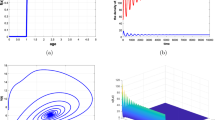
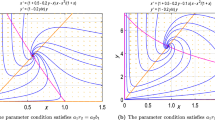
Abstract
In this paper, a stochastic delay three-species food chain model with imprecise biological parameters has been developed. For this model, the sharp sufficient conditions for the existence of a unique ergodic stationary distribution and the extinction are established. We also discuss the effects of imprecise parameters on the persistence, extinction and existence of the stationary distribution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbalat I (1959) Systems d’equations differentielles d’osci d’oscillations nonlineaires. Rev Roum Math Pures Appl 42:67–70
Beddington JR, May RM (1977) Harvesting natural populations in a randomly fluctuating environment. Science 197:463–465
Braumann CA (2007) Itô versus Stratonovich calculus in random population growth. Math Biosci 206:81–107
Evans SN, Ralph P, Schreiber SJ, Sen A (2013) Stochastic population growth in spatially heterogeneous environments. J Math Biol 66:423–476
Freedman HI, Ruan SG (1995) Uniform persistence in functional differential equations. J Diff Equa 115:173–192
He X, Liu M (2017) Dynamics of a stochastic delay competition model with imprecise parameters. J Nonlinear Sci Appl 10:4776–4788
Hung LC (2009) Stochastic delay population systems. Appl Anal 88:1303–1320
Ikeda N, Watanabe S (1977) A comparison theorem for solutions of stochastic dfferential equations and its applications. Osaka J Math 14:619–633
Jiang D, Shi N (2005) A note on non-autonomous logistic equation with random perturbation. J Math Anal Appl 303:164–172
Li MY, Shuai Z (2010) Global-stability problem for coupled systems of differential equations on networks. J Diff Equ 248:1–20
Liu M, Du C, Deng M (2018) Persistence and extinction of a modified Leslie-Gower Holling-type II stochastic predator-prey model withimpulsive toxicant input in polluted environments. Nonlinear Anal Hybrid Syst 27:177–190
Liu M, Bai C (2016) Analysis of a stochastic tri-trophic food-chain model with harvesting. J Math Biol 73:597–625
Liu M, Fan M (2017) Stability in distributionof a three-species stochastic cascade predator-prey system with time delays. IMA J Appl Math 82:396–423
Liu M, He X, Yu J (2018) Dynamics of a stochastic regime-switching predator-prey model with harvesting and distributed delays. Nonlinear Anal Hybrid Syst 28:87–104
Liu M, Wang K, Wu Q (2011) Survival analysis of stochastic competitive models in a polluted environment and stochastic competitive exclusion principle. Bull Math Biol 73:1969–2012
Liu M, Zhu Y (2018) Stability of a budworm growth model with random perturbations. Appl Math Lett 79:13–19
Lotka AJ (1925) Elements of physical biology. Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia
Mao X (2008) Stochastic differential equations and applications, 2nd edn. Woodhead Publishing, Sawston
Mao X (2011) Stationary distribution of stochastic population systems. Syst Control Lett 60:398–405
May RM (1975) Stability and complexity in model ecosystems. Princeton Univ Press, Princeton
Paine RT (1988) Food webs: road maps of interactions or grist for theoretical development?. Ecology 69:1648–1654
Pal D, Mahapatra GS (2016) Dynamic behavior of a predator-prey system of combined harvesting with interval-valued rate parameters. Nonlinear Dyn 83:2113–2123
Pal D, Mahaptra GS, Samanta GP (2013) Optimal harvesting of prey-predator system with interval biological parameters: a bioeconomic model. Math Biosci 241:181–187
Pal D, Mahaptra GS, Samanta GP (2016) Stability and bionomic analysis of fuzzy prey-predator harvesting model in presence of toxicity: a dynamic approach. Bull Math Biol 78:1493–1519
Pal N, Samanta S, Biswas S, Alquran M, Al-Khaled K, Chattopadhyay J (2015) Stability and bifurcation analysis of a three-species food chain model with delay. Int J Bifurcation Chaos 25:1550123
Peixoto M, Barros L, Bassanezi RC (2008) Predator-prey fuzzy model. Ecol Model 214:39–44
Pimm SL (1982) Food webs. Chapman and Hall, New York
Prato D, Zabczyk J (1996) Ergodicity for infinite dimensional systems. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Ruan S (2006) Delay differential equations in single species dynamics. In: Arino O et al (eds) Delay differential equations and applications. Springer, New York, pp 477–517
Rudnicki R, Pichór K (2007) Influence of stochastic perturbation on prey-predator systems. Math Biosci 206:108–119
Sharma S, Samanta GP (2014) Optimal harvesting of a two species competition model with imprecise biological parameters. Nonlinear Dyn 77:1101–1119
Shu H, Hu X, Wang L, Watmough J (2015) Delay induced stability switch, multitype bistability and chaos in an intraguild predation model. J Math Biol 71:1269–1298
Song ZG, Zhen B, Xu J (2014) Species coexistence and chaotic behavior induced by multiple delays in a food chain system. Ecol Complex 19:9–17
Volterra V (1926) Variazioni e fluttuazioni del numero d’individui in specie animali conviventi. Mem Acad Lincei Roma 2:31–113
Zhao Y, Yuan S, Zhang Q (2015) Numerical solution of a fuzzy stochastic single-species age-structure model in a polluted environment. Appl Math Comput 260:385–396
Acknowledgments
The author thanks the National Natural Science Foundation of P.R. China (Nos. 11401302).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J. Analysis of a Three-Species Stochastic Delay Predator-Prey System with Imprecise Parameters. Methodol Comput Appl Probab 21, 43–67 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11009-018-9640-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11009-018-9640-5