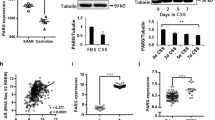
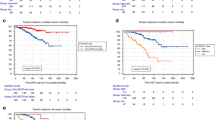
Abstract
Prostate cancer is a multifactorial, multistep progressive disorder that is undruggable to date because of stumbling blocks in the standardization of therapy. It is triggered by a broad range of proteins, signaling networks and DNA damage response modulators. It is becoming increasingly apparent that DNA repair mediators have split personalities, as they are instrumental in suppressing and promoting carcinogenesis. In this article, we discuss on post-transcriptional processing of regulators of DNA damage response, and how DNA repair proteins trigger shuttling of androgen receptor. Substantial fraction of information has been added into the existing literature of ATM biology; however, the particular area of post-transcriptional processing errors and gene therapy for reprogramming of ATM has been left unaddressed in prostate cancer. It is therefore noteworthy that the facet of targeting strategy, antisense morpholino oligonucleotides chemistry, and systematic delivery of AOs has promising outlook in splice-targeted antisense-mediated therapy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal C, Tyagi A, Agarwal R (2006) Gallic acid causes inactivating phosphorylation of cdc25A/cdc25C-cdc2 via ATM-Chk2 activation, leading to cell cycle arrest, and induces apoptosis in human prostate carcinoma DU145 cells. Mol Cancer Ther 5(12):3294–3302
Bhatti S, Kozlov S, Farooqi AA, Naqi A, Lavin M, Khanna KK (2011) ATM protein kinase: the linchpin of cellular defenses to stress. Cell Mol Life Sci 68(18):2977–3006
Browning RE, Li H, Shinohara ET, Cai Q, Chen H, Courtney R, Cao C, Zheng W, Lu B (2006) ATM polymorphism IVS62 + 60G>A is not associated with disease aggressiveness in prostate cancer. Urology 67(6):1320–1323
Chen HM, Chang FR, Hsieh YC, Cheng YJ, Hsieh KC, Tsai LM, Lin AS, Wu YC, Yuan SS (2011) A novel synthetic protoapigenone analogue, WYC02–9, induces DNA damage and apoptosis in DU145 prostate cancer cells through generation of reactive oxygen species. Free Radic Biol Med 50(9):1151–1162
Collis SJ, Swartz MJ, Nelson WG, DeWeese TL (2003) Enhanced radiation and chemotherapy-mediated cell killing of human cancer cells by small inhibitory RNA silencing of DNA repair factors. Cancer Res 63(7):1550–1554
Cuffe S, Dowling CM, Claffey J, Pampillón C, Hogan M, Fitzpatrick JM, Carty MP, Tacke M, Watson RW (2011) Effects of titanocene dichloride derivatives on prostate cancer cells, specifically DNA damage-induced apoptosis. Prostate 71(2):111–124
Dhir A, Buratti E, van Santen MA, Lührmann R, Baralle FE (2010) The intronic splicing code: multiple factors involved in ATM pseudoexon definition. EMBO J 29(4):749–760
Dombernowsky SL, Weischer M, Allin KH, Bojesen SE, Tybjaerg-Hansen A, Nordestgaard BG (2008) Risk of cancer by ATM missense mutations in the general population. J Clin Oncol 26(18):3057–3062
Du L, Kayali R, Bertoni C, Fike F, Hu H, Iversen PL, Gatti RA (2011) Arginine-rich cell-penetrating peptide dramatically enhances AMO-mediated ATM aberrant splicing correction and enables delivery to brain and cerebellum. Hum Mol Genet 20(16):3151–3160
Du L, Pollard JM, Gatti RA (2007) Correction of prototypic ATM splicing mutations and aberrant ATM function with antisense morpholino oligonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(14):6007–6012
Fan C, Quan R, Feng X, Gillis A, He L, Matsumoto ED, Salama S, Cutz JC, Kapoor A, Tang D (2006) ATM activation is accompanied with earlier stages of prostate tumorigenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1763(10):1090–1097
Fan Z, Chakravarty P, Alfieri A, Pandita TK, Vikram B, Guha C (2000) Adenovirus-mediated antisense ATM gene transfer sensitizes prostate cancer cells to radiation. Cancer Gene Ther 7(10):1307–1314
Hall J, Marcel V, Bolin C, Fernet M, Tartier L, Vaslin L, Hainaut P (2009) The associations of sequence variants in DNA-repair and cell-cycle genes with cancer risk: genotype-phenotype correlations. Biochem Soc Trans 37(Pt 3):527–533
Hsiao CJ, Ho YF, Hsu JT, Chang WL, Chen YC, Shen YC, Lyu PC, Guh JH (2008) Mana-Hox displays anticancer activity against prostate cancer cells through tubulin depolymerization and DNA damage stress. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 378(6):599–608
Ide H, Yu J, Lu Y, China T, Kumamoto T, Koseki T, Muto S, Horie S (2011) Testosterone augments polyphenol-induced DNA damage response in prostate cancer cell line, LNCaP. Cancer Sci 102(2):468–471
Jäämaa S, Af Hällström TM, Sankila A, Rantanen V, Koistinen H, Stenman UH, Zhang Z, Yang Z, De Marzo AM, Taari K, Ruutu M, Andersson LC, Laiho M (2010) DNA damage recognition via activated ATM and p53 pathway in nonproliferating human prostate tissue. Cancer Res 70(21):8630–8641
Katzenberger RJ, Marengo MS, Wassarman DA (2006) ATM and ATR pathways signal alternative splicing of Drosophila TAF1 pre-mRNA in response to DNA damage. Mol Cell Biol 26(24):9256–9267
Katzenberger RJ, Marengo MS, Wassarman DA (2009) Control of alternative splicing by signal-dependent degradation of splicing-regulatory proteins. J Biol Chem 284(16):10737–10746
Konsoula Z, Cao H, Velena A, Jung M (2011) Adamantanyl-histone deacetylase inhibitor H6CAHA exhibits favorable pharmacokinetics and augments prostate cancer radiation sensitivity. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 79(5):1541–1548
Marengo MS, Wassarman DA (2008) A DNA damage signal activates and derepresses exon inclusion in Drosophila TAF1 alternative splicing. RNA 14(8):1681–1695
Meyer A, Wilhelm B, Dörk T, Bremer M, Baumann R, Karstens JH, Machtens S (2007) ATM missense variant P1054R predisposes to prostate cancer. Radiother Oncol 83(3):283–288
Mukhopadhyay UK, Senderowicz AM, Ferbeyre G (2005) RNA silencing of checkpoint regulators sensitizes p53-defective prostate cancer cells to chemotherapy while sparing normal cells. Cancer Res 65(7):2872–2881
Pastor T, Pagani F (2011) Interaction of hnRNPA1/A2 and DAZAP1 with an Alu-derived intronic splicing enhancer regulates ATM aberrant splicing. PLoS One 6(8):e23349
Pastor T, Talotti G, Lewandowska MA, Pagani F (2009) An Alu-derived intronic splicing enhancer facilitates intronic processing and modulates aberrant splicing in ATM. Nucleic Acids Res 37(21):7258–7267
Rashid A, Liu C, Sanli T, Tsiani E, Singh G, Bristow RG, Dayes I, Lukka H, Wright J, Tsakiridis T (2011) Resveratrol enhances prostate cancer cell response to ionizing radiation. Modulation of the AMPK, Akt and mTOR pathways. Radiat Oncol 6:144
Sanli T, Rashid A, Liu C, Harding S, Bristow RG, Cutz JC, Singh G, Wright J, Tsakiridis T (2010) Ionizing radiation activates AMP-activated kinase (AMPK): a target for radiosensitization of human cancer cells. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 78(1):221–229
Sanz DJ, Acedo A, Infante M, Durán M, Pérez-Cabornero L, Esteban-Cardeñosa E, Lastra E, Pagani F, Miner C, Velasco EA (2010) A high proportion of DNA variants of BRCA1 and BRCA2 is associated with aberrant splicing in breast/ovarian cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 16(6):1957–1967
Schütz SV, Cronauer MV, Rinnab L (2010) Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta promotes nuclear export of the androgen receptor through a CRM1-dependent mechanism in prostate cancer cell lines. J Cell Biochem 109(6):1192–1200
Shaheen FS, Znojek P, Fisher A, Webster M, Plummer R, Gaughan L, Smith GC, Leung HY, Curtin NJ, Robson CN (2011) Targeting the DNA double strand break repair machinery in prostate cancer. PLoS One 6(5):e20311
Shank LC, Kelley JB, Gioeli D, Yang CS, Spencer A, Allison LA, Paschal BM (2008) Activation of the DNA-dependent protein kinase stimulates nuclear export of the androgen receptor in vitro. J Biol Chem 283(16):10568–10580
Truman JP, Gueven N, Lavin M, Leibel S, Kolesnick R, Fuks Z, Haimovitz-Friedman A (2005) Down-regulation of ATM protein sensitizes human prostate cancer cells to radiation-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 280(24):23262–23272
Truman JP, Rotenberg SA, Kang JH, Lerman G, Fuks Z, Kolesnick R, Marquez VE, Haimovitz-Friedman A (2009) PKCalpha activation downregulates ATM and radio-sensitizes androgen-sensitive human prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Biol Ther 8(1):54–63
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farooqi, A.A., Fayyaz, S. & Rashid, S. Upon the tightrope in prostate cancer: two acrobats on the same tightrope to cross the finishline. Mol Cell Biochem 364, 53–57 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-1204-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-1204-8