Abstract
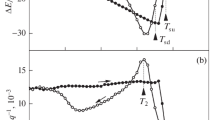
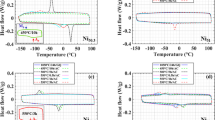
We show that, after the introduction of hydrogen into rapidly quenched Ti50Ni25Cu25 alloys in the crystalline, amorphous, or amorphous-crystalline state, their shear modulus and electric resistance change appreciably. Subsequent thermocycling of these alloys is evidence of the suppression of direct and inverse martensitic transformations B2 ↔ B19 (B19′) due to hydrogen.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
I. A. Stepanov, Yu. M. Flomenblit, and V. A. Zaimovskii, “Effect of hydrogen on the temperature of thermoelastic martensitic transformation in titanium nickelide,” Fiz. Met. Metalloved., 55, No.3, 612–614 (1983).
M. Kh. Shorshorov, I. A. Stepanov, Yu. M. Flomenblit, and V. V. Travkin, “Phase and structural hydrogen-induced transformations in alloys based on titanium nickelide,” Fiz. Met. Metalloved., 60, No.2, 326–333 (1985).
M. Kh. Shorshorov, Yu. M. Flomenblit, S. B. Maslenkov, and N. B. Budigina, “On the causes of the inducing action of hydrogen on thermoelastic martensitic transformations in alloys based on titanium nickelide,” Fiz. Met. Metalloved., 64, No.3, 498–503 (1987).
S. B. Maslenkov, N. B. Budigina, M. Kh. Shorshorov, and Yu. M. Flomenblit, “Effect of hydrogen on the character and succession of thermoelastic martensitic transformations in alloys based on titanium nickelide,” Metalloved. Termoobrab., No. 10, 6–10 (1988).
S. B. Maslenkov, N. B. Budigina, M. Kh. Shorshorov, and Yu. M. Flomenblit, “Effects of shape memory and phase and structural hydrogen-induced transformations in alloys of the Ti-Ni system,” Fiz. Met. Metalloved., 66, No.2, 307–312 (1988).
L. V. Spivak, N. E. Skryabina, and V. N. Khachin, “Deformation effects and hydrogen brittleness of alloys based on titanium nickelide,” Fiz. Met. Metalloved., 79, No.4, 138–147 (1995).
K. Iwasaki and R. R. Hasiguti, “Effect of preannealings on the temperature spectra of internal friction and shear modulus of Ti-51 Ni,” Trans. Jpn. Inst. Metals, 28, No.5, 363–367 (1987).
S. K. Wu and C. M. Wayman, “Interstitial hydrogen induced extra reflections in Ti50Ni45Au5 martensite,” Scripta Met., 21, No.1, 75–77 (1987).
S. K. Wu and C. M. Wayman, “Interstitial ordering of hydrogen and oxygen in TiNi alloys,” Acta Met., 36, No.4, 1005–1013 (1988).
O. Mercier and K. N. Melton, “The substitution of Cu for Ni in TiNi shape memory alloys,” Met. Trans., A10, No.3, 387–393 (1979).
K. H. Brickhell, K. N. Melton, and O. Mercier, “The structure of NiTiCu shape memory alloys,” Met. Trans., A10, No.6, 693–699 (1979).
V. N. Tokarev, A. S. Savinov, and V. N Khachin, “Effect of shape memory in martensitic transformations in TiNi-NiCu alloys,” Fiz. Met. Metalloved., 56, No.2, 340–344 (1983).
N. N. Zakharov, S. L. Kuz’min, and V. A. Likhachev, “Great plastic strains in TiNiCu composition, ” Metallofizika, 3, No.5, 53–63 (1981).
N. M. Matveeva, Yu. K. Kovneristyi, Yu. A. Bykovskii, et al., “A study of the temperature ranges and the character of martensitic transformation in TiNi-TiCu alloys obtained by ultraspeed cooling of the melt,” Metally, No. 4, 171–175 (1989).
N. E. Skryabina, L. V. Spivak, V. P. Vylezhnev, and M. A. Khominskii, “Effect of hydrogen on the properties of amorphous Fe78Nb3.5Cu1 B4 Si13.5 alloy,” Pis’ma Zh. Tekh. Fiz., 22, No.23, 36–39 (1996).
N. E. Skryabina, L. V. Spivak, M. A. Khominskii, et al., “Effect of hydrogen on the properties of amorphous iron-and cobalt-base alloys,” Fiz. Met. Metalloved., 83, No.3, 139–144 (1997).
N. Ye. Skryabina and L. V. Spivak, “Effect of hydrogen on the properties of amorphous alloys type Finemet (PEN-X effect),” Hydrogen Energy, 24, No.9, 795–799 (1999).
A. V. Shelyakov, N. M. Matveeva, and S. G. Larin, “Rapidly quenched TiNi-based shape memory alloys, ” in: F. Trochu and V. Brailovski (editors), Shape Memory Alloys: Fundamentals, Modeling and Industrial Applications, Canadian Institute of Mining, Metallurgy and Petroleum (1999), pp. 295–303.
H. Rosner, P. Schlossmacher, A. V. Shelyakov, and A. M. Glezer, “The influence of coherent TiCu plate-like precipitates on the thermoelastic martensitic transformation in melt-spun Ti50Ni25Cu25 shape memory alloys,” Acta Mater., 49, 1541–1548 (2001).
P. L. Potapov, A. V. Shelyakov, and D. Schryvers, “On the crystal structure of TiNi-Cu martensite, ” Scripta Mater., 44, No.1, 1–7 (2001).
B. A. Kolachev, Hydrogen Brittleness of Metals [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1985).
T. Y. Zhang, W. Y. Chu, and C. M. Hsiao, “Mechanism of hydrogen induced softening,” Scripta Met., 20, No.2, 225–230 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
__________
Translated from Fizyko-Khimichna Mekhanika Materialiv, Vol. 40, No. 6, pp. 28–34, November–December, 2004.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skryabina, N.E., Spivak, L.V., Fruchart, D. et al. Effect of Hydrogen on the Properties of Rapidly Quenched Tini-Ticu Alloys with Shape Memory. Mater Sci 40, 741–748 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11003-005-0110-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11003-005-0110-1