Abstract
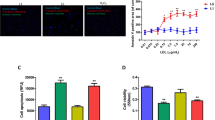
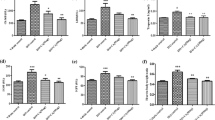
Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is a leading cause of death worldwide. Most cases of AMI result from coronary atherosclerosis (AS). The pathogenic mechanisms underlying AS lesions and AMI are incompletely understood. Calcium-sensing receptors (CaSR) belong to a family of G-protein-coupled receptors. We previously discovered that CaSR was expressed in the heart tissue of adult rats. CaSR may contribute to AMI in AS. We initially established a rat model of AS by injection of vitamin D3 and feeding with a high-fat diet. Isoproterenol (ISO) was used to induce AMI. The MB isoenzyme of creatine kinase (CK-MB), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), cardiac troponin T (cTnT), tetrazolium chloride staining, and cardiac function parameters were selected as indicators of myocardial damage or necrosis. Cardiac apoptosis was analyzed by transferase dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL) assay. Expression of CaSR, Bcl-2, Bax, caspase-3, p-ERK1/2, p-JNK, and p-p38 were determined by Western blot analysis. Compared with the control group, levels of cTnT, CK-MB, and LDH; number of TUNEL-positive cells; and expression of CaSR, Bax, caspase-3, p-ERK1/2, p-JNK and p-p38, were significantly increased, whereas cardiac function and expression of Bcl-2 were decreased markedly in isoproterenol (ISO)-treated group (C/ISO) and AS groups. These changes were significant in the AS/ISO group than in the C/ISO group or AS group. The upregulation of CaSR during AS formation renders hypersensitivity to AMI. Activation of the pro-apoptotic mitochondria pathway and JNK-p38 MAPK pathway triggered by increased expression of CaSR may be one of molecular mechanisms underlying AMI in AS.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
White HD, Chew DP (2008) Acute myocardial infarction. Lancet 372:570–584
Burke AP, Virmani R (2007) Pathophysiology of acute myocardial infarction. Med Clin N Am 91:553–572
Greaves DR, Häkkinen T, Lucas AD, Liddiard K, Jones E, Quinn CM, Senaratne J, Green FR, Tyson K, Boyle J, Shanahan C, Weissberg PL, Gordon S, Ylä-Hertualla S (2011) Linked chromosome 16q13 chemokines, macrophage-derived chemokine, fractalkine, and thymus and activation-regulated chemokine, are expressed in human atherosclerotic lesions. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 21:923–929
Singh H, Jain S, Singh R, Gupta MS, Kishore K (2002) Life and past one year stressful events in coronary artery disease. Indian J Med Sci 56:172–176
Brown EM, MacLeod RJ (2001) Extracellular calcium sensing and extracellular calcium signaling. Physiol Rev 81:239–297
Wang R, Xu C, Zhao W, Zhang J, Cao K, Yang B, Wu L (2003) Calcium and polyamine regulated calcium-sensing receptors in cardiac tissues. Eur J Biochem 270:2680–2688
Tfelt-Hansen J, Hansen JL, Smajilovic S, Terwilliger EF, Haunso S, Sheikh SP (2006) Calcium receptor is functionally expressed in rat neonatal ventricular cardiomyocytes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 290:1165–1171
Jiang CM, Han LP, Li HZ, Qu YB, Zhang ZR, Wang R, Xu CQ, Li WM (2008) Calcium-sensing receptors induce apoptosis in cultured neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes during simulated ischemia/reperfusion. Cell Biol Int 32:792–800
Wang LN, Wang C, Lin Y, Xi YH, Zhang WH, Zhao YJ, Li HZ, Tian Y, Lv YJ, Yang BF, Xu CQ (2008) Involvement of calcium-sensing receptor in cardiac hypertrophy-induced by angiotensin II through calcineurin pathway in cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 369:584–589
Sun YH, Liu MN, Li H, Shi S, Zhao YJ, Wang R, Xu CQ (2006) Calcium-sensing receptor induces rat neonatal ventricular cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 350:942–948
Zhang WH, Fu SB, Lu FH, Wu B, Gong DM, Pan ZW, Lv YJ, Zhao YJ, Li QF, Wang R, Yang BF, Xu CQ (2006) Involvement of calcium-sensing receptor in ischemia/reperfusion-induced apoptosis in rat cardiomyocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 347:872–881
Huang ZY, Yang PY, Almofti MR, Yu YL, Rui YC, Yang PY (2004) Comparative analysis of the proteome of left ventricular heart of arteriosclerosis in rat. Life Sci 75:3103–3131
Ithayarasi AP, Devi CS (1997) Effect of α-tocopherol on lipid peroxidation in isoproterenol induced myocardial infarction in rats. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 41:369–376
Niu J, Azfer A, Kolattukudy PE (2006) Monocyte-specific Bcl-2 expression attenuates inflammation and heart failure in monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1)-induced cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Res 71:139–148
Rajadurai M, Prince PSM (2005) Comparative effects of Aegle marmelos extract and alpha-tocopherol on serum lipids, lipid peroxides and cardiac enzyme levels in rats with isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction. Singap Med J Feb 46(2):78–81
Bai M, Trivedi S, Brown EM (1998) Dimerization of the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor (CaR) on the cell surface of CaR transfected HEK293 cells. J Biol Chem 273:23605–23610
Zhang Z, Sun S, Quinn SJ, Brown EM, Bai M (2001) The extracellular calcium-sensing receptor dimerizes through multiple types of intermolecular interactions. J Biol Chem 276:5316–5322
Bai M, Quinn S, Trivedi S, Kifor O, Pearce SH, Pollak MR, Krapcho K, Hebert SC, Brown EM (1996) Expression and characterization of inactivating and activating mutations in the human Ca-sensing receptor. J Biol Chem 271:19537–19545
Roussanne MC, Gogusev J, Hory B, Duchambon P, Souberbielle JC, Nabarra B, Pierrat D, Sarfati E, Drüeke T, Bourdeau A (1998) Persistence of Ca2+-sensing receptor expression in functionally active, long-term human parathyroid cell cultures. J Bone Miner Res 13:354–362
Mithal A, Kifor O, Kifor I, Vassilev P, Butters R, Krapcho K, Simin R, Fuller F, Hebert SC, Brown EM (1995) The reduced responsiveness of cultured bovine parathyroid cells to extracellular Ca2+ is associated with marked reduction in the expression of extracellular Ca2+-sensing receptor messenger ribonucleic acid and protein. Endocrinology 136:3087–3092
Sun YH, Zhang L, Xu CQ, Li H, Shi S, Zhao YJ, Han LP, Zhang HY (2006) Expression of calcium-sensing receptor in the rat cardiac tissue at different age and its relation with anoxia-reperfusion injury. Chin J Pathophysiol 22:1506–1509
Abbate A, Biondi-Zoccai GG, Baldi A (2002) Pathophysiologic role of myocardial apoptosis in post-infarction left ventricular remodeling. J Cell Physiology 193:145–153
del Monte F, Lebeche D, Guerrero JL, Tsuji T, Doye AA, Gwathmey JK, Hajjar RJ (2004) Abrogation of ventricular arrhythmias in a model of ischemia and reperfusion by targeting myocardial calcium cycling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:5622–5627
Matsumoto Y, Yamamoto S, Suzuki Y, Tsuboi T, Terakawa S, Ohashi N, Umemura K (2004) Na+/H+ exchanger inhibitor, SM-20220, is protective against excitotoxicity in cultured cortical neurons. Stroke 35:185–190
Halestrap AP, Clarke SJ, Javadov SA (2004) Mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening during myocardial reperfusion-a target for cardioprotection. Cardiovasc Res 61:372–385
Jin HW, Ichikawa H, Nomura K, Mukae K, Terayama R, Yamaai T, Sugimoto T (2005) Activation of the caspase cascade underlies the rat trigeminal primary neuronal apoptosis induced by neonatal capsaicin administration. Arch Histol Cytol 68:301–310
Tanaka M, Mokhtari GK, Terry RD, Balsam LB, Lee KH, Kofidis T, Tsao PS, Robbins RC (2004) Overexpression of human copper/zinc superoxide dismutase (SOD1) suppresses ischemia-reperfusion injury and subsequent development of graft coronary artery disease in murine cardiac grafts. Circulation 110:II200–II206
Alnemri ES, Livingston DJ, Nicholson DW, Salvesen G, Thornberry NA, Wong WW, Yuan J (1996) Human ice/ced-3 protease nomenclature. Cell 87:171–182
Guo J, Li HZ, Zhang WH, Wang LC, Wang LN, Zhang L, Li GW, Li HX, Yang BF, Wu L, Wang R, Xu CQ (2010) Increased expression of calcium-sensing receptors induced by ox-LDL amplifies apoptosis of cardiomyocytes during simulated ischaemia/reperfusion. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 37:e128–e135
András S, Gergo S, György C, György H (2008) High- and low-calcium-dependent mechanisms of mitochondrial calcium signaling. Cell Calcium 44:51–63
Missiaen L, de Smedt H, Droogmans GR (1992) Casteels, Ca2+ release induced by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate is a steady-state phenomenon controlled by luminal Ca2+ in permeabilized cells. Nature 357:599–602
White C, Li C, Yang J, Petrenko NB, Madesh M, Thompson CB, Foskett JK (2005) The endoplasmic reticulum gateway to apoptosis by Bcl-X (L) modulation of the InsP3R. Nat Cell Biol 7:1021–1028
Trenker M, Malli R, Fertschai I, Levak-Frank S, Graier WF (2007) Uncoupling proteins 2 and 3 are fundamental for mitochondrial Ca2+ uniport. Nat Cell Biol 9:445–452
Kyriakis JM, Avruch J (2001) Mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation. Physiol Rev 81:807–869
Hobson SA, Wright J, Lee F, McNeil SE, Bilderback T, Rodland KD (2003) Activation of the MAP kinase cascade by exogenous calcium sensing receptor. Mol Cell Endocrinol 200:189–198
Elzi DJ, Bjornsen AJ, MacKenzie T, Wyman TH, Silliman CC (2001) Ionomycin causes activation of p38 and p42/44 mitogen-activated protein kinases in human neutrophils. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 281:C350–C360
Yue TL, Wang C, Gu JL, Ma XL, Kumar S, Lee JC, Feuerstein GZ, Thomas H, Maleeff B, Ohlstein EH (2000) Inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase enhances ischemia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in cultured cardiac myocytes and exaggerates reperfusion injury in isolated perfused heart. Circ Res 86:692–699
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, grant number 2007CB512000); National Natural Science Foundation of China (number 30871012,81000059 and 30700288); Youth Fund of Jiamusi University (number Sq2011-025).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jin Guo and Hong-zhu Li—co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, J., Li, Hz., Wang, Lc. et al. Increased expression of calcium-sensing receptors in atherosclerosis confers hypersensitivity to acute myocardial infarction in rats. Mol Cell Biochem 366, 345–354 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1312-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1312-0