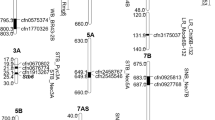
Abstract
Fungal diseases are among the most devastating biotic stresses and often cause significant losses in wheat production worldwide. A set of 173 synthetic hexaploid wheat (SHW) characterized for resistance against fungal pathogens that cause leaf, stem and yellow rusts, yellow leaf spot, Septoria nodorum and crown rot were used in genome-wide association study (GWAS). Diversity Arrays Technology (DArT) and DArTSeq markers were employed for marker–trait association in which 74 markers associated with 35 quantitative trait loci (QTL) were found to be significantly linked with disease resistances using a unified mixed model (P = 10−3 to 10−5); Of these 15 QTL originated from D genome. Six markers on 1BL, 3BS, 4BL, 6B, and 6D conferred resistance to two diseases representing 10 of the 35 QTL. A further set of 147 SHW genotyped with DArT only markers validated 11 QTL detected in the previous 173 SHW. We also confirmed the presence of the gene Lr46/Yr29/Sr58/Pm39/Ltn2 on 1BL in the SHW germplasm. In addition, gene–gene interactions between significantly associated loci and all loci across the genome revealed five significant interactions at FDR <0.05. Two significant leaf rust and one stem rust interactions were thought to be synergistic, while another two QTL for yellow leaf spot involved antagonistic relations. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first GWAS for six fungal diseases using SHW. Identification of markers associated with disease resistance to one or more diseases represents an important resource for pyramiding favorable alleles and introducing multiple disease resistance from SHW accessions into current elite wheat cultivars.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MDR:
-
Multiple disease resistance
- SHW:
-
Synthetic hexaploid wheat
- MLM:
-
Mixed linear model
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait loci
- GWAS:
-
Genome-wide association study
- LD:
-
Linkage disequilibrium
- Lr:
-
Leaf rust
- Sr:
-
Stem rust
- Yr:
-
Yellow rust
- YLS:
-
Yellow leaf spot
- SNG:
-
Septoria Nodorum glume blotch
- SNL:
-
Septoria Nodorum leaf blotch
- Cr:
-
Crown rot
- DArT:
-
Diversity Arrays Technology
References
Adhikari TB, Jackson EW, Gurung S, Hansen JM, Bonman JM (2011) Association mapping of quantitative resistance to Phaeosphaeria nodorum in spring wheat landraces from the USDA National Small Grains Collection. Phytopathology 101(11):1301–1310
Ágnes SH, Szabolcs LK, Mónika V, László P, János P, Csaba L, Ákos M (2014) Differential influence of QTL linked to Fusarium head blight, Fusarium-damaged kernel, deoxynivalenol contents and associated morphological traits in a Frontana-derived wheat population. Euphytica 200(1):9–26
Aguilar V, Stamp P, Winzeler M, Winzeler H, Schachermayr G, Keller B et al (2005) Inheritance of field resistance to Stagonospora nodorum leaf and glume blotch and correlations with other morphological traits in hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 111(2):325–336
Alam KB, Gustafson JP (1988) Tan-spot resistance screening of Aegilops species. Plant Breeding 100:112–118
Appel JA, DeWolf E, Bockus WW, Todd T (Preliminary 2011) Kansas wheat disease loss estimates. Kansas cooperative plant disease survey report, August 18, 2011
Assefa S, Fehrmann H (2000) Resistance to wheat leaf rust in Aegilops tauschii Coss and inheritance of resistance in hexaploid wheat. Genet Resour Crop Evol 47:135–140
Bansal A (2014) Effects of the Lr34 and Lr46 rust-resistance genes on other diseases of wheat. PhD thesis, University of East Anglia
Basnet BR, Singh RP, Ibrahim AMH, Herrera-Foessel SA, Huerta-Espino J, Lan C, Rudd JC (2014) Characterization of Yr54 and other genes associated with adult plant resistance to yellow rust and leaf rust in common wheat Quaiu 3. Mol Breed 33(2):385–399
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc B 57:289–300
Benson JM, Poland JA, Benson BM, Stromberg EL, Nelson RJ (2015) Resistance to gray leaf spot of maize: genetic architecture and mechanisms elucidated through nested association mapping and near isogenic line analysis. PLoS Genet 11:e1005045
Bhavani S, Singh RP, Argillier O, Huerta-Espino J, Singh S, Njau P, Brun S, Lacam S, Desmouceaux N (2011) Mapping durable adult plant stem rust resistance to the race Ug99 group in six CIMMYT wheats. 2011 BGRI Technical Workshop, pp 43–53
Braun HJ, Atlin G, Payne T (2010) Multi-location testing as a tool to identify plant response to global climate change. In: Reynolds CRP (ed) Climate change and crop production. CABI, London
Breseghello F, Sorrells MS (2006) Association mapping of kernel size and milling quality in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars. Genetics 172:1165–1177
Brown JKM, Rant JC (2013) Fitness costs and trade-offs of disease resistance and their consequences for breeding arable crops. Plant Pathol 62:83–95
Buschges R, Hollricher K, Panstruga R, Simons G, Wolter M et al (1997) The barley Mlo gene: a novel control element of plant pathogen resistance. Cell 88:695–705
Cesari S, Moore J, Chen C, Webb D, Periyannan S, Mago R, Bernoux M, Lagudah ES, Dodds PN (2016) Cytosolic activation of cell death and stem rust resistance by cereal MLA-family CC-NLR proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. doi:10.1073/pnas.1605483113
Chen J, Chu C, Souza EJ, Guttieri MJ, Chen X, Xu S et al (2012) Genome-wide identification of QTL conferring high-temperature adult-plant (HTAP) resistance to stripe rust (Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici) in wheat. Mol Breed 29(3):791–800
Cockram J, Scuderi A, Barber T, Furuki E, Gardner KA, Gosman N, Kowalczyk R, Phan HP, Rose GA, Tan KC, Oliver RP (2015) Fine-mapping the wheat Snn1 locus conferring sensitivity to the Parastagonospora nodorum necrotrophic effector SnTox1 using an eight founder multiparent advanced generation inter-Cross population. G3: genes| genomes|. Genetics 5(11):2257–2266
Crossa J, Burgueño J, Dreisigacker S, Vargas M, Herrera-Foessel SA, Lillemo M, Singh RP, Trethowan R, Warburton M, Franco J, Reynolds M, Crouch JH, Ortiz R (2007) Association analysis of historical bread wheat germplasm using additive genetic covariance of relatives and population structure. Genetics 177:1889–1913
Czembor PC, Arseniuk E, Czaplicki A, Song Q, Cregan PB, Ueng PP (2003) QTL mapping of partial resistance in winter wheat to Stagonospora nodorum blotch. Genome 46(4):546–554
Dedryver F, Paillard S, Mallard S, Robert O, Trottet M, Nègre S, Verplancke G, Jahier J (2009) Characterization of genetic components involved in durable resistance to stripe rust in the bread wheat ‘Renan’. Phytopathology 99:968–973
Detering F, Hunter E, Uszynski G, Wenzl P, Andrzej K (2010) A consensus genetic map of wheat: ordering 5000 wheat DArT markers. 20th ITMI & 2nd WGC workshop, 1–5 September, Beijing
Dreisigacker S, Kishii M, Lage J, Warburton M (2008) Use of synthetic hexaploid wheat to increase diversity for CIMMYT bread wheat improvement. Aust J Agric Res 59:413–420
Eastwood RF, Lagudah ES, Appels R, Hannah M, Kollmorgen JF (1991) Triticum tauschii: a novel source of resistance to cereal cyst nematode (Heterodera avenae). Aust J Agric Res 42:69–77
Eberhard FS (2011) Molecular marker assisted selection for crown rot resistance in Triticum turgidum ssp. durum (Doctoral dissertation, University of Southern Queensland)
Faris JD, Friesen TL (2005) Identification of quantitative trait loci for race-nonspecific resistance to tan spot in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 111:386–392
Farrer W (1898) The making and improvement of wheats for Australian conditions. Agric Gaz NSW 9:131–168
Flemmig EL (2012) Molecular markers to deploy and characterize stem rust resistance in wheat. MS Thesis, N. C. State. Univ., Raleigh
Flint-Garcia SA, Thornsberry JM, Buckler ES (2003) Structure of linkage disequilibrium in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 54:357–374
Flint-Garcia SA, Thuillet AC, Yu J, Pressoir G, Romero SM, Mitchell SE, Doebley J, Kresovich S, Goodman MM, Buckler ES (2005) Maize association population: a high-resolution platform for quantitative trait locus dissection. Plant Journal 44:1054–1064
Friesen TL, Faris JD (2004) Molecular mapping of resistance to Pyrenophora tritici-repentis race 5 and sensitivity to PtrToxB in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 109:464–471
Genc Y, Oldach K, Gogel B, Wallwork H, McDonald GK, Smith AB (2013) Quantitative trait loci for agronomic and physiological traits for a bread wheat population grown in environments with a range of salinity levels. Mol Breed 32(1):39–59
Goldstein DB, Tate SK, Sisodiya SM (2003) Pharmacogenetics goes genomics. Nat Rev Genet 4:937–947
Guerrero-Chavez R, Glover KD, Rouse MN, Gonzalez-Hernandez JL (2015) Mapping of two loci conferring resistance to wheat stem rust pathogen races TTKSK (Ug99) and TRTTF in the elite hard red spring wheat line SD4279. Mol Breed 35(1):1–10
Gupta SK, Charpe A, Prabhu KV, Haque QMR (2006) Identification and validation of molecular markers linked to the leaf rust resistance gene Lr19 in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 113(6):1027–1036
Gurung S, Mamidi S, Bonman JM, Jackson EW, del Rio LE, Acevedo M, Mergoum M, Adhikari TB (2011) Identification of novel genomic regions associated with resistance to Pyrenophora tritici-repentis races 1 and 5 in spring wheat landraces using association analysis. Theor Appl Genet 123:1029–1041
Gurung S, Mamidi S, Bonman JM, Xiong M, Brown-Guedira G, Adhikari TB (2014) Genome-wide association study reveals novel quantitative trait Loci associated with resistance to multiple leaf spot diseases of spring wheat. PLoS ONE 9(9):e108179
Hatchett JH, Martin TJ, Livers RW (1981) Expression and inheritance of resistance to Hessian fly in synthetic hexaploid wheats derived from Triticum tauschii (Coss) Schmal. Crop Sci 21:731–734
Hedrick PW (1987) Gametic disequilibrium measures: proceed with caution. Genetics 117:331–374
Herrera-Foessel SA, Singh RP, Huerta-Espino J, Salazar VC, Lagudah ES (2011) First report of slow rusting gene Lr46 in durum wheat. Borlaug Global Rust Initiative, June 13–16, 2011 Technical Workshop, St Paul, Minnesota, USA, p 191
Jansen C, Von Wettstein D, Schafer W, Kogel KH, Felk A, Maier FJ (2005) Infection patterns in barley and wheat spikes inoculated with wild-type and trichodiene synthase gene disrupted Fusarium graminearum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:16892–16897
Jarosch B, Kogel KH, Schaffrath U (1999) The ambivalence of the barley Mlo locus: mutations conferring resistance against powdery mildew (Blumeria graminis f. sp. hordei) enhance susceptibility to the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 12:508–514
Jighly A, Joukhadar R, Alagu M (2015a) SimpleMap: a pipeline to streamline high-density linkage map construction. Plant Genome. doi:10.3835/plantgenome2014.09.0056
Jighly A, Oyiga BC, Makdis F, Nazari K, Youssef O, Tadesse W, Abdalla O, Ogbonnaya FC (2015b) Genome-wide DArT and SNP scan for QTL associated with resistance to stripe rust (Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici) in elite ICARDA wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) germplasm. Theor Appl Genet 128:1277–1295
Joukhadar R, El-Bouhssini M, Jighly A, Ogbonnaya FC (2013) Genomic regions associated with resistance to five major pests in wheat. Mol Breed 32:943–960
Jordan T, Seeholzer S, Schwizer S, Töller A, Somssich IE, Keller B (2011) The wheat Mla homologue TmMla1 exhibits an evolutionarily conserved function against powdery mildew in both wheat and barley. Plant J 65(4):610–621
Krattinger SG, Lagudah ES, Spielmeyer W et al (2009) A putative ABC transporter confers durable resistance to multiple fungal pathogens in wheat. Science 323:1360–1363
Kumar J, Huckelhoven R, Beckhove U, Nagarajan S, Kogel KH (2001) A compromised Mlo pathway affects the response of barley to the necrotrophic fungus Bipolaris sorokiniana (Teleomorph: Cochliobolus sativus) and its toxins. Phytopathology 91:127–133
Kumar U, Joshi AK, Kumar S, Chand R, Röder MS (2010) Quantitative trait loci for resistance to spot blotch caused by Bipolaris sorokiniana in wheat (T. aestivum L.) lines ‘Ning 8201’and ‘Chirya 3’. Mol Breed 26(3):477–491
Lagudah ES (2011) Molecular genetics of race non-specific rust resistance in wheat. Euphytica 179:81–91
Lagudah ES, Krattinger SG, Herrera-Foessel S, Singh RP, Huerta-Espinoso J, Spielmeyer W, Brown-Guedira G, Selter LL, Keller B (2009) Gene-specific markers for the wheat gene Lr34/Yr18/Pm38 which confers resistance to multiple fungal pathogens. Theor Appl Genet 119:889–898
Letta T, Maccaferri M, Badebo A, Ammar K, Ricci A, Crossa J, Tuberosa R (2013) Searching for novel sources of field resistance to Ug99 and Ethiopian stem rust races in durum wheat via association mapping. Theor Appl Genet 126(5):1237–1256
Lipka AE, Tian F, Wang Q, Peiffer J, Li M, Bradbury PJ et al (2012) GAPIT: genome association and prediction integrated tool. Bioinformatics 28(18):2397–2399
Loughman R, Lagudah ES, Trottet M, Wilson RE, Mathews A (2001) Septoria nodorum blotch resistance in Aegilops tauschii and its expression in synthetic amphiploids. Aust J Agric Res 52:1393–1402
Lowe I, Jankuloski L, Chao S, Chen X, See D, Dubcovsky J (2011) Mapping and validation of QTL which confer partial resistance to broadly virulent post-2000 North American races of stripe rust in hexaploid wheat. Theor Appl Genet 123(1):143–157
Lozano-Torres JL, Wilbers RHP, Gawronski P, Boshoven JC, Finkers-Tomczak A et al (2012) Dual disease resistance mediated by the immune receptor Cf-2 in tomato requires a common virulence target of a fungus and a nematode. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:10119–10124
Lutz J, Hsam SLK, Limpert E, Zeller FJ (1994) Powdery mildew resistance in Aegilops tauschii Coss. and synthetic hexaploid wheats. Genet Resour Crop Evol 41:151–158
Ma H, Singh RP, Mujeeb-Kazi A (1995) Resistance to stripe rust in Triticum turgidum, T. tauschii and their synthetic hexaploids. Euphytica 82:117–124
Ma J, Li HB, Zhang CY, Yang XM, Liu YX, Yan GJ, Liu CJ (2010) Identification and validation of a major QTL conferring crown rot resistance in hexaploid wheat. Theor Appl Genet 120(6):1119–1128
Maccaferri M, Sanguineti MC, Natoli E, Araus-Ortega JL, Bensalem M et al (2006) A panel of elite accessions of durum wheat (Triticum durum Desf.) suitable for association mapping studies. Plant Genet Resour 4:79–85
Mackay I, Powell W (2006) Methods for linkage disequilibrium mapping in crops. Trends Plant Sci 12:57–63
Mago R, Brown-Guedira G, Dreisigacker S, Breen J, Jin Y, Singh R, Appels R, Lagudah ES, Ellis J, Spielmeyer W (2011) An accurate DNA marker assay for stem rust resistance gene Sr2 in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 122:735–744. doi:10.1007/s00122-010-1482-7
Mago R, Zhang P, Vautrin S, Šimková H, Bansal U, Luo MC, Rouse M, Karaoglu H, Periyannan S, Kolmer J, Jin Y (2015) The wheat Sr50 gene reveals rich diversity at a cereal disease resistance locus. Nat Plants 1(12):15186
Marais GF, Potgieter GF, Roux HS (1994) An assessment of the variation for stem rust resistance in the progeny of a cross involving the Triticum species aestivum, turgidum and tauschii. S Afr J Plant Soil 11:15–19
McGrann GRD, Stavrinides A, Russell J, Corbitt MM, Booth A, Chartrain L, Tomas WTB, Brown JKM (2014) A tradeoff between mlo resistance to powdery mildew and increased susceptibility of barley to a newly important disease, Ramularia leaf spot. J Exp Bot 65(4):1025–1037
McIntosh RA (1992) Close genetic linkage of genes conferring adult-plant resistance to leaf rust and stripe rust in wheat. Plant Pathology 41:523–527 (Bot 65:1025–37)
Mebrate SA, Oerke EC, Dehne HW, Pillen K (2008) Mapping of the leaf rust resistance gene Lr38 on wheat chromosome arm 6DL using SSR markers. Euphytica 162(3):457–466
Michelmore RW, Christopoulou M, Caldwell KS (2013) Impacts of resistance gene genetics, function, and evolution on a durable future. Ann Rev Phytopathol 51:291–319
Moore JH, White BC (2007) Tuning relief for genome-wide genetic analysis. In: Marchiori E, Moore JH, Rajapakse JC (eds) Lecture notes in computer science, vol 4447. Springer, New York, pp 166–175
Moore JW, Herrera-Foessel S, Lan C, Schnippenkoetter W, Ayliffe M, Huerta-Espino J, Lillemo M, Viccars L, Milne R, Periyannan S, Kong X (2015) A recently evolved hexose transporter variant confers resistance to multiple pathogens in wheat. Nat Genet 47:1494–1498
Mujeeb-Kazi A, Cano S, Rosas V, Cortes A, Delgado R (2001a) Registration of five synthetic hexaploid wheat and seven bread wheat lines resistant to wheat spot blotch. Crop Sci 41:1653–1654
Mujeeb-Kazi A, Delgado R, Juarez L, Cano S (2001b) Scab resistance (Type II: spread) in synthetic hexaploid germplasm. Ann Wheat Newsl 47:118–120
Mulki MA, Jighly A, Ye G, Emebiri LC, Moody D, Ansari O, Ogbonnaya FC (2013) Association mapping for soilborne pathogen resistance in synthetic hexaploid wheat. Mol Breed 3:299–311
Neumann K, Kobiljski B, Denčić S, Varshney RK, Börner A (2011) Genome-wide association mapping: a case study in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Mol Breed 27:37–58
Nombela G, Williamson VM, Muniz M (2003) The root-knot nematode resistance gene Mi-1.2 of tomato is responsible for resistance against the whitefly Bemisia tabaci. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 16:645–649
Ogbonnaya FC (2011) Development, management and utilization of synthetic hexaploid in wheat improvement. In: Bonjean AP, Angus WJ, van Ginkel M (eds) The world wheat book—a history of wheat breeding, vol 2. Lavoisier, Paris, pp 823–843
Ogbonnaya FC, Seah S, Delibes A, Jahier J, Lopez-Brana I, Eastwood RF, Lagudah ES (2001) Molecular-genetic characterisation of a new nematode resistance gene in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 102:623–629
Ogbonnaya FC, Imtiaz M, Bariana HS, McLean M, Shankar M, Hollaway GJ, Trethowan R, Lagudah ES, van Ginkel M (2008) Mining synthetic hexaploids for multiple disease resistance to improve wheat. Aust J Agric Res 59:421–431
Ogbonnaya FC, Abdalla O, Mujeeb-Kazi A, Kazi AG, Steven Xu, Gosman N, Lagudah ES, Bonnett D, Sorells ME, Tsujimoto H (2013) Synthetic hexaploids: Harnessing species of primary gene pool for wheat improvement. Plant Breed Rev 37:35–122
Oliver RP, Tucker M, Rybak K, Antoni E, Lichtenzveig J (2011) Managing fungicide resistance in broad acre cropping in Australia. Research update report in GRDC Australia. (http://www.grdc.com.au/director/events/researchupdates?item_id=C13F2CCD0DF0838ED195B4C05D522FD5&pageNumber=1)
Periyannan S, Moore J, Ayliffe M, Bansal U, Wang X, Huang L, Deal K, Luo M, Kong X, Bariana H, Mago R (2013) The gene Sr33, an ortholog of barley Mla genes, encodes resistance to wheat stem rust race Ug99. Science 341(6147):786–788
Perrier X, Jacquemoud-Collet JP (2006) DARwin software. http://darwin.cirad.fr/
Poole GJ, Smiley RW, Paulitz TC, Walker CA, Carter AH, See DR, Garland-Campbell K (2012) Identification of quantitative trait loci (QTL) for resistance to Fusarium crown rot (Fusarium pseudograminearum) in multiple assay environments in the Pacific Northwestern US. Theor Appl Genet 125(1):91–107
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959
Rosewarne GM, Herrera-Foessel SA, Singh RP, Huerta-Espino J, Lan CX, He ZH (2013) Quantitative trait loci of stripe rust resistance in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 126(10):2427–2449
Santra DK, Chen XM, Santra M, Campbell KG, Kidwell KK (2008) Identification and mapping QTL for high-temperature adult-plant resistance to stripe rust in winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivar ‘Stephens’. Theor Appl Genet 117:793–802
Schnurbusch T, Paillard S, Fossati D, Messmer M, Schachermayr G, Winzeler M, Keller B (2003) Detection of QTLs for Stagonospora glume blotch resistance in Swiss winter wheat. Theor Appl Genet 107(7):1226–1234
Segrè D, DeLuna A, Church GM, Kishony R (2005) Modular epistasis in yeast metabolism. Nat Genet 37:77–83
Sehgal D, Vikram P, Sansaloni CP, Ortiz C, Saint Pierre C, Payne T et al (2015) Exploring and mobilizing the gene bank biodiversity for wheat improvement. PLoS ONE 10(7):e0132112
Shankar M, Walker E, Golzar H, Loughman R, Wilson RE, Francki MG (2008) Quantitative trait loci for seedling and adult plant resistance to Stagonospora nodorum in wheat. Phytopathology 98(8):886–893
Shirasu K, Schulze-Lefert P (2003) Complex formation, promiscuity and multi-functionality: protein interactions in disease-resistance pathways. Trends Plant Sci 8(6):252–258
Siedler H, Obst A, Hsam SLK, Zeller FJ (1994) Evaluation for resistance to Pyrenophora tritici-repentis in Aegilops tauschii Coss. and synthetic hexaploid amphiploids. Genet Resour Crop Evol 41:27–34
Singh RP (1993) Genetic association of gene Bdv1 for tolerance to barley yellow dwarf virus with genes Lr34 and Yr18 for adult plant resistance to rusts in bread wheat. Plant Disease 77:1103–1106 (Genet 108(4):586–591)
Singh S, Franks CD, Huang L, Brown-Guedira GL, Marshall DS, Gill BS, Fritz A (2004) Lr41, Lr39, and a leaf rust resistance gene from Aegilops cylindrica may be allelic and are located on wheat chromosome 2DS. Theor Appl Genet 108:586–591
Singh PK, Mergoum M, Ali S, Adhikari TB, Elias EM, Hughes GR (2006) Identification of new sources of resistance to tan spot, Stagonospora nodorum blotch, and Septoria tritici blotch of wheat. Crop Sci 46(5):2047–2053
Singh A, Pandey MP, Singh AK, Knox RE, Ammar K, Clarke JM, Clarke F, Singh RP, Pozniak CJ, DePauw RM, McCallum B, Cuthbert RD, Randhawa HS, Fetch T (2013) Identification and mapping of leaf, stem and stripe rust resistance QTL and their interactions in durum wheat. Mol Breed 31:405–418
Solh M, Nazari K, Tadesse W, Wellings CR (2012) The growing threat of stripe rust worldwide. Paper presented at: Borlaug Global Rust Initiative (BGRI) conference, Beijing, China. 1–4 Sept 2012
Spielmeyer W, McIntosh RA, Kolmer J, Lagudah ES (2005) Powdery mildew resistance and Lr34/Yr18 genes for durable resistance to leaf and stripe rust co-segregate at a locus on the short arm of chromosome 7D of wheat. Theor Appl Genet 111:731–735
Spielmeyer W, Singh RP, McFadden H, Wellings CR, Huerta-Espino J, Kong X, Appels R, Lagudah ES (2008) Fine scale genetic and physical mapping using interstitial deletion mutants of Lr34/Yr18: a disease resistance locus effective against multiple pathogens in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 116:481–490
Sukhwinder-Singh Hernandez MV, Crossa J, Singh PK, Bains NS, Singh K, Sharma I (2012) Multi-trait and multi-environment QTL analysis for resistance to wheat diseases. PLoS ONE 7(6):e38008
Sun X, Bai G, Carver BF, Bowden R (2010) Molecular mapping of wheat leaf rust resistance gene. Crop Sci 50(1):59–66
Tadesse W, Hsam SL, Wenzel G, Zeller FJ (2006) Identification and monosomic analysis of tan spot resistance genes in synthetic wheat lines (L. × Coss.). Crop Sci 46(3):1212–1217
Tadesse W, Hsam SLK, Zeller FJ (2007) Evaluation of common wheat cultivars for tan spot resistance and chromosomal location of a resistance gene in the cultivar ‘Salamouni’. Plant Breed 125:318–322
Tadesse W, Ogbonnaya FC, Jighly A, Nazari K, Rajaram S, Baum M (2014) Association mapping of resistance to yellow rust in winter wheat cultivars and elite genotypes. Crop Sci 54(2):607–616
Tadesse W, Ogbonnaya FC, Jighly A, Sanchez-Garcia M, Sohail Q, Rajaram S, Baum M (2015) Genome-wide association mapping of yield and grain quality traits in winter wheat genotypes. PLoS ONE 10(10):e0141339
Thompson JP (2008) Resistance to root-lesion nematodes (Pratylenchusthornei and P. neglectus) in synthetic hexpaloid wheats and their durum and Aegilops tauschii parents. Aust J Agric Res 59:432–446
Van Baarlen P, Staats M, Van Kan JAL (2004) Induction of programmed cell death in lily by the fungal pathogen Botrytis elliptica. Mol Plant Pathol 5:559–574
van Ginkel M, Ogbonnaya FC (2007) Novel genetic diversity from synthetic wheats in breeding cultivars for changing production conditions. Field Crops Res 104:86–94
Vanegas CDG, Garvin DF, Kolmer JA (2008) Genetics of stem rust resistance in the spring wheat cultivar Thatcher and the enhancement of stem rust resistance by Lr34. Euphytica 159:391–401. doi:10.1007/s10681-007-9541-0
Villareal RL, Mujeeb-Kazi A, Fuentes-Davila G, Rajaram S, Toro ED (1994) Resistance to karnal bunt (Tilletia indica Mitra) in synthetic hexaploid wheats derived from Triticum turgidum × T. tauschii. Plant Breed 112(1):63–69
Wallace JG, Bradbury PJ, Zhang N, Gibon Y, Stitt M, Buckler ES (2014) Association mapping across numerous traits reveals patterns of functional variation in maize. PLoS Genet 10:e1004845
Weir BS (1996) Genetic data analysis II: methods for discrete populations genetic data. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland
White J, Law JR, Mackay I, Chalmers KJ, Smith JSC, Kilian A, Powell W (2008) The genetic diversity of UK, US and Australian cultivars of Triticum aestivum measured by DArT markers and considered by genome. Theor Appl Genet 116:439–453
Wiesner-Hanks T, Nelson R (2016) Multiple disease resistance in plants. Annu Rev Phytopathol 54:8.1–8.24
William M, Singh RP, Huerta-Espino J, Islas SO, Hoisington D (2003) Molecular marker mapping of leaf rust resistance gene Lr46 and its association with stripe rust resistance gene Yr29 in wheat. Phytopathology 93:153–159
Wissera RJ, Kolkmanb JM, Patzoldta ME, Hollandc JB, Yud J, Krakowskyc M, Nelsonb RJ, Balint-Kurtie PJ (2011) Multivariate analysis of maize disease resistances suggests a pleiotropic genetic basis and implicates a GST gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(18):7339–7344
Xu SS, Friesen TL, Mujeeb-Kazi A (2004) Seedling resistance to tan spot and stagonospora nodorum blotch in synthetic hexaploid wheats. Crop Sci 44:2238–2245
Yan W (2001) GGEBiplot—a Windows application for graphical analysis of multi-environment trial data and other types of two-way data. Agron J 93:1111–1118
Yan W, Kang MS (2002) Cultivar evaluation based on multiple traits. In: GGE biplot analysis: a graphical tool for breeders, geneticists, and agronomists. CRC Press, London
Yu J, Buckler ES (2006) Genetic association mapping and genome organization of maize. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17:155–160
Yu LX, Lorenz A, Rutkoski J, Singh RP, Bhavani S, Huerta-Espino J, Sorrells ME (2011) Association mapping and gene-gene interaction for stem rust resistance in spring wheat germplasm. Theor Appl Genet 123:1257–1268
Yu LX, Barbier H, Rouse MN, Singh S, Singh RP, Bhavani S et al (2014) A consensus map for Ug99 stem rust resistance loci in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 127(7):1561–1581
Yu G, Zhang Q, Friesen TL, Rouse MN, Jin Y, Zhong S et al (2015) Identification and mapping of Sr46 from Aegilops tauschii accession CIae 25 conferring resistance to race TTKSK (Ug99) of wheat stem rust pathogen. Theor Appl Genet 128(3):431–443
Zegeye H, Rasheed A, Makdis F, Badebo A, Ogbonnaya FC (2014) Genome-wide association mapping for seedling and adult plant resistance to stripe rust in synthetic hexaploid wheat. PLoS ONE 9(8):e105593
Zhang Z, Ersoz E, Lai CQ, Todhunter RJ, Tiwari HK, Gore MA, Bradbury PJ, Yu J, Arnett DK, Ordovas JM, Buckler ES (2010) Mixed linear model approach adapted for genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 42(4):355–360
Zwart RS, Thompson JP, Milgate AW, Bansal UK, Williamson PM, Raman H, Bariana HS (2010) QTL mapping of multiple foliar disease and root-lesion nematode resistances in wheat. Mol Breed 26:107–124
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge financial support from the Grains Research and Development Corporation, International Centre for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA), the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Centre (CIMMYT) and Department of Environment and Primary Industries, Victoria. They thank J. Wilson, M. S. McLean, S. P. Taylor, J. P. Thompson, H. S. Bariana, M. M. Shankar, and A. Milgate for their assistance with disease phenotyping.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11032_2016_541_MOESM1_ESM.xlsx
Table S1 List of the 320 synthetic hexaploid wheat genotypes used in this study, their pedigrees and their phenotypes scored from 1 (susceptible) to 9 (resistant) (XLSX 34 kb)
11032_2016_541_MOESM6_ESM.png
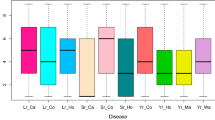
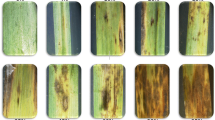
Figure S1 Results of the response of 320 SHWs to each of the six diseases evaluated. YLS = yellow leaf spot, Cr = crown rot, Lr = leaf rust, Sr = stem rust, Yr = yellow rust, SNL = Stagonospora nodorum leaf blotch, SNG = Stagonospora nodorum glume blotch. S = susceptible, MS = moderately susceptible, MR = moderately resistant, and R = resistant (PNG 2 kb)
11032_2016_541_MOESM9_ESM.png
Figure S4 Phylogenetic tree of the 320 SHWs, red genotypes represent the main set while blue genotypes represent the validation set (PNG 123 kb)
11032_2016_541_MOESM11_ESM.png
Figure S6 Scatter plot for the genetic distance against R2 value for each pair of markers on the same chromosome (LD decay) for a) whole genome; b) genome A; c) genome B; d) genome D. Red lines represent the LOESS second degree smoothing while the blue horizontal lines represents the R2 cut off 0.2 (PNG 199 kb)
11032_2016_541_MOESM13_ESM.pdf
Figure S8 Manhattan and QQ plots for studied traits. Cr = crown rot, Lr = leaf rust, Sr = stem rust, Yr = yellow rust, SNL = Stagonospora nodorum leaf blotch, SNG = Stagonospora nodorum glume blotch and YLS = yellow leaf spot. Chromosomes were numbered starting from the homoeologous chromosome group one to seven with within group order of A, B and D genome, respectively. Chromosome 22 represents the unmapped markers (PDF 1379 kb)
11032_2016_541_MOESM14_ESM.png
Figure S9 The average disease score (the allelic effect) for the alleles of the markers with multiple associations. For the 6D QTL, we used only the marker 1126778 (PNG 42 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jighly, A., Alagu, M., Makdis, F. et al. Genomic regions conferring resistance to multiple fungal pathogens in synthetic hexaploid wheat. Mol Breeding 36, 127 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-016-0541-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-016-0541-4