Abstract
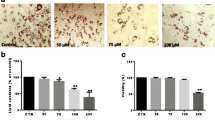
Baicalin is a flavonoid derived from the root of Scutellaria baicalensis and exhibits a broad spectrum of biological activities including anti-adipogenesis. However, the inhibitory role of baicalin in the early stage of 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation relevant to the signaling up-stream of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPAR-γ) and CCAAT/enhancer binding proteins (C/EBPs) expression is unclear, and is the subject of the present investigation. We used 3T3-L1 preadipocytes for adipocyte differentiation, Oil Red-O staining for the intracellular lipid accumulation assay, and real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) for assaying the expression of major adipocyte transcription factors. We found that baicalin markedly suppressed the Akt phosphorylation in early stage of adipocytes differentiation. In addition, we observed that baicalin and LY294002 (as an inhibitor of Akt phosphorylation) significantly inhibited adipocyte differentiation by down-regulating several adipocyte-specific transcription factors, including PPAR-γ and C/EBPs in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Furthermore, we observed that baicalin significantly suppressed the Akt phosphorylation by inhibiting phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 (PDK1). These results indicate that the anti-adipogenesis effect of baicalin involves down-regulation of major transcription factors in 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation including PPAR-γ, C/EBP-β, and C/EBP-α through the down-regulation of PDK1/Akt phosphorylation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao JJ (2011) Effects of obesity on bone metabolism. J Orthop Surg Res 6:30. doi:10.1186/1749-799X-6-30
Song H, O’Connor KC, Papadopoulos KD, Jansen DA (2002) Differentiation kinetics of in vitro 3T3-L1 preadipocyte cultures. Tissue Eng 8:1071–1081. doi:10.1089/107632702320934164
Tang QQ, Otto TC, Lane MD (2003) Mitotic clonal expansion: a synchronous process required for adipogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:44–49. doi:10.1073/pnas.0137044100
Sprott KM, Chumley MJ, Hanson JM, Dobrowsky RT (2002) Decreased activity and enhanced nuclear export of CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein beta during inhibition of adipogenesis by ceramide. Biochem J 365:181–191. doi:10.1042/BJ20020215
Liu PC, Phillips MA, Matsumura F (1996) Alteration by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein correlates with suppression of adipocyte differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells. Mol Pharmacol 49:989–997
Cho SY, Park PJ, Shin HJ, Kim YK, Shin DW, Shin ES, Lee HH, Lee BG, Baik JH, Lee TR (2007) (−)-Catechin suppresses expression of Kruppel-like factor 7 and increases expression and secretion of adiponectin protein in 3T3-L1 cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 292:E1166–E1172. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00436.2006
Jou PC, Ho BY, Hsu YW, Pan TM (2010) The effect of Monascus secondary polyketide metabolites, monascin and ankaflavin, on adipogenesis and lipolysis activity in 3T3-L1. J Agric Food Chem 58:12703–12709. doi:10.1021/jf103121c
Thompson GM, Trainor D, Biswas C, LaCerte C, Berger JP, Kelly LJ (2004) A high-capacity assay for PPARgamma ligand regulation of endogenous aP2 expression in 3T3-L1 cells. Anal Biochem 330:21–28. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2004.03.061
Sale EM, Atkinson PG, Sale GJ (1995) Requirement of MAP kinase for differentiation of fibroblasts to adipocytes, for insulin activation of p90 S6 kinase and for insulin or serum stimulation of DNA synthesis. EMBO J 14:674–684
Hu E, Kim JB, Sarraf P, Spiegelman BM (1996) Inhibition of adipogenesis through MAP kinase-mediated phosphorylation of PPARgamma. Science 274:2100–2103
Wang M, Wang JJ, Li J, Park K, Qian X, Ma JX, Zhang SX (2009) Pigment epithelium-derived factor suppresses adipogenesis via inhibition of the MAPK/ERK pathway in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 297:E1378–E1387. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00252.2009
Liu HS, Chen YH, Hung PF, Kao YH (2006) Inhibitory effect of green tea (−)-epigallocatechin gallate on resistin gene expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes depends on the ERK pathway. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 290:E273–E281. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00325.2005
Naiki T, Saijou E, Miyaoka Y, Sekine K, Miyajima A (2007) TRB2, a mouse tribbles ortholog, suppresses adipocyte differentiation by inhibiting AKT and C/EBPbeta. J Biol Chem 282:24075–24082. doi:10.1074/jbc.M701409200
Yoshiga D, Sato N, Torisu T, Mori H, Yoshida R, Nakamura S, Takaesu G, Kobayashi T, Yoshimura A (2007) Adaptor protein SH2-B linking receptor-tyrosine kinase and Akt promotes adipocyte differentiation by regulating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma messenger ribonucleic acid levels. Mol Endocrinol 21:1120–1131. doi:10.1210/me.2006-0413
Chan FL, Choi HL, Chen ZY, Chan PS, Huang Y (2000) Induction of apoptosis in prostate cancer cell lines by a flavonoid, baicalin. Cancer Lett 160:219–228
Krakauer T, Li BQ, Young HA (2001) The flavonoid baicalin inhibits superantigen-induced inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. FEBS Lett 500:52–55
Li BQ, Fu T, Dongyan Y, Mikovits JA, Ruscetti FW, Wang JM (2000) Flavonoid baicalin inhibits HIV-1 infection at the level of viral entry. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 276:534–538. doi:10.1006/bbrc 2000.3485
Lee H, Kang R, Hahn Y, Yang Y, Kim SS, Cho SH, Chung SI, Yoon Y (2009) Antiobesity effect of baicalin involves the modulations of proadipogenic and antiadipogenic regulators of the adipogenesis pathway. Phytother Res 23:1615–1623
Feve B (2005) Adipogenesis: cellular and molecular aspects. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 19:483–499. doi:10.1016/j.beem.2005.07.007
Farmer SR (2008) Molecular determinants of brown adipocyte formation and function. Genes Dev 22:1269–1275. doi:10.1101/gad.1681308
Backesjo CM, Li Y, Lindgren U, Haldosen LA (2006) Activation of Sirt1 decreases adipocyte formation during osteoblast differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J Bone Miner Res 21:993–1002. doi:10.1359/jbmr.060415
Yang JY, Della-Fera MA, Baile CA (2008) Guggulsterone inhibits adipocyte differentiation and induces apoptosis in 3T3-L1 cells. Obesity (Silver Spring) 16:16–22. doi:10.1038/oby.2007.24
Zhang M, Ikeda K, Xu JW, Yamori Y, Gao XM, Zhang BL (2009) Genistein suppresses adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 cells via multiple signal pathways. Phytother Res 23:713–718. doi:10.1002/ptr.2724
Hsu CL, Yen GC (2007) Effects of capsaicin on induction of apoptosis and inhibition of adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells. J Agric Food Chem 55:1730–1736. doi:10.1021/jf062912b
Uto-Kondo H, Ohmori R, Kiyose C, Kishimoto Y, Saito H, Igarashi O, Kondo K (2009) Tocotrienol suppresses adipocyte differentiation and Akt phosphorylation in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. J Nutr 139:51–57. doi:10.3945/jn.108.096131
Kim H, Sakamoto K (2012) (−)-Epigallocatechin gallate suppresses adipocyte differentiation through the MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways. Cell Biol Int 36:147–153. doi:10.1042/CBI20110047
Prusty D, Park BH, Davis KE, Farmer SR (2002) Activation of MEK/ERK signaling promotes adipogenesis by enhancing peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) and C/EBPalpha gene expression during the differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. J Biol Chem 277:46226–46232. doi:10.1074/jbc.M207776200
Lii CK, Huang CY, Chen HW, Chow MY, Lin YR, Huang CS, Tsai CW (2012) Diallyl trisulfide suppresses the adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes through ERK activation. Food Chem Toxicol 50:478–484. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2011.11.020
Kim GS, Park HJ, Woo JH, Kim MK, Koh PO, Min W, Ko YG, Kim CH, Won CK, Cho JH (2012) Citrus aurantium flavonoids inhibit adipogenesis through the Akt signaling pathway in 3T3-L1 cells. BMC Complement Altern Med 12:31. doi:10.1186/1472-6882-12-31
Bhattacharya I, Ullrich A (2006) Endothelin-1 inhibits adipogenesis: role of phosphorylation of Akt and ERK1/2. FEBS Lett 580:5765–5771. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2006.09.032
Baudry A, Yang ZZ, Hemmings BA (2006) PKBalpha is required for adipose differentiation of mouse embryonic fibroblasts. J Cell Sci 119:889–897. doi:10.1242/jcs.02792
Zhang HH, Huang J, Duvel K, Boback B, Wu S, Squillace RM, Wu CL, Manning BD (2009) Insulin stimulates adipogenesis through the Akt-TSC2-mTORC1 pathway. PLoS ONE 4:e6189. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0006189
Hofler A, Nichols T, Grant S, Lingardo L, Esposito EA, Gridley S, Murphy ST, Kath JC, Cronin CN, Kraus M, Alton G, Xie Z, Sutton S, Gehring M, Ermolieff J (2011) Study of the PDK1/AKT signaling pathway using selective PDK1 inhibitors, HCS, and enhanced biochemical assays. Anal Biochem 414:179–186. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2011.03.013
Tang QQ, Zhang JW, Daniel Lane M (2004) Sequential gene promoter interactions of C/EBPbeta, C/EBPalpha, and PPARgamma during adipogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 319:235–239. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.04.176
Yim MJ, Hosokawa M, Mizushina Y, Yoshida H, Saito Y, Miyashita K (2011) Suppressive effects of Amarouciaxanthin A on 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation through down-regulation of PPARgamma and C/EBPalpha mRNA expression. J Agric Food Chem 59:1646–1652. doi:10.1021/jf103290f
Motojima K (1995) Toward the treatment of obesity: role of PPAR gamma in adipogenesis. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso 40:1936–1941
Rosen ED, Hsu CH, Wang X, Sakai S, Freeman MW, Gonzalez FJ, Spiegelman BM (2002) C/EBPalpha induces adipogenesis through PPARgamma: a unified pathway. Genes Dev 16:22–26. doi:10.1101/gad.948702
Wu Z, Xie Y, Bucher NL, Farmer SR (1995) Conditional ectopic expression of C/EBP beta in NIH-3T3 cells induces PPAR gamma and stimulates adipogenesis. Genes Dev 9:2350–2363
Hamm JK, Park BH, Farmer SR (2001) A role for C/EBPbeta in regulating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma activity during adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. J Biol Chem 276:18464–18471. doi:10.1074/jbc.M100797200
Farmer SR (2005) Regulation of PPARgamma activity during adipogenesis. Int J Obes (Lond) 29(Suppl 1):S13–S16. doi:10.1038/sj.ijo.0802907
Christy RJ, Kaestner KH, Geiman DE, Lane MD (1991) CCAAT/enhancer binding protein gene promoter: binding of nuclear factors during differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:2593–2597
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by the Grant K13050 awarded to Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine (KIOM) from Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (MEST), Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwak, D.H., Lee, JH., Song, K.H. et al. Inhibitory effects of baicalin in the early stage of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes differentiation by down-regulation of PDK1/Akt phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biochem 385, 257–264 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1834-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1834-0