Abstract
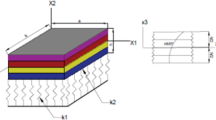
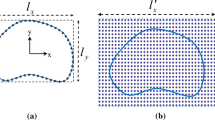
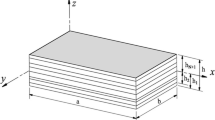
This paper deals with the static and dynamic analyses of multi-layered plates with discontinuities. The two-dimensional first-order shear deformation theory is used to derive the fundamental system of equations in terms of generalized displacements. The fundamental set, with its boundary conditions, is solved in its strong form. A new method termed strong formulation finite element method is considered in the present paper to solve this kind of plates. This numerical methodology is the cohesion of derivative evaluation of partial differential systems of equations and a domain sub-division. The numerical results in terms of natural frequencies and maximum deflections are compared to literature and to the same results obtained with a finite element code. The stability, accuracy and reliability of the present methodology is shown through several numerical applications.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pagano NJ (1994) Exact solutions for rectangular bidirectional composites and sandwich plates. In: Reddy JN (ed) Mechanics of composite materials, vol 34., Solid mechanics and its applicationsSpringer, Dordrecht, pp 86–101
Wang CM, Ang KK, Yang L, Watanabe E (2001) Vibration analysis of arbitrarily shaped sandwich plates via Ritz method. Mech Compos Mater Struct 8:101–118
Reddy JN (2003) Mechanics of laminated composite plates and shells. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Ferreira AJM (2008) MATLAB codes for finite element analysis: solids and structures., Solid mechanics and its applicationsSpringer, New York
Ferreira AJM, Castro LMS, Bertoluzza S (2011) Analysis of plates on winkler foundation by wavelet collocation. Meccanica 46(4):865–873
Akbarzadeh AH, Abbasi M, Hosseinizad SK, Eslami MR (2011) Dynamic analysis of functionally graded plates using the hybrid Fourier-Laplace transform under thermomechanical loading. Meccanica 46(6):1373–1392
Jedrysiak J, Radzikowska A (2012) Tolerance averaging of heat conduction in transversally graded laminates. Meccanica 47(1):95–107
Yas MH, Jodaei A, Irandoust S, Nasiri Aghdam M (2012) Three-dimensional free vibration analysis of functionally graded piezoelectric annular plates on elastic foundations. Meccanica 47(6):1401–1423
Roque CMC, Rodrigues JD, Ferreira AJM (2012) Analysis of thick plates by local radial basis functions-finite differences method. Meccanica 47(5):1157–1171
Malekzadeh P, Golbahar Haghighi MR, Alibeygi Beni A (2012) Buckling analysis of functionally graded arbitrary straight-sided quadrilateral plates on elastic foundations. Meccanica 47(2):321–333
Asemi K, Akhlaghi M, Salehi M (2012) Dynamic analysis of thick short length FGM cylinders. Meccanica 47(6):1441–1453
Michalak B, Wirowski A (2012) Dynamic modelling of thin plate made of certain functionally graded materials. Meccanica 47(6):1487–1498
Liu B, Xing YF, Eisenberger M, Ferreira AJM (2014) Thickness-shear vibration analysis of rectangular quartz plates by a numerical extended Kantorovich method. Compos Struct 107:429–435
Gottlieb D, Orszag SA (1997) Numerical analysis of spectral methods: theory and applications. In: CBMS-NSF regional conference series in applied mathematics. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Philadelphia
Shu C (1991) Generalized differential: integral quadrature and application to the simulation of incompressible viscous flows including parallel computation. PhD thesis, Glasgow University, Glasgow
Boyd JP (2001) Chebyshev and Fourier spectral methods, 2nd edn. Dover, Mineola
Canuto C, Hussaini MY, Quarteroni A, Zang TA (2006) Spectral method: fundamentals in single domains. Springer, New York
Kansa EJ (1990) Multiquadrics-a scattered data approximation scheme with applications to computational fluid-dynamics-i surface approximations and partial derivative estimates. Comput. Math. Appl. 19(8–9):127–145
Kansa EJ (1990) Multiquadrics-a scattered data approximation scheme with applications to computational fluid-dynamics-ii solutions to parabolic, hyperbolic and elliptic partial differential equations. Comput. Math. Appl. 19(8–9):147–161
Wendland H (1995) Piecewise polynomial, positive definite and compactly supported radial functions of minimal degree. Adv. Comput. Math. 4(1):389–396
Wendland H (1998) Error estimates for interpolation by compactly supported radial basis functions of minimal degree. J Approx Theory 93(2):258–272
Wendland H (1999) Meshless Galerkin methods using radial basis functions. Math Comput 68(228):1521–1531
Fasshauer GE (1999) Solving differential equations with radial basis functions: multilevel methods and smoothing. Adv Comput Math 11(2–3):139–159
Buhmann MD (2003) Radial basis functions. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Ferreira AJM, Roque CMC, Martins PALS (2003) Analysis of composite plates using higher-order shear deformation theory and a finite point formulation based on the multiquadric radial basis function method. Compos Part B 34(7):627–636
Ferreira AJM, Roque CMC, Jorge RMN (2005) Analysis of composite plates by trigonometric shear deformation theory and multiquadrics. Comput Struct 83(27):2225–2237
Fasshauer GE, Zhang JG (2007) On choosing “optimal” shape parameters for RBF approximation. Numer Algorithms, 45(1–4):345–368. cited By (since 1996)55.
Xiang S, Wang K-M (2009) Free vibration analysis of symmetric laminated composite plates by trigonometric shear deformation theory and inverse multiquadric RBF. Thin-Walled Struct 47(3):304–310
Xiang S, Jiang S-X, Bi Z-Y, Jin Y-X, Yang M-S (2011) A nth-order meshless generalization of Reddy’s third-order shear deformation theory for the free vibration on laminated composite plates. Compos Struct 93(2):299–307
Rodrigues JD, Roque CMC, Ferreira AJM, Carrera E, Cinefra M (2011) Radial basis functions-finite differences collocation and a unified formulation for bending, vibration and buckling analysis of laminated plates, according to Murakami’s zig-zag theory. Compos Struct 93(7):1613–1620
Ferreira AJM, Roque CMC, Neves AMA, Jorge RMN, Soares CMM, Liew KM (2011) Buckling and vibration analysis of isotropic and laminated plates by radial basis functions. Compos Part B 42(3):592–606
Ferreira AJM, Carrera E, Cinefra M, Roque CMC, Polit O (2011) Analysis of laminated shells by a sinusoidal shear deformation theory and radial basis functions collocation, accounting for through-the-thickness deformations. Compos Part B 42:1276–1284
Gherlone M, Iurlaro L, Di Sciuva M (2012) A novel algorithm for shape parameter selection in radial basis functions collocation method. Compos Struct 94(2):453–461
Neves AMA, Ferreira AJM, Carrera E, Cinefra M, Roque CMC, Jorge RMN, Soares CMM (2012) A quasi-3D hyperbolic shear deformation theory for the static and free vibration analysis of functionally graded plates. Compos Struct 94(5):1814–1825
Giunta G, Biscani F, Belouettar S, Ferreira AJM, Carrera E (2013) Free vibration analysis of composite beams via refined theories. Compos Part B 44(1):540–552
Tornabene F, Fantuzzi N, Viola E, Ferreira AJM (2013) Radial basis function method applied to doubly-curved laminated composite shells and panels with a general higher-order equivalent single layer theory. Compos Part B 55:642–659
Iurlaro L, Gherlone M, Di Sciuva M (2014) Energy based approach for shape parameter selection in radial basis functions collocation method. Compos Struct 107:70–78
Maturi DA, Ferreira AJM, Zenkour AM, Mashat DS (2014) Analysis of sandwich plates with a new layerwise formulation. Compos Part B 56:484–489
Bert CW, Malik M (1996) The differential quadrature method for irregular domains and application to plate vibration. Int J Mech Sci 38(6):589–606
Shu C, Chew YT (1999) Application of multi-domain GDQ method to analysis of waveguides with rectangular boundaries. Prog Electromagn Res 21:1–19
Shu C (2000) Differential quadrature and its applications in engineering. Springer, New York
Shu C, Chen W, Du H (2000) Free vibration analysis of curvilinear quadrilateral plates by the differential quadrature method. J Comput Phys 163(2):452–466
Karami G, Malekzadeh P (2003) Application of a new differential quadrature methodology for free vibration analysis of plates. Int J Numer Methods Eng 56(6):847–868
Viola E, Tornabene F (2005) Vibration analysis of damaged circular arches with varying cross-section. Struct Integr Durab (SID-SDHM) 1(2):155–169
Viola E, Tornabene F (2006) Vibration analysis of conical shell structures using GDQ method. Far East J Appl Math 25(1):23–39
Tornabene F (2007) Modellazione e soluzione di strutture a guscio in materiale anisotropo. PhD thesis, University of Bologna, Bologna
Tornabene F, Viola E (2007) Vibration analysis of spherical structural elements using the GDQ method. Comput Math Appl 53(10):1538–1560
Viola E, Dilena M, Tornabene F (2007) Analytical and numerical results for vibration analysis of multi-stepped and multi-damaged circular arches. J Sound Vib 299(1–2):143–163
Marzani A, Tornabene F, Viola E (2008) Nonconservative stability problems via generalized differential quadrature method. J Sound Vib 315(1–2):176–196
Tornabene F, Viola E (2008) 2D solution for free vibrations of parabolic shells using generalized differential quadrature method. Eur J Mech 27(6):1001–1025
Tornabene F, Viola E (2009) Free vibration analysis of functionally graded panels and shells of revolution. Meccanica 44(3):255–281
Viola E, Tornabene F (2009) Free vibrations of three parameter functionally graded parabolic panels of revolution. Mech Res Commun 36(5):587–594
Tornabene F, Viola E (2009) Free vibrations of four-parameter functionally graded parabolic panels and shells of revolution. Eur J Mech 28(5):991–1013
Tornabene F (2009) Free vibration analysis of functionally graded conical, cylindrical shell and annular plate structures with a four-parameter power-law distribution. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 198(37–40):2911–2935
Tornabene F, Viola E, Inman DJ (2009) 2D differential quadrature solution for vibration analysis of functionally graded conical, cylindrical shell and annular plate structures. J Sound Vib 328(3):259–290
Tornabene F, Marzani A, Viola E, Elishakoff I (2010) Critical flow speeds of pipes conveying fluid by the generalized differential quadrature method. Adv Theor Appl Mech 3(3):121–138
Tornabene F, Liverani A, Caligiana G (2011) FGM and laminated doubly-curved shells and panels of revolution with a free-form meridian: a 2D GDQ solution for free vibrations. Int J Mech Sci 53:446–470
Tornabene F (2011) Free vibrations of laminated composite doubly-curved shells and panels of revolution via the GDQ method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 200:931–952
Malekzadeh P, Golbahar Haghighi MR, Atashi MM (2011) Free vibration analysis of elastically supported functionally graded annular plates subjected to thermal environment. Meccanica 46(5):893–913
Tornabene F (2011) 2D GDQ solution for free vibrations of anisotropic doubly-curved shells and panels of revolution. Compos Struct 93:1854–1876
Tornabene F (2011) Free vibrations of anisotropic doubly-curved shells and panels of revolution with a free-form meridian resting on Winkler–Pasternak elastic foundations. Compos Struct 94:186–206
Soleimani S, Qajarjazi A, Bararnia H, Barari A, Domairry G (2011) Entropy generation due to natural convection in a partially heated cavity by local RBF-DQ method. Meccanica 46(5):1023–1033
Viola E, Rossetti L, Fantuzzi N (2012) Numerical investigation of functionally graded cylindrical shells and panels using the generalized unconstrained third order theory coupled with the stress recovery. Compos Struct 94:3736–3758
Tornabene F, Liverani A, Caligiana G (2012) Laminated composite rectangular and annular plates: a GDQ solution for static analysis with a posteriori shear and normal stress recovery. Compos Part B 43:1847–1872
Tornabene F, Liverani A, Caligiana G (2012) Static analysis of laminated composite curved shells and panels of revolution with a posteriori shear and normal stress recovery using generalized differential quadrature method. Int J Mech Sci 61:71–87
Tornabene F, Liverani A, Caligiana G (2012) General anisotropic doubly-curved shell theory: a differential quadrature solution for free vibrations of shells and panels of revolution with a free-form meridian. J Sound Vib 331:4848–4869
Tornabene F (2012) Meccanica delle strutture a guscio in materiale composito. Il Metodo generalizzato di quadratura differenziale. Esculapio, New York
Tornabene F, Ceruti A (2013) Free-form laminated doubly-curved shells and panels of revolution on Winkler–Pasternak elastic foundations: A 2D GDQ solution for static and free vibration analysis. World J Mech 3:1–25
Tornabene F, Viola E, Fantuzzi N (2013) General higher-order equivalent single layer theory for free vibrations of doubly-curved laminated composite shells and panels. Compos Struct 104:94–117
Eftekhari SA, Jafari AA (2014) A mixed modal-differential quadrature method for free and forced vibration of beams in contact with fluid. Meccanica 49:535–564
Tornabene F, Ceruti A (2013) Mixed static and dynamic optimizazion of four-parameter functionally graded completely doubly-curved and degenerate shells and panels using GDQ method. Math Probl Eng 2013:1–33. Article ID 867079, http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/867079
Tornabene F, Viola E (2013) Static analysis of functionally graded doubly-curved shells and panels of revolution. Meccanica 48:901–930
Viola E, Tornabene F, Fantuzzi N (2013) General higher-order shear deformation theories for the free vibration analysis of completely doubly-curved laminated shells and panels. Compos Struct 95:639–666
Viola E, Tornabene F, Fantuzzi N (2013) Static analysis of completely doubly-curved laminated shells and panels using general higher-order shear deformation theories. Compos Struct 101:59–93
Ferreira AJM, Viola E, Tornabene F, Fantuzzi N, Zenkour AM (2013) Analysis of sandwich plates by generalized differential quadrature method. Math Probl Eng 2013:1–12. Article ID 964367. http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/964367
Tornabene F, Reddy JN (2013) FGM and laminated doubly-curved and degenerate shells resting on nonlinear elastic foundation: a GDQ solution for static analysis with a posteriori stress and strain recovery. J Indian Inst Sci 93(4):635–688
Tornabene F, Fantuzzi N, Viola E, Reddy JN (2014) Winkler–Pasternak foundation effect on the static and dynamic analyses of laminated doubly-curved and degenerate shells and panels. Compos Part B 57:269–296
Eftekhari SA, Jafari AA (2013) A simple and accurate mixed FE-DQ formulation for free vibration of rectangular and skew mindlin plates with general boundary conditions. Meccanica 48(5):1139–1160
Tornabene F, Fantuzzi N, Viola E, Carrera E (2014) Static analysis of doubly-curved anisotropic shells and panels using CUF approach, differential geometry and differential quadrature method. Compos Struct 107:675–697
Ferreira AJM, Carrera E, Cinefra M, Viola E, Tornabene F, Fantuzzi N, Zenkour AM (2014) Analysis of thick isotropic and cross-ply laminated plates by generalized differential quadrature method and a unified formulation. Compos Part B 58:544–552
Viola E, Rossetti L, Fantuzzi N, Tornabene F (2014) Static analysis of functionally graded conical shells and panels using the generalized unconstrained third order theory coupled with the stress recovery. Compos Struct 112(1):44–65
Tornabene F, Fantuzzi N (2014) Mechanics of laminated composite doubly-curved shell structures. Esculapio, New York
Cottrell JA, Reali A, Bazilevs Y, Hughes TJR (2006) Isogeometric analysis of structural vibrations. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 195(41–43):5257–5296
Schillinger D, Evans JA, Reali A, Scott MA, Hughes TJR (2013) Isogeometric collocation: cost comparison with Galerkin methods and extension to adaptive hierarchical NURBS discretizations. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 267:170–232
Nguyen-Xuan H, Thai CH, Nguyen-Thoi T (2013) Isogeometric finite element analysis of composite sandwich plates using a higher order shear deformation theory. Compos Part B 55:558–574
Evans JA, Hughes TJR (2013) Isogeometric divergence-conforming B-splines for the Darcy–Stokes–Brinkman equations. Math Models Methods Appl Sci 23(4):671–741
Thai CH, Ferreira AJM, Carrera E, Nguyen-Xuan H (2013) Isogeometric analysis of laminated composite and sandwich plates using a layerwise deformation theory. Compos Struct 104:196–214
Patera AT (1984) A spectral element method for fluid dynamics: laminar flow in a channel expansion. J Comput Phys 54(3):468–488
Funaro D (1986) A multidomain spectral approximation of elliptic equations. Numer Methods Partial Differ Equ 2(3):187–205
Quarteroni A (1987) Domain decomposition techniques using spectral methods. Calcolo 24(2):141–177
Gonzalez David, Cueto Elias, Doblare Manuel (2009) Towards an isogeometric meshless natural element method. Comput Methods Appl Sci 11:237–257
Fischer P, Mergheim J, Steinmann P (2010) On the c1 continuous discretization of non-linear gradient elasticity: a comparison of nem and fem based on bernstein-bezier patches. Int J Numer Methods Eng 82:1282–1307
Rajagopal Amirtham, Fischer Paul, Kuhl Ellen, Steinmann Paul (2010) Natural element analysis of the Cahn–Hilliard phase-field model. Comput Mech 46:471–493
Striz AG, Chen WL, Bert CW (1994) Static analysis of structures by the quadrature element method (QEM). Int J Solids Struct 31(20):2807–2818
Striz AG, Chen WL, Bert CW (1997) Free vibration of plates by the high accuracy quadrature element method. J Sound Vib 202(5):689–702
Wang X, Gu H (1997) Static analysis of frame structures by the differential quadrature element method. Int J Numer Methods Eng 40(4):759–772
Zhong H, He Y (1998) Solution of poisson and laplace equations by quadrilateral quadrature element. Int J Solids Struct 35(21):2805–2819
Wang X, Wang Y-L, Chen R-B (1998) Static and free vibrational analysis of rectangular plates by the differential quadrature element method. Commun Numer Methods Eng 14(12):1133–1141
Liu FL, Liew KM (1998) Static analysis of reissner-mindlin plates by differential quadrature element method. J Appl Mech ASME 65:705–710
Liu F-L, Liew KM (1999) Vibration analysis of discontinuous mindlin plates by differential quadrature element method. J Vib Acoust 121:204–208
Liu F-L (1999) Differential quadrature element method for static analysis of shear deformable cross-ply laminates. Int J Numer Methods Eng 46(8):1203–1219
Chen C-N (1999) The differential quadrature element method irregular element torsion analysis model. Appl Math Model 23(4):309–328
Chen C-N (1999) The development of irregular elements for differential quadrature element method steady-state heat conduction analysis. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 170(1–2):1–14
Chen C-N (2000) A generalized differential quadrature element method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 188(1–3):553–566
Chen C-N (2003) DQEM and DQFDM for the analysis of composite two-dimensional elasticity problems. Compos Struct 59(1):3–13
Zong Z, Lam KY, Zhang YY (2005) A multidomain differential quadrature approach to plane elastic problems with material discontinuity. Math Comput Model 41(4–5):539–553
Xing Y, Liu B (2009) High-accuracy differential quadrature finite element method and its application to free vibrations of thin plate with curvilinear domain. Int J Numer Methods Eng 80(13):1718–1742
Zhong H, Yu T (2009) A weak form quadrature element method for plane elasticity problems. Appl Math Model 33(10):3801–3814
Zong Z, Zhang Y (2009) Advanced differential quadrature methods. Chapman & Hall/CRC Applied Mathematics & Nonlinear Science. Taylor & Francis
Xing Y, Liu B, Liu G (2010) A differential quadrature finite element method. Int J Appl Mech 2:207–227
Fantuzzi N (2013) Generalized differential quadrature finite element method applied to advanced structural mechanics. PhD thesis, University of Bologna, Bologna
Viola E, Tornabene F, Fantuzzi N (2013) Generalized differential quadrature finite element method for cracked composite structures of arbitrary shape. Compos Struct 106:815–834
Fantuzzi N, Tornabene F, Viola E (2014) Generalized differential quadrature finite element method for vibration analysis of arbitrarily shaped membranes. Int J Mech Sci 79:216–251
Fantuzzi N, Tornabene F (2014) Strong formulation finite element method for arbitrarily shaped laminated plates - I. Theoretical analysis. Adv Aircr Spacecr Sci 1(2):125–143
Fantuzzi N, Tornabene F (2014) Strong formulation finite element method for arbitrarily shaped laminated plates II. Numerical analysis. Adv Aircr Spacecr Science 1(2):145–175
Matuszyk Pawel J, Demkowicz Leszek F (2013) Parametric finite elements, exact sequences and perfectly matched layers. Comput Mech 51:35–45
Viola E, Tornabene F, Ferretti E, Fantuzzi N (2013) Soft core plane state structures under static loads using GDQFEM and cell method. Comput Model Eng Sci 94:301–329
Viola E, Tornabene F, Ferretti E, Fantuzzi N (2013) On static analysis of composite plane state structures via GDQFEM and cell method. Comput Model Eng Sci 94:421–458
Viola E, Tornabene F, Ferretti E, Fantuzzi N (2013) GDQFEM numerical simulations of continuous media with cracks and discontinuities. Comput Model Eng Sci 94:331–369
Hughes TJR (2000) The finite element method: linear static and dynamic finite element analysis., Dover civil and mechanical engineering seriesDover Publications, Mineola
Evans JA, Hughes TJR (2012) Discrete spectrum analyses for various mixed discretizations of the Stokes eigenproblem. Comput Mech 50(6):667–674
Acknowledgments
The research topic is one of the subjects of the Center of Study and Research for the Identification of Materials and Structures (CIMEST)-“M. Capurso” of the University of Bologna (Italy).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Preliminary results were presented by the authors at the XXI° National Conference of Italian Association of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics (AIMETA 2013)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fantuzzi, N., Tornabene, F., Viola, E. et al. A strong formulation finite element method (SFEM) based on RBF and GDQ techniques for the static and dynamic analyses of laminated plates of arbitrary shape. Meccanica 49, 2503–2542 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-014-0014-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-014-0014-y