Abstract
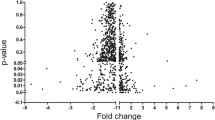
Human atrial and ventricular myocardium has distinct structure and physiology. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are the central players in the regulation of gene expression, participating in many physiological processes. A comprehensive knowledge of miRNA expression in the human heart is essential for the understanding of myocardial function. The aim of this study was to compare the miRNA signature in human right atrial and ventricular myocardium. Agilent human miRNA arrays were used to indicate the miRNA expression signatures of the right atrial (n = 8) and ventricular (n = 9) myocardium of healthy individuals. Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reactions (qRT-PCRs) were used to validate the array results. DIANA-mirPath was used to incorporate the miRNAs into pathways. MiRNA arrays showed that 169 miRNAs were expressed at different levels in human right atrial and ventricular myocardium. The unsupervised hierarchical clustering analysis based on the 169 dysregulated miRNAs showed that miRNA expression categorized two well-defined clusters that corresponded to human right atrial and ventricular myocardium. The qRT-PCR results correlated well with the microarray data. Bioinformatic analysis indicated the potential miRNA targets and molecular pathways. This study indicates that distinct miRNA expression signatures in human right atrial and ventricular myocardium. The findings provide a novel understanding of the molecular differences between human atrial and ventricular myocardium and may establish a framework for an anatomically detailed evaluation of cardiac function regulation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barth AS, Merk S, Arnoldi E, Zwermann L, Kloos P, Gebauer M, Steinmeyer K, Bleich M, Kaab S, Pfeufer A, Uberfuhr P, Dugas M, Steinbeck G, Nabauer M (2005) Functional profiling of human atrial and ventricular gene expression. Pflugers Arch 450:201–208
Ng SY, Wong CK, Tsang SY (2010) Differential gene expressions in atrial and ventricular myocytes: insights into the road of applying embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes for future therapies. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 299:C1234–C1249
Burstein B, Libby E, Calderone A, Nattel S (2008) Differential behaviors of atrial versus ventricular fibroblasts: a potential role for platelet-derived growth factor in atrial-ventricular remodeling differences. Circulation 117:1630–1641
Ellinghaus P, Scheubel RJ, Dobrev D, Ravens U, Holtz J, Huetter J, Nielsch U, Morawietz H (2005) Comparing the global mRNA expression profile of human atrial and ventricular myocardium with high-density oligonucleotide arrays. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 129:1383–1390
Reiser PJ, Portman MA, Ning XH, Schomisch Moravec C (2001) Human cardiac myosin heavy chain isoforms in fetal and failing adult atria and ventricles. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 280:H1814–H1820
Flagg TP, Kurata HT, Masia R, Caputa G, Magnuson MA, Lefer DJ, Coetzee WA, Nichols CG (2008) Differential structure of atrial and ventricular KATP: atrial KATP channels require SUR1. Circ Res 103:1458–1465
Wiese S, Breyer T, Dragu A, Wakili R, Burkard T, Schmidt-Schweda S, Fuchtbauer EM, Dohrmann U, Beyersdorf F, Radicke D, Holubarsch CJ (2000) Gene expression of brain natriuretic peptide in isolated atrial and ventricular human myocardium: influence of angiotensin II and diastolic fiber length. Circulation 102:3074–3079
Asp J, Synnergren J, Jonsson M, Dellgren G, Jeppsson A (2012) Comparison of human cardiac gene expression profiles in paired samples of right atrium and left ventricle collected in vivo. Physiol Genomics 44:89–98
Kostin S, Schaper J (2001) Tissue-specific patterns of gap junctions in adult rat atrial and ventricular cardiomyocytes in vivo and in vitro. Circ Res 88:933–939
Narolska NA, van Loon RB, Boontje NM, Zaremba R, Penas SE, Russell J, Spiegelenberg SR, Huybregts MAJM, Visser FC, de Jong JW, van der Velden J, Stienen GJM (2005) Myocardial contraction is 5-fold more economical in ventricular than in atrial human tissue. Cardiovasc Res 65:221–229
Vozzi C, Dupont E, Coppen SR, Yeh HI, Severs NJ (1999) Chamber-related differences in connexin expression in the human heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol 31:991–1003
Small EM, Olson EN (2011) Pervasive roles of microRNAs in cardiovascular biology. Nature 469:336–342
van Rooij E (2011) The art of microRNA research. Circ Res 108:219–234
Latronico MV, Condorelli G (2011) microRNAs in hypertrophy and heart failure. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 236:125–131
Latronico MV, Catalucci D, Condorelli G (2008) MicroRNA and cardiac pathologies. Physiol Genomics 34:239–242
Xu J, Zhao J, Evan G, Xiao C, Cheng Y, Xiao J (2012) Circulating microRNAs: novel biomarkers for cardiovascular diseases. J Mol Med. doi:10.1007/s00109-011-0840-5
Xiao J, Liang D, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Zhang H, Liu Y, Li L, Liang X, Sun Y, Chen YH (2011) MicroRNA expression signature in atrial fibrillation with mitral stenosis. Physiol Genomics 43:655–664
Biggar KK, Storey KB (2011) The emerging roles of microRNAs in the molecular responses of metabolic rate depression. J Mol Cell Biol 3:167–175
Kosik KS (2011) MicroRNAs and cellular phenotype. Cell 143:21–26
Kukreja RC, Yin C, Salloum FN (2011) MicroRNAs: new players in cardiac injury and protection. Mol Pharmacol 80:558–564
Latronico MV, Condorelli G (2009) MicroRNAs and cardiac pathology. Nat Rev Cardiol 6:419–429
Liu N, Olson EN (2010) MicroRNA regulatory networks in cardiovascular development. Dev Cell 18:510–525
Shivdasani RA (2006) MicroRNAs: regulators of gene expression and cell differentiation. Blood 108:3646–3653
Thum T, Catalucci D, Bauersachs J (2008) MicroRNAs: novel regulators in cardiac development and disease. Cardiovasc Res 79:562–570
Kriegel AJ, Liu Y, Fang Y, Ding X, Liang M (2012) The miR-29 family: genomics, cell biology, and relevance to renal and cardiovascular injury. Physiol Genomics 44:237–244
Papadopoulos GL, Alexiou P, Maragkakis M, Reczko M, Hatzigeorgiou AG (2009) DIANA-mirPath: integrating human and mouse microRNAs in pathways. Bioinformatics 25:1991–1993
Latronico MV, Catalucci D, Condorelli G (2007) Emerging role of microRNAs in cardiovascular biology. Circ Res 101:1225–1236
Schroen B, Heymans S (2012) Small but smart–microRNAs in the centre of inflammatory processes during cardiovascular diseases, the metabolic syndrome, and ageing. Cardiovasc Res 93:605–613
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30872544 and 81170158) and Jiangsu Province Health Department Program Grant (H200821).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yangyang Zhang, Xiaowei Wang and Xiaohan Xu have contributed equally to this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Wang, X., Xu, X. et al. Distinct microRNA expression signatures in human right atrial and ventricular myocardium. Mol Cell Biochem 371, 23–29 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1417-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1417-5