Abstract
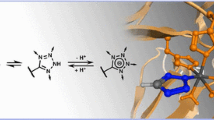
Thiazolidinone derivatives have been found to exhibit a wide range of pharmacological activities. 2-Thiazolylimino-5-benzylidene-thiazolidin-4-one derivatives show antibacterial activity in in vitro tests which are comparable to marketed drugs. However, the target for this scaffold remains yet to be identified. In our work, we identified seven putative targets for this scaffold using web servers such as DRAR-CPI, PharmMapper, and TarFisDock and databases such as BindingDB and ChEMBL. Each of these servers used different algorithms and scoring functions for protein target identification. Further, these targets are substantiated by molecular docking analysis. Based on the docking studies, scaffold 2-thiazolylimino-5-benzylidene-thiazolidin-4-one is observed to exhibit affinity against diverse targets, particularly, towards COX-2, acetylcholinesterase, aldose reductase, and thyroid hormone receptor alpha. This study describes an initial probability that these proteins may be targeted by this scaffold.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rao VS, Srinivas K (2011) Modern drug discovery process: an in silico approach. J Bioinform Seq Anal 2:89–94. doi:10.5897/JBSA
Tang Y, Zhu W, Chen K, Jiang H (2006) New technologies in computer-aided drug design: toward target identification and new chemical entity discovery. Drug Discov Today Technol 3:307–313. doi:10.1016/j.ddtec.2006.09.004
Lindsay MA (2003) Target discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2:831–838. doi:10.1038/nrd1202
Jenkins JL, Bender A, Davies JW (2007) In silico target fishing: predicting biological targets from chemical structure. Drug Discov Today Technol 3:413–421. doi:10.1016/j.ddtec.2006.12.008
Zhou H, Wu S, Zhai S, Liu A, Sun Y, Li R, Zhang Y, Ekins S, Swaan PW, Fang B (2008) Design, synthesis, cytoselective toxicity, structure-activity relationships, and pharmacophore of thiazolidinone derivatives targeting drug-resistant lung cancer cells. J Med Chem 51:1242–1251. doi:10.1021/jm7012024
Vicini P, Geronikaki A, Anastasia K, Incerti M, Zani F (2006) Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of novel 2-thiazolylimino-5-arylidene-4-thiazolidinones. Bioorg Med Chem 14:3859–3864. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2006.01.043
Vicini P, Geronikaki A, Incerti M, Zani F, Dearden J, Hewitt M (2008) 2-Heteroarylimino-5-benzylidene-4-thiazolidinones analogues of 2-thiazolylimino-5-benzylidene-4-thiazolidinones with antimicrobial activity: Synthesis and structure-activity relationship. Bioorg Med Chem 16:3714–3724. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2008.02.001
Verma A, Saraf SK (2008) 4-Thiazolidinone-A biologically active scaffold. Eur J Med Chem 43:897–905. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2007.07.017
Abhinit M, Ghodke M, Pratima NA (2009) Exploring potential of 4-thiazolidinone: a brief review. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 1:47–64
Li H, Gao Z, Kang L, Zhang H, Yang K, Yu K, Luo X, Zhu W, Chen K, Shen J (2006) TarFisDock: a web server for identifying drug targets with docking approach. Nucleic Acids Res 34:W219–W224. doi:10.1093/nar/gkl114
Gao Z, Li H, Zhang H, Liu X, Kang L, Luo X, Zhu W, Chen K, Wang X, Jiang H (2008) PDTD: a web-accessible protein database for drug target identification. BMC Bioinform 9:104. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-9-104
Luo H, Chen J, Shi L, Mikailov M, Zhu H, Wang K, He L, Yang L (2011) DRAR-CPI: a server for identifying drug repositioning potential and adverse drug reactions via the chemical-protein interactome. Nucleic Acids Res 39:W492–W498. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr299
Liu X, Ouyang S, Yu B, Liu Y, Huang K, Gong J, Zheng S, Li Z, Li H, Jiang H (2010) PharmMapper server: a web server for potential drug target identification using pharmacophore mapping approach. Nucleic Acids Res 38:W609–W614. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq300
Geronikaki A, Eleftheriou P, Vicini P, Alam I, Dixit A, Saxena AK (2008) 2-Thiazolylimino/heteroarylimino-5-arylidene-4-thiazolidinones as new agents with SHP-2 inhibitory action. J Med Chem 51:5221–5228. doi:10.1021/jm8004306
Gaulton A, Bellis LJ, Bento AP, Chambers J, Davies M, Hersey A, Light Y, McGlinchey S, Michalovich D, Al-Lazikani B (2012) ChEMBL: a large-scale bioactivity database for drug discovery. Nucleic Acids Res 40:D1100–D1107. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr777
Eleftheriou P, Geronikaki A, Hadjipavlou-Litina D, Vicini P, Filz O, Filimonov D, Poroikov V, Chaudhaery SS, Roy KK, Saxena A (2011) Fragment-based design, docking, synthesis, biological evaluation and structure-activity relationships 2-benzo/benzisothiazolimino-5-aryliden-4-thiazolidinones as cycloxygenase/ lipoxygenase inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 47:111–124. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2011.10.029
Geronikaki AA, Lagunin AA, Hadjipavlou-Litina DI, Eleftheriou PT, Filimonov DA, Poroikov VV, Alam I, Saxena AK (2008) Computer-aided discovery of anti-inflammatory thiazolidinones with dual cyclooxygenase/ lipoxygenase inhibition. J Med Chem 51:1601–1609. doi:10.1021/jm701496h
Maestro, Version 9.0 (2009) Schrödinger, LLC, New York
Glide, Version 5.5 (2009) Schrödinger, LLC, New York
Friesner RA, Banks JL, Murphy RB, Halgren TA, Klicic JJ, Daniel T, Repasky MP, Knoll EH, Shelley M, Perry JK (2004) Glide: a new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 1. Method and assessment of docking accuracy. J Med Chem 47:1739–1749. doi:10.1021/jm0306430
Verdonk ML, Cole JC, Hartshorn MJ, Murray CW, Taylor RD (2003) Improved protein-ligand docking using GOLD. Proteins Struct Funct Bioinform 52:609–623. doi:10.1002/prot.10465
DeLano WL (2001) Pymol: an open source molecular graphics. CCP4 Newsl On Protein Crystallogr 40:82–92
Laurie ATR, Jackson RM (2005) Q-SiteFinder: an energy-based method for the prediction of protein—ligand binding sites. Bioinformatics 21:1908–1916. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bti315
ROCS, Version 3.0.0 (2009) OpenEye Scientific Software, Santa Fe, NM
Fontaine F, Bolton E, Borodina Y, Bryant SH (2007) Fast 3D shape screening of large chemical databases through alignment-recycling. Chem Cent J 1:1–14. doi:10.1186/1752-153X-1-12
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R (2007) Clustal W and clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL\_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882. doi:10.1093/nar/25.24.4876
Kotera M, McDonald AG, Boyce S, Tipton KF (2008) Functional group and substructure searching as a tool in metabolomics. PLoS ONE 3:e1537. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0001537
Stobaugh RE (1985) Chemical substructure searching. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 25:271–275. doi:10.1021/ci00047a025
Keller TH, Pichota A, Yin Z (2006) A practical view of ‘druggability’. Curr Opin Chem Biol 10:357–361. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2006.06.014
LigPrep, Version 2.3 (2009) Schrödinger, LLC, New York
QikProp, Version, 3.2 (2009) Schrödinger, LLC, New York
Chen XP, Du GH (2007) Target validation: a door to drug discovery. Drug Discov Ther 1:23–29
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11030_2015_9578_MOESM4_ESM.doc
Fig. (S4). Multiple sequence alignment of proteins 2H77, 3DCT, and 3K8S using ClustalX. The active-site residues are represented in box (doc 258 KB)
11030_2015_9578_MOESM7_ESM.doc
Fig. (S7). Structures of core moieties present in (a) Thiazole series and (b) Benzothiazole series of compounds (doc 320 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iyer, P., Bolla, J., Kumar, V. et al. In silico identification of targets for a novel scaffold, 2-thiazolylimino-5-benzylidin-thiazolidin-4-one. Mol Divers 19, 855–870 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-015-9578-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-015-9578-2