Abstract
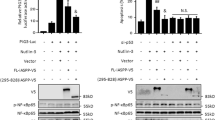
In this study, in order to investigate the p53-independent function of p14ARF, we established p14ARF-inducible clones in the p53-deficient HCT cell line using the doxycycline-inducible expression system. A strong cell growth inhibition and G1/S arrest were observed after doxycycline induction in p53-/-HCT cells, and the cells also exhibited an obvious decrease of DNA synthesis. We further examined if the MEK/ERK pathway is involved in the G1 arrest induced by p14ARF in p53-/-HCT cells. The results indicate that ERK1/2 and p21 were activated upon p14ARF induction. Totally, the functional roles of ERK and p21 for ARF in p53-independent tumor suppression were demonstrated.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- MEK:
-
MARK/ERK kinase 1
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MDM2:
-
Murine double minute 2
- PI:
-
Propidium iodide
References
Dominguez-Brauer C, Brauer PM, Chen YJ, Pimkina J, Raychaudhuri P (2010) Tumor suppression by ARF: gatekeeper and caretaker. Cell Cycle 9:86–89
Sherr CJ, Weber JD (2000) The ARF/p53 pathway. Curr Opin Genet Dev 10:94–99
Sharpless NE, Ramsey MR, Balasubramanian P, Castrillon DH, DePinho RA (2004) The differential impact of p16INK4a or p19ARF deficiency on cell growth and tumorigenesis. Oncogene 23:379–385
Kamijo T, Bodner S, Van de Kamp E, Randle DH, Sherr CJ (1999) Tumor spectrum in ARF-deficient mice. Cancer Res 59:2217–2222
Kamijo T, Zindy F, Roussel MF, Quelle DE, Downing JR, Ashmun RA et al (1997) Tumor suppression at the mouse INK4a locus mediated by the alternative reading frame product p19ARF. Cell 91:649–659
Matheu A, Maraver A, Serrano M (2008) The Arf/p53 pathway in cancer and aging. Cancer Res 68:6031–6034
Rozenblum E, Schutte M, Goggins M, Hahn SA, Panzer S, Zahurak M et al (1997) Tumor-suppressive pathways in pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer Res 57:1731–1734
Moore LS, Venkatachalam H, Vogel JC, Watt JC, Wu CL, Steinman H et al (2003) Cooperativity of p19ARF, MDM2, and p53 in murine tumorigenesis. Oncogene 22:7831–7837
Weber JD, Jeffers JR, Rehg JE, Randle DH, Lozano G, Roussel MF et al (2000) p53-independent functions of the p19ARF tumor suppressor. Genes Dev 14:2358–2365
Kelly-Spratt KS, Gurley KE, Yasui Y, Kemp CJ (2004) P19Arf suppresses growth, progression, and metastasis of Hras-driven carcinomas through p53-dependent and -independent pathways. PLoS Biol 2:1138–1149
Yarbrough WG, Bessho M, Zanation A, Bisi JE, Xiong Y (2002) Human tumor suppressor ARF impedes S-phase progression independent of p53. Cancer Res 62:1171–1177
Datta A, Nag A, Raychaudhuri P (2002) Differential regulation of E2F1, DP1, and the E2F1/DP1 complex by ARF. Mol Cell Biol 22:8398–8408
Datta A, Nag A, Pan W, Hay N, Gartel AL, Colamonici O et al (2004) Myc-ARF (alternate reading frame) interaction inhibits the functions of Myc. J Biol Chem 279:36698–36707
Itahana K, Bhat KP, Jin A, Itahana Y, Hawke D, Kobayashi R et al (2003) Tumor suppressor ARF degrades B23, a nucleolar protein involved in ribosome biogenesis and cell proliferation. Mol Cell 12:1151–1164
Korgaonkar C, Hagen J, Tompkins V, Frazier AA, Allamargot C, Quelle FW et al (2005) Nucleophosmin (B23) targets ARF to nucleoli and inhibits its function. Mol Cell Biol 25:1258–1271
Mebratu Y, Tesfaigzi Y (2009) How ERK1/2 activation controls cell proliferation and cell death: Is subcellular localization the answer? Cell Cycle 8:1168–1175
Meloche S, Pouysségur J (2007) The ERK1/2 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway as a master regulator of the G1- to S-phase transition. Oncogene 26:3227–3239
Woods D, Parry D, Cherwinski H, Bosch E, Lees E, McMahon M (1997) Raf-induced proliferation or cell cycle arrest is determined by the level of Raf activity with arrest mediated by p21Cip1. Mol Cell Biol 17:5598–5611
Eymin B, Claverie P, Salon C, Brambilla C, Brambilla E, Gazzeri S (2006) P14ARF triggers G2 arrest through ERK-mediated Cdc25C phosphorylation, ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Cell Cycle 5:759–765
Wu D, Ingram A, Lahti JH, Mazza B, Grenet J, Kapoor A et al (2002) Apoptotic release of histones from nucleosomes. J Biol Chem 277:12001–12008
Li Y, Wu D, Chen B, Ingram AJ, He L, Liu L et al (2004) ATM activity contributes to the tumor suppressing functions of p14ARF. Oncogene 23:7355–7365
Tang D, Wu D, Hirao A, Lahti JM, Liu L, Mazza B et al (2002) ERK activation mediates cell cycle arrest and apoptosis after DNA damage independently of p53. J Biol Chem 277:12710–12717
Kovi RC, Paliwal S, Pande S, Grossman SR (2010) An ARF/CtBP2 complex regulates BH3-only gene expression and p53-independent apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 17:513–521
Li Y, He L, Bruce A, Parihar K, Ingram A, Liu L, Tang D (2006) P14ARF inhibits the growth of p53 deficient cells in a cell-specific manner. Biochim Biophys Acta 1763:787–796
Paliwal S, Pande S, Kovi RC, Sharpless NE, Bardeesy N, Grossman SR (2006) Targeting of C-terminal binding protein (CtBP) by ARF results in p53-independent apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 26:2360–2372
Chen D, Kon N, Li M, Zhang W, Qin J, Gu W (2005) ARF-BP1/Mule is a critical mediator of the ARF tumor suppressor. Cell 121:1071–1083
Bartek J, Lukas J (2007) DNA damage checkpoints: from initiation to recovery or adaptation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 19:238–245
Liebermann DA, Hoffman B, Vesely D (2007) P53 induced growth arrest versus apoptosis and its modulation by survival cytokines. Cell Cycle 6:166–170
Han JA, Kim JI, Ongusaha PP, Hwang DH, Ballou LR, Mahale A et al (2002) P53-mediated induction of Cox-2 counteracts p53- or genotoxic stress-induced apoptosis. Eur Mol Biol Organ J 21:5635–5644
Wu D, Chen B, Parihar K, He L, Fan C, Zhang J et al (2006) ERK activity facilitates activation of the S-phase DNA damage checkpoint by modulating ATR function. Oncogene 25:1153–1164
Malmlöf M, Roudier E, Högberg J, Stenius U (2007) MEK-ERK-mediated phosphorylation of MDM2 at Ser-166 in hepatocytes. MDM2 is activated in response to inhibited Akt signaling. J Biol Chem 282:2288–2296
Mogila V, Xia F, Li WX (2006) An intrinsic cell cycle checkpoint pathway mediated by MEK and ERK in drosophila. Dev Cell 11:575–582
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Damu Tang of the McMaster University for providing the p53-/-HCT 116 cells and the dominant-negative MEK1 (MEK1K97M) plasmid. This study was funded by grants 30670813 of the Natural Science Foundation of the People’s Republic of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, H., Yao, W., Fang, M. et al. ARF triggers cell G1 arrest by a P53 independent ERK pathway. Mol Cell Biochem 357, 415–422 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-0912-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-0912-4