Abstructs
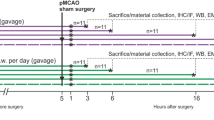
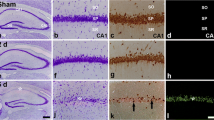
We investigated the immunohistochemical alterations of the transcription nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) and transcription factor p53 in the hippocampus after transient cerebral ischemia in gerbils. We also examined the effect of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase inhibitor pitavastatin against the alterations of NF-κB, p53 and neuronal nuclei in the hippocampus after ischemia. Severe neuronal damage was observed in the hippocampal CA1 neurons 5 and 14 days after ischemia. In the present study, the increase of NF-κB immunoreactivity in glial cells and p53 immunoreactivity in neurons preceded neuronal damage in the hippocampal CA1 sector after ischemia. Thereafter, NF-κB immunoreactivity was induced highly in reactive astrocytes and microglia of the hippocampal CA1 sector where severe neuronal damage was observed. Our immunohistochemical study showed that pitavastatin prevented the alterations of NF-κB and p53 in the hippocampal CA1 sector 5 days after transient ischemia. Furthermore, our results with neuronal nuclei immunostaining indicate that pitavastatin dose-dependently prevented the neuronal cell death in the hippocampal CA1 sector 5 days after transient cerebral ischemia. These results suggest that the up-regulations of NF-κB in glia and p53 in neurons can cause neuronal cell death after ischemia. Our findings also support the hypothesis that NF-κB- and/or p53-mediated neuronal cell death is prevented through decreasing oxidative stress by pitavastatin. Thus, NF-κB and p53 may provide an attractive target for the development of novel therapeutic approaches for brain stroke.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoki T, Nishimura H, Nakagawa S, Kojima J, Suzuki H, Tamaki T, Wada Y, Yokoo N, Sato F, Kimata H, Kitahara M, Toyoda K, Sakashita M, Saito Y (1997) Pharmacological profile of a novel synthetic inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase. Arzneimittelforschung 47:904–909
Araki T, Kato H, Kogure K (1989) Selective neuronal vulnerability following transient cerebral ischemia in gerbils: Distribution and time course. Acta Neurol Scand 80:548–533
Banasiak KJ, Haddad GG (1998) Hypoxia-induced apoptosis: effect of hypoxic severity and role of p53 in neuronal cell death. Brain Res 797:295–304
Bhakar AL, Tannis LL, Zeindler C, Russo MP, Jobin C, Park D, MacPherson S, Barker PA (2002) Constitutive nuclear factor-kappa B activity is required for central neuron survival. J Nuerosci 22:8466–8475
Buttini M, Sauter A, Boddeke HW (1994) Induction of interleukin-1β mRNA after focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. Mol Brain Res 23:126–134
Carter BD, Kaltschmidt C, Kaltschmidt B, Offenhauser N, Bohm-Matthaei R, Baeuerle PA, Barde YA (1996) Selective activation of NF-kappa B by nerve growth factor through the neurotrophin receptor p75. Science 272:542–545
Chan PH (2001) Reactive oxygen radicals in signaling and damage in the ischemic brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 21:2–14
Crumrine RC, Thomas AL, Morgan PF (1994) Attenuation of p53 expression protects against focal ischemic damage in transgenic mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 14:887–891
Culmsee C, Siewe J, Junker V, Retiounskaia M, Schwarz S, Camandola S, El-Metainy S, Behnke H, Mattson MP, Krieglstein J (2003) Reciprocal inhibition of p53 and nuclear factor-kappaB transcriptional activities determines cell survival or death in neurons. J Neurosci 23:8586–8595
Endres M, Laufs U, Huang Z, Nakamura T, Huang P, Moskowitz MA, Liao JK (1998) Stroke protection by 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl (HMG)-CoA reductase inhibitors mediated by endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:8880–8885
Feuerstein GZ, Liu T, Barone FC (1994) Cytokines, inflammation, and brain injury: role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev 6:341–360
Fridmacher V, Kaltschmidt B, Goudeau B, Ndiaye D, Rossi FM, Pfeiffer J, Kaltschmidt C, Israel A, Memet S (2003) Forebrain-specific neuronal inhibition of nuclear factor-κB activity leads to loss of neuroprotection. J Neurosci 23:9403–9408
Fujimoto H, Kojima J, Yamada Y, Kanda H, Kimata H (1999) Studies on the metabolic fate of pitavastatin, a new inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase (4): interspecies variation in laboratory animals and humans. Xenobiot Metab Dispos 14:79–91
Gabriel C, Justicia C, Camins A, Planas AM (1999) Activation of nuclear factor-kappa B in the rat brain after transient focal ischemia. Mol Brain Res 65:61–69
Guo Q, Robinson N, Mattson MP (1998) Secreted β-amyloid precursor protein counteracts the proapoptotic action of mutant presenilin-1 by activation of NF-κB and stabilization of calcium homeostasis. J Biol Chem 273:12341–12351
Halterman MW, Miller CC, Federoff HJ (1999) Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha mediates hypoxia-induced delayed neuronal death that involves p53. J Neurosci 19:6818–6824
Hayashi T, Hamakawa K, Nagotani S, Jin G, Li F, Deguchi K, Sehera Y, Zhang H, Nagano I, Shoji M, Abe K (2005) HMG CoA reductase inhibitors reduce ischemic brain injury of rats through decreasing oxidative stress on neurons. Brain Res 1037:52–58
Himeda T, Hayakawa N, Tounai H, Sakuma M, Kato H, Araki T (2005) Alterations of interneurons of the gerbil hippocampus after transient cerebral ischemia: effect of pitavastatin. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:2014–2025
Kajinami K, Koizumi J, Ueda K, Miyamoto S, Takegoshi T, Mabuchi H (2000) Effects of NK-104, a new hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme reductase inhibitor, on low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Am J Cardiol 85:178–183
Kato H, Kogure K, Araki T, Itoyama Y (1995) Graded expression of immunomolecules on activated microglia in the hippocampus following ischemia in a rat model of ischemic tolerance. Brain Res 694:85–93
Kirino T (1982) Delayed neuronal death in the gerbil hippocampus following ischemia. Brain Res 239:57–69
Kojima J, Fujino H, Abe H, Yoshimura M, Kanda H, Kimata H (1999) Identification of metabolites of NK-104, an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, in rat, rabbit and dog bile. Biol Pharm Bull 22:142–150
Kumagai R, Oki C, Muramatsu Y, Kurosaki R, Kato H, Araki T (2004) Pitavastatin, a 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-conenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitor, reduces hippocampal damage after transient cerebral ischemia in gerbils. J Neural Transm 111:1103–1120
Kurosaki R, Muramatsu Y, Michimata M, Matsubara M, Kato H, Imai Y, Itoyama Y, Araki T (2002) Role of nitric oxide synthase against MPTP neurotoxicity in mice. Neurol Res 24:655–662
Makarov SS (2000) NF-κB activity as a therapeutic target in chronic inflammation: recent advances. Mol Med Today 6:441–448
Mattson MP, Camandola S (2001) NF-κB in neuronal plasticity and neurodegenerative disorders. J Clin Invest 107:247–254
Mattson MP (2005) NF-κB in the survival and plasticity of neurons. Neurochem Res 30:883–893
McGahan L, Hakim AM, Robertson GS (1998) Hippocampal Myc and p53 expression following transient global ischemia. Mol Brain Res 56:133–145
Morris EJ, Keramaris E, Rideout HJ, Slack RS, Dyson NJ, Stefanis L, Park DS (2001) Cyclin-dependent kinases and p53 pathways are activated independently and mediate Bax activation in neurons after DNA damage. J Neurosci 21:5017–5026
Morrison RS, Wenzel HJ, Kinoshita Y, Robbins CA, Donehower LA, Schwartzkroin PA (1996) Loss of the p53 tumor suppressor gene protects neurons from kainate-induced cell death. J Neurosci 16:1337–1345
Morrison RS, Kinoshita Y (2000) The role of p53 in neuronal cell death. Cell Death Differ 7:868–879
Moynagh PN, Williams DC, O’Neill LA (1993) Interleukin-1 activates transcription factor NF kappa B in glial cells. Biochem J 294:343–347
Muramatsu Y, Kurosaki R, Watanabe H, Michimata M, Matsubara M, Imai Y, Araki T (2003) Expression of S-100 protein is related to neuronal damage in MPTP-treated mice. Glia 42:307–313
Nitatori T, Sato N, Waguri S, Karasawa Y, Araki H, Shibanai K, Kominami E, Uchiyama Y (1995) Delayed neuronal death in the CA1 pyramidal cell layer of the gerbil hippocampus following transient ischemia is apoptosis. J Neurosci 15:1001–1011
Nurmi A, Lindsberg PJ, Koistinaho M, Zhang W, Juettler E, Karjalainen-Lindsberg ML, Weih F, Frank N, Schwaninger M, Koistinaho J (2004) Nuclear factor-kB contributes to infarction after permanent focal ischemia. Stroke 35:987–991
Pettmann B, Henderson CE (1998) Neuronal cell death. Neuron 20:633–647
Portera-Gailliau C, Henderson JC, Price DL, Koliatsos VE (1995) Evidence for apoptotic cell death in Huntington disease and excitotoxic animal models. J Neurosci 15:3775–3787
Rosenson RS (2000) Biological basis for statin therapy in stroke prevention. Curr Opin Neurol 13:57–62
Schmidt-Kastner R, Freund TF (1991) Selective vulnerability of the hippocampus in brain ischemia. Neuroscience 40:599–636
Schneider A, Martin-Villalba A, Weih F, Vogel J, Wirth T, Schwaninger M (1999) NF-kB is activated and promotes cell death in focal cerebral ischemia. Nat Med 5:554–559
Schreck R, Rieber P, Baeuerle PA (1991) Reactive oxygen intermediates as apparently widely used messengers in the activation of NF-κB transcription factor and HIV-1. EMBO J 10:2247–2258
Smale G, Nichols NR, Brady DR, Finch CE, Horton WE Jr (1995) Evidence for apoptotic cell death in Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Neurol 133:225–230
Stephenson D, Yin T, Smalstig EB, Hsu MA, Panetta J, Little S, Clemens J (2000) Transcription factor nuclear factor-κB is activated in neurons after focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 20:592–603
Urabe T, Yamasaki Y, Hattori N, Yoshikawa M, Uchida K, Mizuno Y (2000) Accumulation of 4-hydroxynonenal-modified proteins in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons precedes delayed neuronal damage in the gerbil brain. Neuroscience 100:241–250
Xiang H, Hochman DW, Saya H, Fujiwara T, Schwartzkroin PA, Morrison RS (1996) Evidence for p53-mediated modulation of neuronal viability. J Neurosci 16:6753–6765
Xiang H, Kinoshita Y, Knudson CM, Korsmeyer SJ, Schwartzkroin PA, Morrison RS (1998) Bax involvement in p53-mediated neuronal cell death. J Neurosci 18:1363–1373
Yakovlev AG, Knoblach SM, Fan L, Fox GB, Goodnight R, Faden AI (1997) Activation of CPP32-like caspases contributes to neuronal apoptosis and neurological dysfunction after traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci 17:7415–7424
Yu Z, Zhou D, Bruce-Keller AJ, Kindy MS, Mattson MP (1999) Lack of the p50 subunit of nuclear factor-kB increase the vulnerability of hippocampal neurons to excitotoxic injury. J Neurosci 19:8856–8865
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciatively acknowledge Kowa Company, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan, for providing pitavastatin, and helpful advice. This study was supported in part by the Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (12877163, 13671095 and 13670627) from the Ministry of Science and Education in Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Hiroko Tounai and Natsumi Hayakawa equally contributed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tounai, H., Hayakawa, N., Kato, H. et al. Immunohistochemical Study on Distribution of NF-κB and p53 in Gerbil Hippocampus after Transient Cerebral Ischemia: Effect of Pitavastatin. Metab Brain Dis 22, 89–104 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-006-9040-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-006-9040-3