Abstract
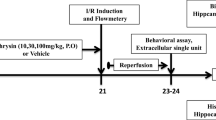
Oxidative stress is strongly implicated in the pathogenesis of stroke. Strategies using antioxidants to improve neurological functions after stroke have, thus, gained significant attention. Ocimum basilicum L. is used traditionally to treat CNS disorders. Its antioxidant capacity is well established. Our laboratory has reported protective effects of pre-treatment with O. basilicum in experimental stroke, but its curative (post-treatment) effects in ischemic stroke have not been documented. Hence, the present study was aimed to evaluate the effect of O. basilicum leaf extract (OBLE) on functional outcomes following cerebral injury in mice. Cerebral injury was induced in the experimental animals by bilateral common carotid artery occlusion (BCCAO) followed by reperfusion. OBLE treatment (200 and 400 mg/kg; orally, once daily) was given for 7 days after BCCAO. Cognitive outcomes and sensorimotor disturbances were evaluated with Morris Water Maze, Elevated Plus Maze and neurological severity score, respectively. TTC (2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride) staining was used to measure cerebral infarct size. Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances, reduced glutathione levels and superoxide dismutase activity in mice brain homogenate were estimated to elucidate the neuroprotective mechanism of OBLE. Treatment with OBLE resulted in marked improvement in memory and motor coordination. OBLE also decreased cerebral infarct size and oxidative stress in mice. The extract was standardised with respect to total phenol content; an HPLC-PDA analysis showed the presence of eight phenolic acids in OBLE. It is concluded that treatment with OBLE improves functional outcomes after ischemic stroke and this may be developed as a neuroprotective drug.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auer RN, Jensen ML, Whishaw IQ (1989) Neurobehavioral deficit due to ischemic brain damage limited to half of the CA1 sector of the hippocampus. J Neurosci 9:1641–1647
Beutler E, Duron O, Kell BM (1963) Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J Lab Clin Med 61:882–888
Bora KS, Arora S, Shri R (2011) Role of Ocimum basilicum L. in prevention of ischemia and reperfusion-induced cerebral damage, and motor dysfunctions in mice brain. J Ethnopharmacol 137:1360–1365
Cheng CY, Su SY, Tang NY, Ho TY, Chiang SY, Hsieh CL (2008) Ferulic acid provides neuroprotection against oxidative stress-related apoptosis after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting ICAM-1 mRNA expression in rats. Brain Res 13:136–150
Dasgupta T, Rao AR, Yadava PK (2004) Chemomodulatory efficacy of basil leaf (Ocimum basilicum) on drug metabolizing and antioxidant enzymes, and on carcinogen-induced skin and forestomach papillomagenesis. Phytomedicine 11:139–151
Farnsworth NR (1966) Biological and phytochemical screening of plants. J Pharm Sci 55:225–276
Grayer RJ, Kite GC, Veitch NC, Eckert MR, Marin PD, Senanayake P, Paton AJ (2002) Leaf flavonoid glycosides as chemosystematic characters in Ocimum. Biochem Syst Ecol 30:327–342
Gülçin I, Elmastaş M, Aboul-Enein HY (2007) Determination of antioxidant and radical scavenging activity of Basil (Ocimum basilicum L. Family Lamiaceae) assayed by different methodologies. Phytother Res 21:354–361
Hagerman A, Harvey-Mueller I, Makkar HPS (2000) Quantification of tannins in tree foliage – a laboratory manual. FAO/IAEA, Vienna, pp 4–7
Harnafi H, Caid HS, el Houda BN, Aziz M, Amrani S (2008) Hypolipemic activity of polyphenol-rich extracts from Ocimum basilicum in Triton WR-1339-induced hyperlipidemic mice. Food Chem 108:205–212
Himori N, Watanabe H, Akaike N, Kurasawa M, Itoh J, Tanaka Y (1990) Cerebral ischemia model with conscious mice; involvement of NMDA receptor activation and derangement of learning and memory ability. J Pharmacol Methods 23:311
Itoh J, Nabeshima T, Kameyama T (1990) Utility of an elevated plus maze for the evaluation of memory in mice. Effects of nootropics, scopolamine and electroconvulsive shock. Psychopharmacology 101:27–33
Jayasinghe C, Gotoh N, Aoki T, Wada S (2003) Phenolics composition and antioxidant activity of sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) J Agric Food Chem 51:4442–4449
Jivad N, Rabiei Z (2015) Review on herbal medicine on brain ischemia and reperfusion. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 5:789–795
Jiwa NS, Garrard P, Hainsworth AH (2010) Experimental models of vascular dementia and vascular cognitive impairment: a systematic review. J Neurochem 115:814–828
Joshi CN, Jain SK, Murthy PS (2004) An optimized triphenyltetrazolium chloride method for identification of cerebral infarcts. Brain Res Brain Res Protoc 13:11–17
Kakkar P, Das B, Viswanathan PN (1984) A modified spectrophotometric assay of superoxide dismutase. Indian J Biochem Biophys 21:130–132
Kaur H, Kumar A, Jaggi AS, Singh N (2015) Pharmacologic investigations on the role of Sirt-1 in neuroprotective mechanism of postconditioning in mice. J Surg Res 197:191–200
Kiryk A, Pluta R, Figiel I, Mikosz M, Ulamek M, Niewiadomska G, Jablonski M, Kaczmarek L (2011) Transient brain ischemia due to cardiac arrest causes irreversible long-lasting cognitive injury. Behav Brain Res 219:1–7
Kumar GP, Khanum F (2012) Neuroprotective potential of phytochemicals. Pharmacogn Rev 6:81–90
Lee K, Lee JS, Jang HJ, Kim SM, Chang MS, Park SH, Kim KS, Bae J, Park JW, Lee B, Choi HY (2012) Chlorogenic acid ameliorates brain damage and edema by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-2 and 9 in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia. Eur J Pharmacol 689:89–95
Liang G, Shi B, Luo W, Yang J (2015) The protective effect of caffeic acid on global cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Behav Brain Funct 11:18
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mancuso C, Santangelo R (2014) Ferulic acid: pharmacological and toxicological aspects. Food Chem Toxicol 65:185–195
Margaill I, Plotkine M, Lerouet D (2005) Antioxidant strategies in the treatment of stroke. Free Radic Biol Med 39:429–443
Meera R, Devi P, Kameswari B, Madhumitha B, Merlin NJ (2009) Antioxidant and hepatoprotective activities of Ocimum basilicum Linn. and Trigonella foenum-graecum Linn. against H2O2 and CCl4 induced hepatotoxicity in goat liver. Indian J Exp Biol 47:584–590
Morris R (1984) Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 11:47–60
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (2001) Acute oral toxicity – acute toxic class method. OECD guideline for the testing of chemicals, Guideline 423
Pan J, Konstas A, Bateman B, Ortolano GA, Pile-Spellman J (2007) Reperfusion injury following cerebral ischemia: pathophysiology, MR imaging, and potential therapies. Neuroradiology 49:93–102
Phippen WB, Simon JE (1998) Anthocyanins in basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) J Agric Food Chem 46:1734–1738
Pulsinelli WA, Brierley JB, Plum F (1982) Temporal profile of neuronal damage in a model of transient forebrain ischemia. Ann Neurol 11:491–498
Ramassamy C (2006) Emerging role of polyphenolic compounds in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases: a review of their intracellular targets. Eur J Pharmacol 545:51–64
Rehni AK, Singh N, Jaggi AS, Singh M (2007) Amniotic fluid derived stem cells ameliorate focal cerebral ischaemia-reperfusion injury induced behavioural deficits in mice. Behav Brain Res 183:95–100
Rogers DC, Campbell CA, Stretton JL, Mackay KB (1997) Correlation between motor impairment and infarct volume after permanent and transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. Stroke 28:2060–2065
Sathya A, Siddhuraju P (2013) Protective effect of bark and empty pod extracts from Acacia auriculiformis against paracetamol intoxicated liver injury and alloxan induced type II diabetes. Food Chem Toxicol 56:162–170
Schaar LK, Brenneman MM, Savitz SI (2010) Functional assessments in the rodent stroke model. Exp Transl Stroke Med 2:13
Siddiqui BS, Aslam H, Begum S, Ali ST (2007) New cinnamic acid esters from Ocimum basilicum. Nat Prod Res 21:736–741
Singh V, Kahol A, Singh IP, Saraf I, Shri R (2016) Evaluation of anti-amnesic effect of extracts of selected Ocimum species using in-vitro and in-vivo models. J Ethnopharmacol 193:490–499
Surapaneni S, Prakash T, Ansari M, Manjunath P, Kotresha D, Goli D (2016) Study on cerebroprotective actions of Clerodendron glandulosum leaves extract against long term bilateral common carotid artery occlusion in rats. Biomed Pharmacother 80:87–94
Wang T, Duan S, Wang H, Sun S, Han B, Fu F (2016) Neurological function following cerebral ischemia/reperfusion is improved by the Ruyi Zhenbao pill in a rats. Biomed Rep 4:161–166
Warner DS, Sheng H, Batinić-Haberle I (2004) Oxidants, antioxidants and the ischemic brain. J Exp Biol 207:3221–3231
Woodruff TM, Thundyil J, Tang SC, Sobey CG, Taylor SM, Arumugam TV (2011) Pathophysiology, treatment, and animal and cellular models of human ischemic stroke. Mol Neurodegener 6:11
Zeggwagh NA, Sulpice T, Eddouks M (2007) Antihyperglycaemic and hypolipidemic effects of Ocimum basilicum aqueous extract in diabetic rats. Am J Pharmacol Toxicol 2:123–129
Acknowledgements
The authors would like thanks University Grants Commission, New Delhi, India for providing UGC-BSR research fellowship (No.F.7-265/2009(BSR)) to Mr. Varinder Singh to carry this research work. The authors are also thankful to Prof. Nirmal Singh, Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Drug Research, Punjabi University, Patiala, Punjab, India for providing lab facilities and guidance for pharmacological studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The experimental protocol was approved by Institutional Animal Ethics Committee (approval no. 107/99/CPCSEA/2015–09) and is in accordance with the guidelines of the Committee for the Purpose of Control and Supervision of Experiments on Animals (CPCSEA), Ministry of Environment and Forest, Government of India.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, V., Krishan, P. & Shri, R. Improvement of memory and neurological deficit with Ocimum basilicum L. extract after ischemia reperfusion induced cerebral injury in mice. Metab Brain Dis 33, 1111–1120 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0215-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0215-5