Abstract
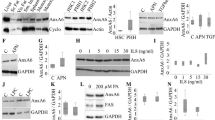
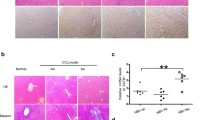
Tubulin alpha 8 (TUBA8) is highly abundant in murine liver tumors suggesting a role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is a risk factor for HCC. In mice that are fed with a methionine-choline deficient diet for two weeks to induce advanced murine NASH, we do see increased hepatic levels of TUBA8 protein. In animals given a high-fat diet for 14 weeks or an atherogenic diet for 12 weeks, hepatic TUBA8 is unchanged. TUBA8 is highly expressed in human hepatic stellate cells (HSC) and co-localizes with the HSC marker desmin in the murine liver. Inflammatory (TNF, LPS, IL-6) and profibrotic mediators (TGF-beta) do not regulate TUBA8 in HepG2 cells, primary HSC and the HSC cell line LX-2, when stimulated for 24 h. Agonists of the farnesoid X receptor and peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma, which are nuclear receptors involved in NASH and HCC pathophysiology, have no effect on TUBA8 in HepG2 and LX-2 cells. In human HCC tissues of 18 patients TUBA8 is significantly upregulated when compared to the corresponding non-tumorous tissues. Compared to non-transformed hepatocytes, TUBA8 protein is strongly expressed in transformed cells. Thus, TUBA8 is a marker of HSC whose cell number is increased in NASH, while higher levels in HCC may be related to induction of TUBA8 in parenchymal cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buechler C, Wanninger J, Neumeier M (2011) Adiponectin, a key adipokine in obesity related liver diseases. World J Gastroenterol 17:2801–2811. doi:10.3748/wjg.v17.i23.2801
Buechler C, Weiss TS (2011) Does hepatic steatosis affect drug metabolizing enzymes in the liver? Curr Drug Metab 12:24–34
Yeh MM, Brunt EM (2014) Pathological features of fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 147:754–764. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2014.07.056
Konno Y, Negishi M, Kodama S (2008) The roles of nuclear receptors CAR and PXR in hepatic energy metabolism. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 23:8–13
Yamazaki Y, Kakizaki S, Horiguchi N, Sohara N, Sato K, Takagi H, Mori M, Negishi M (2007) The role of the nuclear receptor constitutive androstane receptor in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Gut 56:565–574. doi:10.1136/gut.2006.093260
Takizawa D, Kakizaki S, Horiguchi N, Yamazaki Y, Tojima H, Mori M (2011) Constitutive active/androstane receptor promotes hepatocarcinogenesis in a mouse model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Carcinogenesis 32:576–583. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgq277
Kamino H, Moore R, Negishi M (2011) Role of a novel CAR-induced gene, TUBA8, in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Genet 204:382–91. doi:10.1016/j.cancergen.2011.05.007
Stanchi F, Corso V, Scannapieco P, Ievolella C, Negrisolo E, Tiso N, Lanfranchi G, Valle G (2000) TUBA8: a new tissue-specific isoform of alpha-tubulin that is highly conserved in human and mouse. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 270:1111–1118. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2000.2571
La Merrill M, Kuruvilla BS, Pomp D, Birnbaum LS, Threadgill DW (2009) Dietary fat alters body composition, mammary development, and cytochrome p450 induction after maternal TCDD exposure in DBA/2 J mice with low-responsive aryl hydrocarbon receptors. Environ Health Perspect 117:1414–1419. doi:10.1289/ehp.0800530
Yoshinari K, Takagi S, Sugatani J, Miwa M (2006) Changes in the expression of cytochromes P450 and nuclear receptors in the liver of genetically diabetic db/db mice. Biol Pharm Bull 29:1634–1638
Damm G, Pfeiffer E, Burkhardt B, Vermehren J, Nussler AK, Weiss TS (2013) Human parenchymal and non-parenchymal liver cell isolation, culture and characterization. Hepatol Int 7:951–8. doi:10.1007/s12072-013-9475-7
Greene FL, Sobin LH (2009) A worldwide approach to the TNM staging system: collaborative efforts of the AJCC and UICC. J Surg Oncol 99:269–272. doi:10.1002/jso.21237
Bauer S, Wanninger J, Schmidhofer S, Weigert J, Neumeier M, Dorn C, Hellerbrand C, Zimara N, Schaffler A, Aslanidis C, Buechler C (2011) Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 2 (SREBP2) activation after excess triglyceride storage induces chemerin in hypertrophic adipocytes. Endocrinology 152:26–35. doi:10.1210/en.2010-1157
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW (2012) NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 9:671–675
Ballardini G, Fallani M, Biagini G, Bianchi FB, Pisi E (1988) Desmin and actin in the identification of Ito cells and in monitoring their evolution to myofibroblasts in experimental liver fibrosis. Virchows Arch B 56:45–9.
Ramboer E, Vanhaecke T, Rogiers V, Vinken M (2015) Immortalized Human Hepatic Cell Lines for In Vitro Testing and Research Purposes. Methods Mol Biol 1250:53–76. doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-2074-7_4
Cave MC, Clair HB, Hardesty JE, Falkner KC, Feng W, Clark BJ, Sidey J, Shi H, Aqel BA, McClain CJ, Prough RA (2016) Nuclear receptors and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1859:1083–1099. doi:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2016.03.002
Fiorucci S, Rizzo G, Antonelli E, Renga B, Mencarelli A, Riccardi L, Morelli A, Pruzanski M, Pellicciari R (2005) Cross-talk between farnesoid-X-receptor (FXR) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma contributes to the antifibrotic activity of FXR ligands in rodent models of liver cirrhosis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 315:58–68. doi:10.1124/jpet.105.085597
Eisinger K, Krautbauer S, Hebel T, Schmitz G, Aslanidis C, Liebisch G, Buechler C (2014) Lipidomic analysis of the liver from high-fat diet induced obese mice identifies changes in multiple lipid classes. Exp Mol Pathol 97:37–43. doi:10.1016/j.yexmp.2014.05.002
Krautbauer S, Wanninger J, Eisinger K, Hader Y, Beck M, Kopp A, Schmid A, Weiss TS, Dorn C, Buechler C (2013) Chemerin is highly expressed in hepatocytes and is induced in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis liver. Exp Mol Pathol 95:199–205. doi:10.1016/j.yexmp.2013.07.009
Matsuzawa N, Takamura T, Kurita S, Misu H, Ota T, Ando H, Yokoyama M, Honda M, Zen Y, Nakanuma Y, Miyamoto K, Kaneko S (2007) Lipid-induced oxidative stress causes steatohepatitis in mice fed an atherogenic diet. Hepatology 46:1392–1403. doi:10.1002/hep.21874
Hinz B, Phan SH, Thannickal VJ, Galli A, Bochaton-Piallat ML, Gabbiani G (2007) The myofibroblast: one function, multiple origins. Am J Pathol 170:1807–1816. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2007.070112
Sahai A, Pan X, Paul R, Malladi P, Kohli R, Whitington PF (2006) Roles of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and osteopontin in steatosis and aminotransferase release by hepatocytes treated with methionine-choline-deficient medium. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 291:G55–G62. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00360.2005
Kuramitsu Y, Takashima M, Yokoyama Y, Iizuka N, Tamesa T, Akada JK, Wang Y, Toda T, Sakaida I, Okita K, Oka M, Nakamura K (2011) Up-regulation of 42 kDa tubulin alpha-6 chain fragment in well-differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma tissues from patients infected with hepatitis C virus. Anticancer Res 31:3331–3336
Lu C, Zhang J, He S, Wan C, Shan A, Wang Y, Yu L, Liu G, Chen K, Shi J, Zhang Y, Ni R (2013) Increased alpha-tubulin1b expression indicates poor prognosis and resistance to chemotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci 58:2713–2720. doi:10.1007/s10620-013-2692-z
Fanale D, Bronte G, Passiglia F, Calo V, Castiglia M, Di Piazza F, Barraco N, Cangemi A, Catarella MT, Insalaco L, Listi A, Maragliano R, Massihnia D, Perez A, Toia F, Cicero G, Bazan V (2015) Stabilizing versus destabilizing the microtubules: a double-edge sword for an effective cancer treatment option? Anal Cell Pathol 2015:690–916. doi:10.1155/2015/690916
Braeuning A, Gavrilov A, Brown S, Wolf CR, Henderson CJ, Schwarz M (2014) Phenobarbital-mediated tumor promotion in transgenic mice with humanized CAR and PXR. Toxicol Sci 140:259–270. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfu099
LeBaron MJ, Rasoulpour RJ, Gollapudi BB, Sura R, Kan HL, Schisler MR, Pottenger LH, Papineni S, Eisenbrandt DL (2014) Characterization of nuclear receptor-mediated murine hepatocarcinogenesis of the herbicide pronamide and its human relevance. Toxicol Sci 142:74–92. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfu155
Lee JS, Heo J, Libbrecht L, Chu IS, Kaposi-Novak P, Calvisi DF, Mikaelyan A, Roberts LR, Demetris AJ, Sun Z, Nevens F, Roskams T, Thorgeirsson SS (2006) A novel prognostic subtype of human hepatocellular carcinoma derived from hepatic progenitor cells. Nat Med 12:410–416. doi:10.1038/nm1377
Lee YJ, Hah YJ, Kang YN, Kang KJ, Hwang JS, Chung WJ, Cho KB, Park KS, Kim ES, Seo HY, Kim MK, Park KG, Jang BK (2013) The autophagy-related marker LC3 can predict prognosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 8:e81540. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0081540
Pons F, Varela M, Llovet JM (2005) Staging systems in hepatocellular carcinoma. HPB 7:35–41. doi:10.1080/13651820410024058
Thompson AI, Conroy KP, Henderson NC (2015) Hepatic stellate cells: central modulators of hepatic carcinogenesis. BMC Gastroenterol 15:63. doi:10.1186/s12876-015-0291-5
Greene MW, Burrington CM, Ruhoff MS, Johnson AK, Chongkrairatanakul T, Kangwanpornsiri A (2010) PKC{delta} is activated in a dietary model of steatohepatitis and regulates endoplasmic reticulum stress and cell death. J Biol Chem 285:42115–42129. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.168575
Schaefer KL, Takahashi H, Morales VM, Harris G, Barton S, Osawa E, Nakajima A, Saubermann LJ (2007) PPARgamma inhibitors reduce tubulin protein levels by a PPARgamma, PPARdelta and proteasome-independent mechanism, resulting in cell cycle arrest, apoptosis and reduced metastasis of colorectal carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer 120:702–713. doi:10.1002/ijc.22361
Arndt S, Wacker E, Dorn C, Koch A, Saugspier M, Thasler WE, Hartmann A, Bosserhoff AK, Hellerbrand C (2015) Enhanced expression of BMP6 inhibits hepatic fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut 64:973–981. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2014-306968
Sanchez-Gurmaches J, Guertin DA (2014) Adipocyte lineages: tracing back the origins of fat. Biochim Biophys Acta 1842:340–351. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.05.027
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by the German Research Foundation (BU 1141/12 − 1) to CB and the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (Virtual Liver Network Grants 0315753) to TSW. The authors are grateful to Professor Charalampos Aslanidis for helpful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Experimental procedures complied with the guidelines of the charitable state controlled foundation Human Tissue and Cell Research. The study was approved by the local ethical committee of the University of Regensburg. Written informed patient’s consent was obtained. All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. Animal studies were authorized by the University of Regensburg Laboratory Animal Committee and complied with the German Law on Animal Protection and the Institute for Laboratory Animal Research Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 1999. Experiments were conducted according to institutional and governmental regulations for animal use (Government of the Oberpfalz).
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rein-Fischboeck, L., Pohl, R., Haberl, E.M. et al. Tubulin alpha 8 is expressed in hepatic stellate cells and is induced in transformed hepatocytes. Mol Cell Biochem 428, 161–170 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-016-2926-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-016-2926-4