Abstract
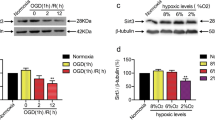
To investigate the potential neuroprotection of oxymatrine in hypoxic-ischemic injury in rat’s brain and the associated underlying mechanisms, modified neurological severity scores (mNSS) for neurological functional deficits, 2,3,5-triphenyl-tetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining for infarct volume, TUNEL assay and flow cytometry analysis for apoptosis were assessed. The expressions of Akt, glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3β), phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt), phosphorylated GSK3β (p-GSK3β), nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and hemeoxygenase-1 (HO-1) were measured by western blot. Our results showed that infarct volume and the apoptosis of NeuN-positive cells were significantly reduced in rats that administrated oxymatrine, with a corresponding improvement in neurological function after H/I. Upregulated p-Akt, p-GSK3β, Nrf-2 and HO-1 expressions were observed in response to oxymatrine treatment. Moreover, the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor LY294002 counteracted the protective effect of oxymatrine, evidenced by western blot and histological outcomes. To conclude, our results suggested that oxymatrine could exert efficacious neuroprotective effect against H/I injury by inhibiting apoptosis and oxidative stress, which might be related to the activation of Akt and GSK3β and modulation of Nrf-2/HO-1 signaling pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali T, Kim T, Rehman SU, Khan MS, Amin FU, Khan M, Ikram M, Kim MO (2017) Natural dietary supplementation of anthocyanins via PI3K/Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 pathways mitigate oxidative stress, neurodegeneration, and memory impairment in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Mol Neurobiol 55(7):6076–6093
Buendia I, Michalska P, Navarro E, Gameiro I, Egea J, Leon R (2016) Nrf2-ARE pathway: an emerging target against oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Pharmacol Ther 157:84–104
Cao S, Du J, Hei Q (2017) Lycium barbarum polysaccharide protects against neurotoxicity via the Nrf2-HO-1 pathway. Exp Ther Med 14:4919–4927
Cheng L, Jin Z, Zhao R, Ren K, Deng C, Yu S (2015) Resveratrol attenuates inflammation and oxidative stress induced by myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: role of Nrf2/ARE pathway. Int J Clin Exp Med 8:10420–10428
Cui L, Zhang X, Yang R, Wang L, Liu L, Li M, Du W (2011) Neuroprotection and underlying mechanisms of oxymatrine in cerebral ischemia of rats. Neurol Res 33:319–324
Fan H, Li L, Zhang X, Liu Y, Yang C, Yang Y, Yin J (2009) Oxymatrine downregulates TLR4, TLR2, MyD88, and NF-kappaB and protects rat brains against focal ischemia. Mediat Inflamm 2009:704706
He M, Siow RC, Sugden D, Gao L, Cheng X, Mann GE (2011) Induction of HO-1 and redox signaling in endothelial cells by advanced glycation end products: a role for Nrf2 in vascular protection in diabetes. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 21:277–285
Hu Y, Zhan Q, Zhang H, Liu X, Huang L, Li H, Yuan Q (2017) Increased susceptibility to ischemic brain injury in Neuroplastin 65-deficient mice likely via glutamate excitotoxicity. Front Cell Neurosci 11:110
Jiang G, Liu X, Wang M, Chen H, Chen Z, Qiu T (2015) Oxymatrine ameliorates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury from oxidative stress through Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Acta Cir Bras 30:422–429
Jiang LJ, Zhang SM, Li CW, Tang JY, Che FY, Lu YC (2017) Roles of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in the anti-oxidative stress response to ischemia-reperfusion brain injury in rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 21:1532–1540
Kilic U, Caglayan AB, Beker MC, Gunal MY, Caglayan B, Yalcin E, Kelestemur T, Gundogdu RZ, Yulug B, Yilmaz B, Kerman BE, Kilic E (2017) Particular phosphorylation of PI3K/Akt on Thr308 via PDK-1 and PTEN mediates melatonin's neuroprotective activity after focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Redox Biol 12:657–665
Li M, Zhang X, Cui L, Yang R, Wang L, Liu L, Du W (2011) The neuroprotection of oxymatrine in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion is related to nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (nrf2)-mediated antioxidant response: role of nrf2 and hemeoxygenase-1 expression. Biol Pharm Bull 34:595–601
Liu Y, Zhang XJ, Yang CH, Fan HG (2009) Oxymatrine protects rat brains against permanent focal ischemia and downregulates NF-kappaB expression. Brain Res 1268:174–180
Lu ML, Xiang XH, Xia SH (2016) Potential signaling pathways involved in the clinical application of Oxymatrine. Phytother Res 30:1104–1112
Vannucci RC, Vannucci SJ (2005) Perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage: evolution of an animal model. Dev Neurosci 27:81–86
Zhai X, Lin H, Chen Y, Chen X, Shi J, Chen O, Li J, Sun X (2016) Hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning ameliorates hypoxia-ischemia brain damage by activating Nrf2 expression in vivo and in vitro. Free Radic Res 50:454–466
Zhang Y, Sun S, Chen J, Ren P, Hu Y, Cao Z, Sun H, Ding Y (2014) Oxymatrine induces mitochondria dependent apoptosis in human osteosarcoma MNNG/HOS cells through inhibition of PI3K/Akt pathway. Tumour Biol 35:1619–1625
Zhao P, Zhou R, Li HN, Yao WX, Qiao HQ, Wang SJ, Niu Y, Sun T, Li YX, Yu JQ (2015) Oxymatrine attenuated hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats via improving antioxidant enzyme activities and inhibiting cell death. Neurochem Int 89:17–27
Zhao SM, Gao HL, Wang YL, Xu Q, Guo CY (2017) Attenuation of high glucose-induced rat cardiomyocyte apoptosis by Exendin-4 via intervention of HO-1/Nrf-2 and the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Chin J Phys 60:89–96
Zhu H, Zhang Y, Shi Z, Lu D, Li T, Ding Y, Ruan Y, Xu A (2016) The neuroprotection of Liraglutide against Ischaemia-induced apoptosis through the activation of the PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathways. Sci Rep 6:26859
Funding
This work was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81370254).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Declaration of conflicting interests
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ge, XH., Shao, L. & Zhu, GJ. Oxymatrine attenuates brain hypoxic-ischemic injury from apoptosis and oxidative stress: role of p-Akt/GSK3β/HO-1/Nrf-2 signaling pathway. Metab Brain Dis 33, 1869–1875 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0293-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0293-4