Abstract
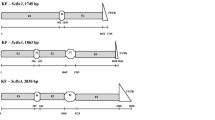
A BAC library from common bean has been used in order to isolate the entire multigene Bowman–Birk serine protease inhibitor family and to study its genome organization. Using a previously isolated trypsin/chymotrypsin inhibitor nucleotide sequence as probe, two positive BAC clones were identified. The P2B8 BAC clone, of about 135 kbp and containing the complete BBI family, was chosen and partially sequenced. Our results confirm that a small multigene family codes for three double-headed inhibitors named: tc-BBI-1, tc-BBI-2 and et-BBI. They contain the binding loop trypsin/chymotrypsin (tc-BBI-1 and tc-BBI-2) and the elastase/trypsin one (et-BBI), respectively. Genes coding for tc-BBI-1 and et-BBI, were found to be very close to each other and arranged in a head to head fashion. Southern blot hybridisation on genomic DNA digested with PstI enzyme suggests that all three genes are present in a fragment of 19 kbp. Northern blot analyses on RNA isolated from various common bean organs showed that the expression of tc-BBI-1 and et-BBI was restricted to the developing cotyledons.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong WB, Wan XS, Kennedy AR, Taylor TH (2003) Development of the Bowman–Birk inhibitor for oral cancer chemoprevention and analysis of Neu immunohistochemical staining intensity with Bowman–Birk inhibitor concentrate treatment. Laryngoscope 113:1687–1702. doi:10.1097/00005537-200310000-00007
Barampama Z, Simard RE (1993) Nutrient composition, protein quality and antinutritional factors of some varieties of dry beans (Phaseolus vulgaris) grown in Burundi. Food Chem 47:159–167. doi:10.1016/0308-8146(93)90238-B
Clemente A, Gee JM, Johnson IT, MacKenzie DA, Domoney C (2005) Pea (Pisum sativum L.) protease inhibitors from the Bowman–Birk class influence the growth of human colorectal adenocarcinoma HT29 cells in vitro. J Agric Food Chem 53:8979–8986. doi:10.1021/jf051528w
Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB (1983) A plant DNA minipreparation: version II. Plant Mol Biol Rep 1:19–21. doi:10.1007/BF02712670
Domoney C, Welham T, Ellis N, Hellens R (1994) Inheritance of qualitative and quantitative trypsin inhibitor variants in Pisum. Theor Appl Genet 89:387–391. doi:10.1007/BF00225370
Domoney C, Welham T, Sidebottom C, Firmin JL (1995) Multiple isoforms of Pisum trypsin inhibitors result from modification of two primary gene products. FEBS Lett 360:15–20. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(95)00070-P
Durigan JF, Sgarbieri VC (1987) Antinutritional factors and toxicity in row dry beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) of 12 Brazilian cultivars. J Food Biochem 11:185–200. doi:10.1111/j.1745-4514.1987.tb00122.x
Kennedy AR, Billings PC, Wan XS, Newberne PM (2002) Effects of Bowman–Birk inhibitor on rat colon carcinogesesis. Nutr Cancer 43:174–186. doi:10.1207/S15327914NC432_8
Koes R, Spelt K, Mol J (1987) Tissue-specificity and coordinated inducibility of PAL, CHS and CHI in different lines of Petunia using enzyme measurements and northern hybridisation. EMBO Practical Course: Petunia hybrida as a model system for molecular research, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, August 23–September 9, 1987, pp 50–55
Lescot M, De’hais P, Thijs G, Marchal K, Moreau Y, Van de Peer Y, Rouzé P, Rombauts S (2002) PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 30:325–327. doi:10.1093/nar/30.1.325
Lioi L, Piergiovanni AR, Pignone D, Puglisi S, Santantonio M, Sonnante G (2005) Genetic diversity of some surviving on-farm Italian common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) landraces. Plant Breed 124:576–581. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0523.2005.01153.x
Odani S, Ikenaka T (1978) Studies on soybean trypsin inhibitors. XIV. Change of the inhibitory activity of Bowman–Birk inhibitor upon replacements of the a-chymotrypsin reactive site serine residue by other amino acids. J Biochem 84:1–9
Piergiovanni AR, Galasso I (2004) Polymorphism of trypsin and chymotrypsin binding loops in Bowman–Birk inhibitors from common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Plant Sci 166:1525–1531. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2004.02.005
Piergiovanni AR, Pignone D (2003) Effect of year-to-year variation and genotype on trypsin inhibitor level in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) seeds. J Sci Food Agric 83:473–476. doi:10.1002/jsfa.1404
Piergiovanni AR, Cerbino D, Della Gatta C (2000a) Diversity in seed quality traits of common bean populations from Basilicata (Southern Italy). Plant Breed 119:513–516. doi:10.1046/j.1439-0523.2000.00531.x
Piergiovanni AR, Cerbino D, Brandi M (2000b) The common bean populations from Basilicata (Southern Italy). An evaluation of their variation. Genet Resour Crop Evol 47:489–495. doi:10.1023/A:1008719105895
Qi RF, Song ZW, Chi CW (2005) Structural features and molecular evolution of Bowman–Birk protease inhibitors and their potential application. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 37:283–292. doi:10.1111/j.1745-7270.2005.00048.x
Ryan CA (1990) Protease inhibitors in plants: genes for improving defences against insects and pathogens. Annu Rev Phytopathol 28:425–449. doi:10.1146/annurev.py.28.090190.002233
Sasaki T, Matsumoto T, Yamamoto K et al (2002) The genome sequence and structure of rice chromosome 1. Nature 420:312–316. doi:10.1038/nature01184
Schechter J, Berger A (1967) On the size of the active site proteases. I. Papain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 27:157–162. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(67)80055-X
Shewry PR, Lucas JA (1997) Plant proteins that confer resistance to pests and pathogens. Adv Bot Res 26:135–192. doi:10.1016/S0065-2296(08)60120-2
Sparvoli F, Martin C, Scienza A, Gavazzi G, Tonelli C (1994) Cloning and molecular analysis of structural genes involved in flavonoid and stilbene biosynthesis in grape (Vitis vinifera L.). Plant Mol Biol 24:743–755. doi:10.1007/BF00029856
Wilson KA, Laskowski SR (1975) The partial amino acid sequence of trypsin inhibitor II from garden bean, Phaseolus vulgaris, with location of the trypsin and elastase-reactive sites. J Biol Chem 250:4261–4267
Acknowledgments
Research partially supported by Ministry of Agriculture Food and forestry policies with funds released by C.I.P.E (Resolution 17/2003). We thank Mrs. M.G. Daminati for technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galasso, I., Piergiovanni, A.R., Lioi, L. et al. Genome organization of Bowman–Birk inhibitor in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Mol Breeding 23, 617–624 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-009-9260-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-009-9260-4