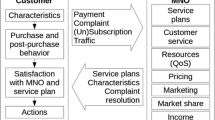
Abstract
The current use of 3G technologies has created significant demands for capacity, such as cell TV, and this needs to be balanced with the capital constraints of many firms. Providers face price pressures on margins and the need to update cell networks to 4G in the post-GFC era where capital is scarce. Understanding consumer behavior in this area by use of simulations may be a time- and cost-efficient method, but how accurate is it? This study demonstrates that the use of a simple, agent-based model can lead to accurate initial prediction of parameters of satisfaction with a cell phone provider, and provides a basis of understanding factors of cell phone subscriber choice in the context of the introduction of new technology.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, H. J. (2010). Evaluating customer aid functions of online stores with agent-based models of customer behavior and evolution strategy. Journal Information Sciences, 180(9), 1555–1570.
Aydin, S., & Özer, G. (2005). The analysis of antecedents of customer loyalty in the Turkish mobile telecommunication market. European Journal of Marketing, 39(7/8), 910–925.
Bansal, H. S., & Taylor, S. F. (1999). The service provider switching model (SPSM). Journal of Service Research, 2(2), 200–218.
Ben-Akiva, M., McFadden, D., Abe, M., Böckenholt, U., Bolduc, D., Gopinath, D., Morikawa, T., Ramaswamy, V., Rao, V., Revelt, D., & Steinberg, D. (1997). Modeling methods for discrete choice analysis. Marketing Letters, 8(3), 273–286.
Bohlmann, J. D., Calantone, R. J., & Meng, Z. (2010). The effects of market network heterogeneity on innovation diffusion: an agent-based modeling approach. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 27(5), 741–760.
Chuang, Y.-F. (2011). Pull-and-suck effects in Taiwan mobile phone subscribers switching intentions. Telecommunications Policy, 35(2), 128–140.
Colgate, M., & Hedge, R. (2001). An investigation into the switching process in retail banking services. The International Journal of Bank Marketing, 19(5), 201–212.
Colgate, M., & Lang, B. (2001). Switching barriers in consumer markets: an investigation of the financial services industry. Journal of Consumer Marketing, 18(4), 332–347.
Deng, Z., Lu, Y., Wei, K., & Zhang, J. (2010). Understanding customer satisfaction and loyalty: an empirical study of mobile instant messages in China. International Journal of Information Management, 30(4), 289–300.
Dierkes, T., Bichler, M., & Krishnan, R. (2011). Estimating the effect of word of mouth on churn and cross-buying in the mobile phone market with Markov logic networks. Decision Support Systems, 51(3), 361–371.
Dodds, W. (1973). An application of the Bass model in long-term new product forecasting. Journal of Market Research, 10(3), 308–311.
Feldman, J. M., & Lynch, J. G. (1988). Self-generated validity and other effects of measurement on belief, attitude, intention, and behavior. Journal of Applied Psychology, 73(3), 421–435.
Garcia, R. (2005). Uses of agent-based modeling in innovation/new product development research. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 22(5), 380–398.
Garcia, R., Rummel, P., & Hauser, J. (2007). Validating agent-based marketing models through conjoint analysis. Journal of Business Research, 60(8), 848–857.
Goldenberg, J., Mazursky, D., & Solomon, S. (1999). Toward identifying the inventive templates of new products: a channeled ideation approach. Journal of Marketing Research, 36(2), 200–210.
Goldenberg, J., Libai, B., & Muller, E. (2002). Riding the saddle: how cross-market communications can create a major slump in sales. Journal of Marketing, 66(2), 1–16.
Goldenberg, J., Han, S., Lehmann, D. R., & Hong, J. W. (2009). The role of hubs in the adoption process. Journal of Marketing, 73(2), 1–13.
Goode, M., Davies, F., Moutinho, L., & Jamal, A. (2005). Determining customer satisfaction from mobile phones: a neural network approach. Journal of Marketing Management, 21(7/8), 755–778.
Grahn, G. L. (1969). NBD model of repeat-purchase loyalty: an empirical investigation. Journal of Marketing Research, 6(1), 72–78.
Iyengar, R., Jedidi, K., & Kohli, R. (2008). A conjoint approach to multipart pricing. Journal of Marketing Management, 45(2), 195–210.
Keaveney, S. M. (1995). Customer switching behavior in service industries: an exploratory study. Journal of Marketing, 59(2), 71–82.
Labeaga-Azcona, J. M., Lado-Cousté, N., & Martos-Partal, M. (2010). The double jeopardy loyalty effect using discrete choice models. International Journal of Market Research, 52(5), 633–652.
Lee, S.-G., Yu, M., Yang, C., & Kim, C. (2011). A model for analyzing churn effect in saturated markets. Industrial Management & Data Systems, 111(7), 1024–1038.
Lees, G., Garland, R., & Wright, M. (2007). Switching banks: old bank gone but not forgotten. Journal of Financial Services Marketing, 12(2), 146–156.
Levesque, T. J., & McDougall, G. H. (1993). Managing customer satisfaction: the nature of service problems and customer exit, voice and loyalty. Asia Pacific Journal of Quality Management, 2(2), 40–58.
Ma, S., & Büschken, J. (2011). Counting your customers from an ‘always a share’ perspective. Marketing Letters, 22(3), 243–257.
Mah, A. (2004). Product innovation case study: ‘3’—a Hutchinson brand. The Marketing Review, 4(2), 157–188.
McIntyre, S. H., & Miller, C. M. (1992). Social utility and fashion behavior. Marketing Letters, 3(4), 371–382.
Neslin, S. A., & Schneider Stone, L. G. (1996). Consumer inventory sensitivity and the postpromotion dip. Marketing Letters, 7(1), 77–94.
Poynter, K. (2006). Vodafone: ‘stop the clock’. Marketing, 22–22.
Rand, W., & Rust, R. (2011). Agent-based modeling in marketing: guidelines for rigor. International Journal of Market Research, 28(3), 181–193.
Ross, W. T., Moore, M. C., & Staelin, R. (2000). Recurrent marketing decisions: decision complexity, decision focus, and firm performance. Marketing Letters, 11(4), 283–297.
Turnbull, P., Leek, S., & Ying, G. (2000). Customer confusion: the mobile phone market. Journal of Marketing Management, 16(1–3), 143–163.
Wahab, S., Al-Momani, K., & Nor-Azila, M. (2010). The relationship between e-service quality and ease of use on customer relationship management (CRM) performance: an empirical investigation in Jordan mobile phone services. Journal of Internet Banking and Commerce, 15(1), 1–15.
Wedel, M., Kamakura, W., Arora, N., Bemmaor, A., Jeongwen, C., Elrod, T., Johnson, R., Lenk, P., Neslin, S., & Poulsen, C. (1999). Discrete and continuous representations of unobserved heterogeneity in choice modeling. Marketing Letters, 10(3), 219–232.
Winer, R. S. (1986). A reference price model of brand choice for frequently purchased products. Journal of Consumer Research, 13(2), 250–256.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
D’Alessandro, S., Johnson, L., Gray, D. et al. Consumer satisfaction versus churn in the case of upgrades of 3G to 4G cell networks. Mark Lett 26, 489–500 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11002-014-9284-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11002-014-9284-3