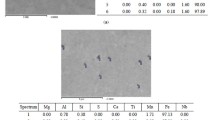
The effect of “soft reduction” technology on chemical inhomogeneity of a continuously-cast slab, and also on the structure and properties of finished rolled product made of low-carbon microalloyed steel is studied. In slabs prepared without soft reduction, a defect is often observed in the form of white bands leading to a reduction in the proportion of ductile component in low-standard rolled product. In a slab transverse section, from the surface into the depth there are coarse grains with ferrite over boundaries and bainite within grains. A white band is formed by fine polyhedral ferrite grains with a small amount of finely acicular bainite. In this case, the microhardness of ferrite and bainite in the axial zone, and in a white band is considerably higher than in other slab zones. Also within the limits of a white band there is formation of an increased amount of sulfides and carbonitrides. It is demonstrated that as a result of liquation processes there is an increase in carbon, manganese, sulfur, and phosphorus, and also microalloying element content within a white band.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. I. Efron, Materials Science in Large Metallurgy, Metallurgizdat, Moscow (2012).
V. V. Moshkunov, A. M. Stolyarov, and A. S. Kazakhov, “Reduction in axial chemical inhomogeneity of pipe steel as a result of continuously-cast slab soft reduction,” Vestn. MGTU im. Nosova, No. 2, 24–25 (2012).
Sh. Ueyama, M. Niizuma, and K. Yonezawa, “Development of high quality heavy plates on steelmaking process at Kimitsu Works,” Nippon Steel Techn. Report, No. 104, 102–108 (2013).
M. O. El-Bealy, “Macrosegregation quality criteria and mechanical soft reduction for central quality problems in continuous casting of steel,” Mater. Sci. Applic., No. 5, 724–744 (2014).
S. V. Denisov, A. N. Zavalishchin, and E. V. Kozhevnikova, “Study of carbides in steel K60 for main pipelines,” Proc. 8th Congr. of Rolling Mill Operators, Magnitogorsk, Oct. 11–15, 2010, pp. 539–542.
V. I. Bol’shakov, G. D. Sukhomlin, D. V. Laukhin, and V. I. Kuksenko, “Effect of heat treatment formation of acicular ferrite and the properties of low-carbon low-alloys steels 10G2FB and 09G2S,” MiTOM, No. 12, 29–33 (2004).
F. Haisterkamp, K. Khulka, Yu. I. Matrosov, et al., Niobium-Containing Low-Alloy Steels, Intermet Inzhiniring, Moscow (1999).
S. V. Denisov, A. N. Zavalishchin, E. V. Kozhevnikova, and M. I. Rumyantsev, “Change in the structure of low-alloy steel during production,” Vestn. MGTU im. Nosova, No. 3(43), 51–54 (2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Metallurg, No. 12, pp. 13–19, December, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zavalishchin, A.N., Kozhevnikova, E.V. Effect of Continuous Casting Technology on Low-Alloy Steel Structure in Different Production Stages. Metallurgist 61, 1048–1054 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-018-0606-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-018-0606-1