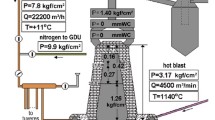
Computer implementation of mathematical models, algorithms, and computer programs is given for resolving a set of production problems in the field of blast furnace production introduced into Magnitogorsk Metallurgical Combine. Requirements are considered for the structure and architecture of a computer system for support of solutions adopted for an MES-level Blast Furnace Technologist workstation. A short description is provided for the main model sub-systems, and also assumptions made during mathematical modeling. Use of the systems makes it possible for engineering and production personnel to perform operational analysis of a blast furnace workshop situation, to resolve a number of production problems for controlling blast furnace heat, gas-dynamic, and slag regimes, and also to calculate the optimum blast furnace charge composition, which finally provides an improvement in blast furnace production technical and economic operating indices.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. A. Spirin (ed.), V. V. Lavrov, V. Yu. Rybolovlev, et al., Models Support Systems for Solutions in a TP Workstation of Blast Furnace Smelting Metallurgy, URFU, Ekaterinburg (2011).
O. P. Onorin, N. A. Spirin (ed.), V. L. Terent’ev, et al., Computer Methods for Modeling Blast Furnace Process, UGTUUPI, Ekaterinburg (2005).
Q. Feng and L. Wang, “Blast furnace hoist charging control system based on ActiveX technology,” Proc. WIT Transactions on Information and Communication Technologies, Wuhan, China, May 7–8, 2013, 46, No. 2, 1853–1858 (2014).
B. H. Dimitrov, H. B. Nenov, and A. S. Marinov, “Comparative analysis between methodologies and their software realizations applied to modeling and simulation of industrial thermal processes,” Proc. 36th Int. Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electronics and Microelectronics, MIPRO 2013, Opatija, Croatia, May 20–24, 2013, Art. No. 6596383.
R. Bartels, Kw. Dohl, H. Uhde, et al., “New process-control computer-system for the blast-furnace plant of an integrated iron and steel works,” Stahl und Eisen, 114, No. 6, 75–79 (1994).
S. V. Emel’yanov, S. K. Korovin, L. P. Myshlayev, et al., Theory and Practice of Prediction in Control Systems, IO Rossiiskie Universitety, Kuzbassvuzizdat ASTSh, Kemerovo (2008).
I. O. Odintsov, Professional Programming. Systematic Approach, BKhV-Peterburg, St. Petersburg (2004).
E. Troelensen, Programming Language C# 5.0 and Platform NET 4.5, Williams, Moscow (2013), 6th ed.
K. J. Deit, Introduction to Database Systems, Williams, Moscow (2006).
N. A. Spirin, V. V. Lavrov, A. A. Burykin, et al., “Complex of model systems for supporting decisions made in managing blast-furnace smelting technology,” Metallurgist, 54, No. 9–10, 566–569 (2011).
N. A. Spirin (ed.), V. V. Lavrov, V. Yu. Rybolovtsev, et al., Mathematical Modeling of Metallurgical Processes in TP Workstation: Teach. Aid, UrFU, Ekaterinburg (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Metallurg, No. 5, pp. 13–19, May, 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spirin, N.A., Lavrov, V.V., Rybolovlev, V.Y. et al. Use of Contemporary Information Technology for Analyzing the Blast Furnace Process. Metallurgist 60, 471–477 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-016-0317-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-016-0317-4