Abstract
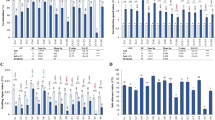
To develop a salt-tolerant upland rice cultivar (Oryza sativa L.), OsNHX1, a vacuolar-type Na+/H+ antiporter gene from rice was transferred into the genome of an upland rice cultivar (IRAT109), using an Agrobacterium-mediated method. Seven independent transgenic calli lines were identified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis. These 35S::OsNHX1 transgenic plants displayed a little accelerated growth during seedling stage but showed delayed flowering time and a slight growth retardation phenotype during late vegetative stage, suggesting that the OsNHX1 has a novel function in plant development. Northern and western blot analyses showed that the expression levels of OsNHX1 mRNA and protein in the leaves of three independent transgenic plant lines were significantly higher than in the leaves of wild type (WT) plants. T2 generation plants exhibited increased salt tolerance, showing delayed appearance and development of damage or death caused by salt stress, as well as improved recovery upon removal from this condition. Several physiological traits, such as increased Na+ content, and decreased osmotic potential in transgenic plants grown in high saline concentrations, further indicated that the transgenic plants had enhanced salt tolerance. Our results suggest the potential use of these transgenic plants for further agricultural applications in saline soil.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amtmann A, Fischer M, Marsh EL, Stefaovic A, Sander D, Schachtman DP (2001) The wheat cDNA LCT1 generates hypersensitivity to sodium in a salt-sensitive yeast strain. Plant Physiol 126:1061–1071
Apse MP, Aharon GS, Snedden WA, Blumwald E (1999) Salt tolerance conferred by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiport in Arabidopsis. Science 285:1256–1258
Apse MP, Sottosanto JB, Blumwald E (2003) Vacuolar cation/H+ exchange, ion homeostasis, and leaf development are altered in a T-DNA insertional mutant of AtNHX1, the Arabidopsis vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter. Plant J 36:229–239
Blumwald E (2000) Sodium transport and salt tolerance in plants. Curr Opin Cell Biol 12:431–434
Flowers TJ (2004) Improving crop salt tolerance. J Exp Bot 55:307–319
Fukuda A, Yazaki Y, Ishikawa T, Koike S, Tanaka Y (1998) Na+/H+ antiporter in tonoplast vesicles from rice roots. Plant Cell Physiol 39:196–201
Fukuda A, Nakamura A, Tanaka Y (1999) Molecular cloning and expression of the Na+/H+ exchanger gene in Oryza sativa. Biochim Biophys Acta 1446:149–155
Fukuda A, Chiba K, Maeda M, Nakamura A, Maeshima M, Tanaka Y (2004a) Effect of salt and osmotic stresses on the expression of genes for the vacuolar H+-pyrophosphatase, H+-ATPase subunit A, and Na+/H+ antiporter from barley. J Exp Bot 55:585–594
Fukuda A, Nakamura A, Tagiri A, Tanaka H, Miyao A, Hirochika H, Tanaka Y (2004b) Function, intracellular localization and the importance in salt tolerance of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter from rice. Plant Cell Physiol 45:146–159
Garciadeblas B, Senn M, Banuelos M, Rodriguez-Navarro A (2003) Sodium transport and HKT transporters: the rice model. Plant J 34:788–801
Hamada A, Shono M, Xia T, Ohta M, Hayashi Y, Tanaka A, Hayakawa T (2001) Isolation and characterization of a Na+/H+ antiporter gene from the halophyte Atriplex gmelini. Plant Mol Biol 46:35–42
Hiei Y, Ohta S, Komari T, Kumashiro T (1994) Efficient transformation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) mediated by Agrobacterium and sequence analysis of the boundaries of the T-DNA. Plant J 6:271–282
Horie T, Yoshida K, Nakayama H, Yamada K, Oiki S, Shinmyo A (2001) Two types of HKT transporters with different properties of Na+ and K+ transport in Oryza sativa. Plant J 27:129–138
Huang JQ, Wei ZM, An HL, Xu SP, Zhang B (2000) High efficiency of genetic transformation of rice using Agrobacterium mediated procedure. Acta Bot Sin 42:1172–1178
Kinclova-Zimmermannova O, Flegelova H, Sychrova H (2004) Rice Na+/H+-antiporter Nhx1 partially complements the alkali–metal–cation sensitivity of yeast strains lacking three sodium transporters. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 49:519–525
Maser P, Gierth M, Schroedr J (2002) Molecular mechanisms of potassium and sodium uptake in plants. Plant Soil 247:43–54
Ohta M, Hayashi Y, Nakashima A, Hamada A, Tanaka A, Nakamura T, Hayakawa T (2002) Introduction of a Na+/H+ antiporter gene from Atriplex gmelini confers salt tolerance to rice. FEBS Lett 532:279–282
Shi H, Zhu JK (2002) Regulation of expression of the vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene AtNHX1 by salt stress and abscisic acid. Plant Mol Biol 50:543–550
Shi H, Quintero FJ, Pardo JM, Zhu JK (2002) The putative plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter SOS1 controls long-distance Na+ transport in plants. Plant Cell 14:465–477
Tester N, Davenport R (2003) Na+ tolerance and Na+ transport in higher plants. Ann Bot 91:1–25
Wang HQ, Bouman BAM, Zhao DL, Wang CG, Maoya PF (2002) Aerobic rice in northern China: opportunities and challenges. In: Bouman BAM, Hengsdijk H, Hardy B, Binddraban PS, Tuong TP, Ladha JK (eds) Water-wise rice production. International Rice Research Institute, Los Banos, Philippines, pp 143–154
Wang J, Zuo K, Wu W, Song J, Sun X, Lin J, Li X, Tang K (2003) Molecular cloning and characterization of a new Na+/H+ antiporter gene from Brassica napus. DNA Seq 14:351–358
Wu CA, Yang GD, Meng QW, Zheng CC (2004) The cotton GhNHX1 gene encoding a novel putative tonoplast Na+/H+ antiporter plays an important role in salt stress. Plant Cell Physiol 45:600–607
Wu LQ, Fan ZM, Guo L, Li YQ, Chen ZL, Qu LJ (2005a) Over-expression of the bacterial nhaA gene in rice enhances salt and drought tolerance. Plant Sci 168:297–302
Wu YY, Chen QJ, Chen M, Wang XC (2005b) Salt-tolerant transgenic perennial Ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) obtained by Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene. Plant Sci 169:65–73
Xia T, Apse MP, Aharon GS, Blumwald E (2002) Identification and characterization of a NaCl-inducible vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter in Beta vulgaris. Physiol Plant 116:206–212
Xu D, Duan X, Wang B, Hong B, David Ho T, Wu R (1996) Expression of a late embryogenesis abundant protein gene, HVA1, from barley confers tolerance to water deficit and salt stress in transgenic rice. Plant Physiol 110:249–257
Xue ZY, Zhi DY, Xue GP, Zhang H, Zhao YX (2004) Enhanced salt tolerance of transgenic wheat (Tritivum aestivum L.) expressing a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene with improved grain yields in saline soils in the field and a reduced level of leaf Na+. Plant Sci 167:849–859
Yin XY, Yang AF, Zhang KW, Zhang JR (2004) Production and analysis of transgenic maize improved salt tolerance by the introduction of AtNHX1 gene. Acta Bot Sin 46:854–861
Zhang HX, Blumwald E (2001) Transgenic salt-tolerant tomato plants accumulate salt in foliage but not in fruit. Nat Biotechnol 19:765–768
Zhang HX, Hodson JN, Williams JP, Blumwald E (2001) Engineering salt-tolerant Brassica plants: characterization of yield and seed oil quality in transgenic plants with increased vacuolar sodium accumulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:12832–12836
Zhu ZQ, Wang JJ, Sun JS, Xu Z, Yin GC, Zhu ZY, Bi FY (1975) Establishment of an efficient medium for another culture of rice through comparative experiments on the nitrogen sources. Sci Sin 18:659–668
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Fukada (Department of Plant Physiology, National institute of Agrobiological Resources, Japan) for kindly providing the vector: pOsNHX1, containing the OsNHX1 cDNA, as well as for supplying the OsNHX1 antibodies. This work was supported by grants from the National Basic Research Program of China (grant nos. 2006CB100100 and 2003CB114307) and from the National Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 30370129 and 30421002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., An, R., Tang, JH. et al. Over-expression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene improves salt tolerance in an upland rice. Mol Breeding 19, 215–225 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-006-9048-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-006-9048-8