/sheep in China. Recent Pat DNA Gene Seq 3:213–218
Sheng X, Song X, Yu Y, Niu L, Li S, Li H, Wei C, Liu T, Zhang L, Du L (2010) Characterization of microRNAs from sheep (Ovis aries) using computational and experimental analyses. Mol Biol Rep 38(5):3161–3171. doi:10.1007/s11033-010-9987-3
Lieto LD, Cothran EG (2001) Characterization of expressed sequence tags generated from skin cDNA clones of Equus caballus by single pass sequencing. Anim Biotechnol 12:87–97
Al-Swailem AM, Shehata MM, Abu-Duhier FM, Al-Yamani EJ, Al-Busadah KA, Al-Arawi MS, Al-Khider AY, Al-Muhaimeed AN, Al-Qahtani FH, Manee MM, Al-Shomrani BM, Al-Qhtani SM, Al-Harthi AS, Akdemir KC, Inan MS, Out HH (2010) Sequencing, analysis, and annotation of expressed sequence tags for Camelus dromedarius. PLoS ONE 5(5):e10720. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0010720
Krammer PH (2000) CD95’s deadly mission in the immune system. Nature 407:789–795
Bonnet D (2003) Biology of human bone marrow stem cells. Clin Exp Med 3:140–149
Lin F (2008) Renal repair: role of bone marrow stem cells. Pediatr Nephrol 23:851–861
Scintu F, Reali C, Pillai R, Badiali M, Sanna MA, Argiolu F, Ristaldi MS, Sogos V (2006) Differentiation of human bone marrow stem cells into cells with a neural phenotype: diverse effects of two specific treatments. BMC Neurosci 7:1186–1198
Kierdorf U, Kierdorf H, Szuwart T (2007) Deer antler regeneration: cells, concepts, and controversies. J Morphol 268:726–738
Zhou Q, Guo Y, Wang L, Wang Y, Liu Y, Wang Y, Wang B (1999) Velvet antler polypeptides promoted proliferation of chondrocytes and osteoblast precursors and fracture healing. Acta Pharmacol Sin 20:279–282
Guan S, Duan L, Li Y, Wang B, Zhou Q (2006) A novel polypeptide from Cervus nippon Temminck proliferation of epidermal cells and NIH3T3 cell line. Acta Biochim Pol 53:395–397
Zhang X, Chang Y, Chen Y, Yu Y (2002) Study on the growth factor-like action of the Sika deer immunocytes. J Jilin Univ (Medicine Edition) 28:603–605
Shao M, Wan M, Wang L, Yu Y (2005) Cloning and analysis of fibroblast growth factor 10 of Cervus nippon Temminck. J Jilin Univ (Medicine Edition) 28:215–218
Lu L, Chen L, Meng X, Yang F, Zhang Z, Chen D (2005) Biological effect of velvet antler polypeptides on neural stem cells from embryonic rat brain. J Chin Med Assoc 118:38–42
Ewing B, Hillier L, Wendl MC, Green P (1998) Base-calling of automated sequencer traces using phred. I. Accuracy assessment. Genome Res 8:175–185
Ewing B, Green P (1998) Base-calling of automated sequencer traces using phred. II. Error probabilities. Genome Res 8:186–194
Tarailo-Graovac M, Chen N (2009) Using RepeatMasker to identify repetitive elements in genomic sequences. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics (Chapter 4: Unit 4.10)
Huang X, Madan A (1999) CAP3: a DNA sequence assembly program. Genome Res 9:868–877
Gordon D, Abajian C, Green P (1998) Consed: a graphical tool for sequence. Genome Res 8:195–202
Olson SA (2002) EMBOSS opens up sequence analysis. European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite. Brief Bioinform 3:87–91
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, Harris MA, Hill DP, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Lewis S, Matese JC, Richardson JE, Ringwald M, Rubin GM, Sherlock G (2000) Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat Genet 25:25–29
The Gene Ontology Consortium (2010) The gene ontology in 2010: extensions and refinements. Nucleic Acids Res 38:D331–D335
Quevillon E, Silventoinen V, Pillai S, Harte N, Mulder N, Apweiler R, Lopez R (2005) InterProScan: protein domains identifier. Nucleic Acids Res 33:W116–W120
Goujon M, McWilliam H, Li W, Valentin F, Squizzato S, Paern J, Lopez R (2010) A new bioinformatics analysis tools framework at EMBL-EBI. Nucleic Acids Res 38:W695–W699
Tatusov RL, Galperin MY, Natale DA, Koonin EV (2000) The COG database: a tool for genome-scale analysis of protein functions and evolution. Nucleic Acids Res 28:33–36
Tatusov RL, Natale DA, Garkavtsev IV, Tatusova TA, Shankavaram UT, Rao BS, Kiryutin B, Galperin MY, Fedorova ND, Koonin EV (2001) The COG database: new developments in phylogenetic classification of proteins from complete genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 29:22–28
Ogata H, Goto S, Sato K, Fujibuchi W, Bono H, Kanehisa M (1999) KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 27:29–34
Kanehisa M, Goto S (2000) KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 28:27–30
Orr SL, Hughes TP, Sawyers CL, Kato RM, Quan SG, Williams SP, Witte ON, Hood L (1994) Isolation of unknown genes from human bone marrow by differential screening and single-pass cDNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:11869–11873
Gregory CA, Prockop DJ, Spees JL (2005) Non-hematopoietic bone marrow stem cells: molecular control of expansion and differentiation. Exp Cell Res 306:330–335
Flowers MT, Ntambi JM (2010) Stearoyl-CoA desaturase and its relation to high-carbohydrate diets and obesity. Biochim Biophys Acta 1791:85–91
Hood DA (1990) Co-ordinate expression of cytochrome c oxidase subunit III and VIc mRNAs in rat tissues. Biochem J 269:503–506
Pridgeon JW, Becnel JJ, Clark GG, Linthicum KJ (2009) Permethrin induces overexpression of cytochrome c oxidase subunit 3 in Aedes aegypti. J Med Entomol 46:810–819
Kang H, Chung J, Lee S (1997) Involvement of cytochrome c oxidasesubunit I gene during neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells. J Biochem Mol Biol 30:285–291
Xu A, Wang Y, Xu JY, Stejskal D, Tam S, Zhang J, Wat NM, Wong WK, Lam KS (2006) Adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein is a plasma biomarker closely associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome. Clin Chem 52:405–413
Yokota T, Meka CS, Kouro T, Medina KL, Igarashi H, Takahashi M, Oritani K, Funahashi T, Tomiyama Y, Matsuzawa Y, Kincade PW (2003) Adiponectin, a fat cell product, influences the earliest lymphocyte precursors in bone marrow cultures by activation of the cyclooxygenase–prostaglandin pathway in stromal cells. J Immunol 171:5091–5099
Sosne G, Qiu P, Kurpakus-Wheater M (2007) Thymosin beta 4: a novel corneal wound healing and anti-inflammatory agent. Clin Ophthalmol 1:201–207
Clark DE, Lord EA, Suttie JM (2006) Expression of VEGF and pleiotrophin in deer antler. Anat Rec A 288:1281–1293
Hoeben AN, Landuyt B, Highley MS, Wildiers H, Oosterom AT, De Bruijn EA (2004) Vascular endothelial growth factor and angiogenesis. Pharmacol Rev 56:549–580
Lingaraj K, Poh CK, Wang W (2010) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is expressed during articular cartilage growth and re-expressed in osteoarthritis. Ann Acad Med Singa 39:399–403
Lu KV, Jong KA, Kim GY, Singh J, Dia EQ, Yoshimoto K, Wang MY, Cloughesy TF, Nelson SF, Mischel PS (2005) Differential induction of glioblastoma migration and growth by two forms of pleiotrophin. J Biol Chem 280:26953–26964
Yeh HJ, He YY, Xu J, Hsu CY, Deuel TF (1998) Upregulation of pleiotrophin gene expression in developing microvasculature, macrophages, and astrocytes after acute ischemic brain injury. J Neurosci 18:3699–3707
Himburg HA, Muramoto GG, Daher P, Meadows SK, Russell JL, Doan P, Chi J, Salter AB, Lento WE, Reya T, Chao NJ, Chute JP (2010) Pleiotrophin regulates the expansion and regeneration of hematopoietic stem cells. Nat Med 16:475–482
Jia L, Young MF, Powell J, Yang L, Ho NC, Hotchkiss R, Robey PG, Francomano CA (2002) Gene expression profile of human bone marrow stromal cells: high-throughput expressed sequence tag sequencing analysis. Genomics 79:7–17
Silva WA Jr, Covas DT, Panepucci RA, Proto-Siqueira R, Siufi JL, Zanette DL, Santos AR, Zago MA (2003) The profile of gene expression of human marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells 21:661–669
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the National Key Technology R&D Program of China (No. 2007BAI38B06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, B., Zhao, Y., Zhang, M. et al. Generation and analysis of expressed sequence tags from the bone marrow of Chinese Sika deer. Mol Biol Rep 39, 2981–2990 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-1060-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-1060-3