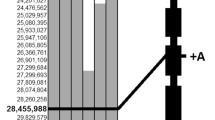
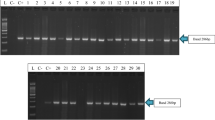
Abstract
Acetolactate synthase (ALS) is responsible for a rate-limiting step in the synthesis of essential branched-chain amino acids. Resistance to ALS-inhibiting herbicides, such as trifloxysulfuron sodium (Envoke®), can be due to mutations in the target gene itself. Alternatively, plants may exhibit herbicide tolerance through reduced uptake and translocation or increased metabolism of the herbicide. The diverse family of cytochrome P450 proteins has been suggested to be a source of novel herbicide metabolism in both weed and crop plants. In this study we generated a mapping population between resistant and susceptible cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) cultivars. We found that both cultivars possess identical and sensitive ALS sequences; however, the segregation of resistance in the F2 progeny was consistent with a single dominant gene. Here we report the closely linked genetic markers and approximate physical location on chromosome 20 of the source of Envoke herbicide susceptibility in the cotton cultivar Paymaster HS26. There are no P450 proteins in the corresponding region of the G. raimondii Ulbr. genome, suggesting that an uncharacterized molecular mechanism is responsible for Envoke herbicide tolerance in G. hirsutum. Identification of this genetic mechanism will provide new opportunities for exploiting sulfonylurea herbicides for management of both weeds and crop plants.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25(17):3389–3402
Askew SD, Wilcut JW (2002) Absorption, translocation, and metabolism of foliar-applied CGA 362622 in cotton, peanut, and selected weeds. Weed Sci 50(3):293–298
Barrett M (1995) Metabolism of herbicides by cytochrome P450 in corn. Drug Metabol Drug Interact 12(3–4):299–315
Blenda A, Fang DD, Rami JF, Garsmeur O, Luo F, Lacape JM (2012) A high density consensus genetic map of tetraploid cotton that integrates multiple component maps through molecular marker redundancy check. PLoS ONE 7(9):e45739
Chaleff RS, Mauvais CJ (1984) Acetolactate synthase is the site of action of two sulfonylurea herbicides in higher plants. Science 224(4656):1443–1445
Chaleff RS, Ray TB (1984) Herbicide-resistant mutants from tobacco cell cultures. Science 223(4641):1148–1151
Délye C (2013) Unravelling the genetic bases of non-target-site-based resistance (NTSR) to herbicides: a major challenge for weed science in the forthcoming decade. Pest Manag Sci 69(2):176–187
Didierjean L, Gondet L, Perkins R, Lau SM, Schaller H, O’Keefe DP, Werck-Reichhart D (2002) Engineering herbicide metabolism in tobacco and Arabidopsis with CYP76B1, a cytochrome P450 enzyme from Jerusalem artichoke. Plant Physiol 130(1):179–189
Duggleby RG, Pang SS, Yu H, Guddat LW (2003) Systematic characterization of mutations in yeast acetohydroxyacid synthase. Euro J Biochem 270(13):2895–2904
Fang DD, Yu J (2012) Addition of 455 microsatellite marker loci to the high density Gossypium hirsutum TM-1 × G. barbadense 3–79 genetic map. J Cotton Sci 16:229–248
Fang DD, Xiao J, Canci PC, Cantrell RG (2010) A new SNP haplotype associated with blue disease resistance gene in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Theor Appl Genet 120(5):943–953
Frear DS (1995) Wheat microsomal cytochrome P450 monooxygenases: characterization and importance in the metabolic detoxification and selectivity of wheat herbicides. Drug Metabol Drug Interact 12(3–4):329–357
Grula JW, Hudspeth RL, Hobbs SL, Anderson DM (1995) Organization, inheritance and expression of acetohydroxyacid synthase genes in the cotton allotetraploid Gossypium hirsutum. Plant Mol Biol 28(5):837–846
Haughn G, Somerville C (1986) Sulfonylurea-resistant mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Gen Genet 204(3):430–434
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Matsunaka S (1968) Propanil hydrolysis: inhibition in rice plants by insecticides. Science 160(3834):1360–1361
McCourt JA, Pang SS, King-Scott J, Guddat LW, Duggleby RG (2006) Herbicide-binding sites revealed in the structure of plant acetohydroxyacid synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(3):569–573
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli RV (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88(21):9828–9832
Minton BW, Senseman SA, Cothren JT, Chandler JM, Wells JW (2005) Cotton response to CGA-362622 applied alone and in combination with selected insecticides. Weed Technol 19(2):244–250
Minton B, Matocha M, Senseman SA (2008) The Influence of malathion on trifloxysulfuron absorption and translocation in cotton. J Cotton Sci 12(1):48–52
Nelson DR (2009) The cytochrome P450 homepage. Hum Genomics 4(1):59–65
Nelson DR, Schuler MA, Paquette SM, Werck-Reichhart D, Bak S (2004) Comparative genomics of rice and Arabidopsis. Analysis of 727 cytochrome P450 genes and pseudogenes from a monocot and a dicot. Plant Physiol 135(2):756–772
Newhouse K, Singh B, Shaner D, Stidham M (1991) Mutations in corn (Zea mays L.) conferring resistance to imidazolinone herbicides. Theor Appl Genet 83(1):65–70
Owen MJ, Goggin DE, Powles SB (2012) Non-target-site-based resistance to ALS-inhibiting herbicides in six Bromus rigidus populations from Western Australian cropping fields. Pest Manag Sci 68(7):1077–1082
Pan G, Zhang X, Liu K, Zhang J, Wu X, Zhu J, Tu J (2006) Map-based cloning of a novel rice cytochrome P450 gene CYP81A6 that confers resistance to two different classes of herbicides. Plant Mol Biol 61(6):933–943
Paterson AH, Wendel JF, Gundlach H, Guo H, Jenkins J et al (2012) Repeated polyploidization of Gossypium genomes and the evolution of spinnable cotton fibres. Nature 492(7429):423–427
Petit C, Duhieu B, Boucansaud K, Délye C (2010) Complex genetic control of non-target-site-based resistance to herbicides inhibiting acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase and acetolactate-synthase in Alopecurus myosuroides Huds. Plant Sci 178(6):501–509
Porterfield D, Wilcut JW, Clewis SB, Edmisten KL (2002) Weed-free yield response of seven cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) cultivars to CGA-362622 postemergence. Weed Technol 16(1):180–183
Porterfield D, Wilcut JW, Wells JW, Clewis SB (2003) Weed management with CGA-362622 in transgenic and nontransgenic cotton. Weed Sci 51(6):1002–1009
Pozniak CJ, Birk IT, O’Donoughue LS, Ménard C, Hucl PJ, Singh BK (2004) Physiological and molecular characterization of mutation-derived imidazolinone resistance in spring wheat. Crop Sci 44(4):1434–1443
Rajasekaran K, Grula J, Hudspeth R, Pofelis S, Anderson D (1996a) Herbicide-resistant Acala and Coker cottons transformed with a native gene encoding mutant forms of acetohydroxyacid synthase. Mol Breed 2(4):307–319
Rajasekaran K, Grula JW, Anderson DM (1996b) Selection and characterization of mutant cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) cell lines resistant to sulfonylurea and imidazolinone herbicides. Plant Sci 119(1):115–124
Richardson RJ, Hatzios KK, Wilson HP (2003) Absorption, translocation, and metabolism of CGA 362622 in cotton and two weeds. Weed Sci 51(2):157–162
Robineau T, Batard Y, Nedelkina S, Cabello-Hurtado F, LeRet M, Sorokine O, Didierjean L, Werck-Reichhart D (1998) The chemically inducible plant cytochrome P450 CYP76B1 actively metabolizes phenylureas and other xenobiotics. Plant Physiol 118(3):1049–1056
Sebastian SA, Fader GM, Ulrich JF, Forney DR, Chaleff RS (1989) Semidominant soybean mutation for resistance to sulfonylurea herbicides. Crop Sci 29(6):1403–1408
Swanson EB, Herrgesell MJ, Arnoldo M, Sippell DW, Wong RSC (1989) Microspore mutagenesis and selection: canola plants with field tolerance to the imidazolinones. Theor Appl Genet 78(4):525–530
Van Ooijen J (2006) JoinMap 4®: Software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps in experimental populations. Kyazma BV, Wageningen
Wright TR, Penner D (1998) Cell selection and inheritance of imidazolinone resistance in sugarbeet (Beta vulgaris). Theor Appl Genet 96(5):612–620
Yu Q, Abdallah I, Han H, Owen M, Powles S (2009) Distinct non-target site mechanisms endow resistance to glyphosate, ACCase and ALS-inhibiting herbicides in multiple herbicide-resistant Lolium rigidum. Planta 230(4):713–723
Yu JZ, Kohel RJ, Fang DD, Cho J, Van Deynze A, Ulloa M et al (2012) A high-density simple sequence repeat and single nucleotide polymorphism genetic map of the tetraploid cotton genome. G3 2(1):43–58
Yuan JS, Tranel PJ, Stewart CN Jr (2007) Non-target-site herbicide resistance: a family business. Trends Plant Sci 12(1):6–13
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by United States Department of Agriculture–Agricultural Research Service CRIS project 6435-21000-017-00D. We thank Mr. Russell Hayes for assisting with the field experiments. Our appreciation goes to Mrs. Sheron Simpson and Dr. Brian Scheffler at the Genomics and Bioinformatics Research Unit at Stoneville, MS for their excellent support in SSR marker analysis. Mention of trade names or commercial products in this article is solely for the purpose of providing specific information and does not imply recommendation or endorsement by the U.S. Department of Agriculture, which is an equal opportunity provider and employer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thyssen, G., McCarty, J.C., Li, P. et al. Genetic mapping of non-target-site resistance to a sulfonylurea herbicide (Envoke®) in Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Mol Breeding 33, 341–348 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-013-9953-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-013-9953-6