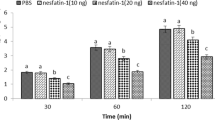
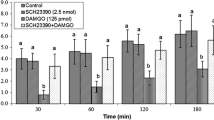
Abstract
RFamide-related Peptide-3(RFRP-3) plays a key role in appetite regulation. The current study aimed to determine the effect of RFRP-3(Neuropeptide VF) on feeding behavior and its interaction with the melanocortin and corticotropin systems on food intake in the neonatal broiler-type chickens. In experiments 1 and 2, chickens received intracerebroventricular (ICV) injection of control solution besides RFRP-3 (4, 8, and 16 nmol) and RF9 (NPFF receptors antagonist; 4, 8 and 16 nmol) respectively to investigate the effective doses of RFRP-3 and RF9. Experiments 3–8 have been designed to investigate the mediatory role of CRF1/CRF2 and MC3R/MC4R on food intake induced by RFRP-3 in chickens. Finally, in experiments 8–11, the synergistic effect between the MC3R and MC4R with RFRP-3 have been investigated via ICV co-injection of sub-effective doses of RFRP-3 + γ1-MSH and PG-931. Then, cumulative food intake was recorded at 30, 60, and 120 min after injection. According to the results, co-injection of astressin-B and RFRP-3, significantly attenuated hypophagic effect of RFRP-3; while astressin2-B reversed this effect of RFRP-3 (p < 0.01). Besides, co-administration of SHU9119 and MCL0020 significantly attenuated the hypophagia induced by RFRP-3 in chickens (p < 0.01). However, co-administration of RFRP-3 and PG-931 synergistically decreased food intake in neonatal chicken (p < 0.01). These results suggested hypophagic effect of RFRP-3 is possibly mediated via corticotropin CRF2 and melanocortin MC4R in neonatal broiler chickens.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi F, Zendehdel M, Babapour V, Panahi N (2019) CRF1/CRF2 and MC3/MC4 receptors affect glutamate-induced food intake in neonatal meat-type chicken. Br J Poult Sci 21(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1590/1806-9061-2018-0821
Anand BK, Brobeck JR (1951) Hypothalamic control of food intake in rats and cats. Yale J Biol Med 24:123–146
Ancel C, Bentsen AH, Sebert ME, Tena-Sempere M, Mikkelsen JD, Simonneaux V (2012) Stimulatory effect of RFRP-3 on the gonadotrophic axis in the male syrian hamster: the exception proves the rule. Endocrinology 153(3):1352–1363. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2011-1622
Blevins JE, Stanley BG, Reidelberger RD (2002) DMSO as a vehicle for central injections: tests with feeding elicited by norepinephrine injected into the paraventricular nucleus. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71:277–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0091-3057(01)00659-1
Bonini JA, Jones KA, Adham N, Forray C, Artymyshyn R, Durkin MM, Smith KE, Tamm JA, Boteju LW, Lakhlani PP, Raddatz R, Yao WJ, Ogozalek KL, Boyle N, Kouranova EV, Quan Y, Vaysse PJ, Wetzel JM, Branchek TA, Gerald C, Borowsky B (2000) Identification and characterization of two G protein-coupled receptors for neuropeptide FF. J Biol Chem 275(50):39324–39331. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M004385200
Cline MA, Bowden CN, Calchary WA, Layne JE (2008) Short-term anorexigenic effects of central neuropeptide VF are associated with hypothalamic changes in chicks. J Neuroendocrinol 20(8):971–977. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2826.2008.01749.x
Davis JL, Masuoka DT, Gerbrandt LK, Cherkin A (1979) Autoradiographic distribution of l-proline in chicks after intracerebral injection. Physiol Behav 22:693–695. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9384(79)90233-6
Finelli C, Rossano R, Padula MC, La Sala N, Sommella L, Martelli G (2014) Nesfatin – 1: role as possible new anti obesity treatment. J Obes Weight Loss Ther 4(3):1–4
Fu LY, van den Pol AN (2010) Kisspeptin directly excit anorexigenic proopiomelanocortin neurons but inhibits orexigenic neuropeptide Y cells by an indirect synaptic mechanism. J Neurosci 30(30):10205–10219. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2098-10.2010
Furuse M, Matsumoto M, Saito N, Sugahara K, Hasegava S (1997) The central corticotropin-releasing factor and glucagon-like peptide-1 in food intake of the neonatal chick. EurJ Pharmacol 339:211–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-2999(97)01391-5
Furuse M, Ando R, Bungo T, Ao R, ShimoJO M, Masuda Y (1999) Intracerebroventricular injection of orexins does not stimulate food intake in neonatal chicks. Br Poult Sci 40:698–700. https://doi.org/10.1080/00071669987115
Hassanpour S, Zendehdel M, Babapour V, Charkhkar S (2015) Endocannabinoid and nitric oxide interaction mediates food intake in neonatal chicken. Br Poult Sci 56(4):443–451. https://doi.org/10.1080/00071668.2015.1059407
Heidarzadeh H, Zendehdel M, Babapour V, Gilanpour H (2017) The effect of Nesfatin-1 on food intake in neonatal chicks: role of CRF1 /CRF2 and H1/H3 receptors. Vet Res Commun 42(1):39–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-017-9706-9
Jonaidi H, Noori Z (2012) Neuropeptide Y-induced feeding is dependent on GABAA receptors in neonatal chicks. J Comp Physiol A 198:827–832. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-012-0753-y
Kaewwongse M, Takayanagi Y, Onaka T (2010) Effects of RFamide-related peptide (RFRP)-1 and RFRP-3 on oxytocin release and anxiety-related behaviour in rats. J Neuroendocrinol 23:20–27. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2826.2010.02077.x
Liu Q, Guan XM, Martin WJ, McDonald TP, Clements MK, Jiang Q, Zeng Z, Jacobson M, Williams DL Jr, Yu H, Bomford D, Figueroa D, Mallee J, Wang R, Evans J, Gould R, Austin CP (2001) Identification and characterization of novel mammalian neuropeptide FF-like peptides that attenuate morphine-induced antinociception. J Biol Chem 276(40):36961–36969. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M105308200
Lu XY, Barsh GS, Akil H, Watson SJ (2003) Interaction between α_melanocyte-stimulating hormone and corticotropin-releasing hormone in the regulation of feeding and hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal responses. J Neurosci 23(21):7863–7872
Murakami M, Matsuzaki T, Iwasa T, Yasui T, Irahara M, Osugi T, Tsutsui K (2008) Hypophysiotropic role of RFamide-related peptide-3 in the inhibition of LH secretion in female rats. J Endocrinol 199(1):105–112. https://doi.org/10.1677/JOE-08-0197
Newmyer BA, Cline MA (2009) Neuropeptide SF is associated with reduced food intake in chicks. Behav Brain Res 205(1):311–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2009.06.013
Olanrewaju HA, Purswell JL, Collier SD, Branton SL (2006) Effect of light intensity adjusted for species-specific spectral sensitivity on blood physiological variables of male broiler chickens. Poult Sci. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pey487
Parker KE, Johns HW, Floros TG, Will MJ (2014) Central amygdala opioid transmission is necessary for increased high-fat intake following 24-h food deprivation, but not following intra-accumbens opioid administration. Behav Brain Res 260:131–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2013.11.014
Poling MC, Quennell JH, Anderson GM, Kauffman AS (2013) Kisspeptin neurons do not directly signal to RFRP-3 neurons but RFRP-3 neurons may directly modulate a subset of hypothalamic kisspeptin cells in mice. J Neuroendocrinol 25:876–886. https://doi.org/10.1111/jne.12084
Qi W, Ding D, Salvi RJ (2008) Cytotoxic effects of dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO) on cochlear organotypic cultures. Hear Res 236:52–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heares.2007.12.002
Qi Y, Oldfield BJ, Clarke IJ (2009) Projections of RFamide-related Peptide-3 neurones in the ovine hypothalamus, with special reference to regions regulating energy balance and reproduction. J Neuroendocrinol 21:690–697. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2826.2009.01886.x
Quelven I, Roussin A, Zajac JM (2005) Comparison of pharmacological activities of Neuropeptide FF1 and Neuropeptide FF2 receptor agonists. Eur J Pharmacol 508(1–3):107–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.12.002
Richards MP (2003) Genetic regulation of feed intake and energy balance in poultry. Poult Sci 82(6):907–916. https://doi.org/10.1093/ps/82.6.907
Rizwan MZ, Porteous R, Herbison AE, Anderson GM (2009) Cells expressing RFamide-related peptide-1⁄3, the mammalian gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone orthologs, are not hypophysiotropic neuroendocrine neurons in the rat. Endocrinology 150:1413–1420. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2008-1287
Saito ES, Kaiya H, Tachibana T, Denbow DM, Kangawa K, Furuse M (2005) Inhibitory effect of ghrelin on food intake is mediated by the corticotropin-releasing factor system in neonatal chicks. Regul Pept 125:201–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regpep.2004.09.003
Schneeberger M, Gomis R, Claret M (2014) Hypothalamic and brainstem neuronal circuits controlling homeostatic energy balance. J Endocrinol 220:T25–T46. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-13-0398
Sharkey KA, Darmani NA, Parker LA (2014) Regulation of nausea and vomiting by cannabinoids and the endocannabinoid system. Eur J Pharmacol 722:134–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.09.068
Silberman Y, Winder DG (2013) Corticotropin releasing factor and catecholamines enhance glutamatergic neurotransmission in the lateral subdivision of the central amygdala. Neuropharmacology 150:4911–4919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.02.014
Stengel A, Goebel M, Wang L, Rivier J, Kobelt P, Monnikes H, Lambrecht NWG, Tache Y (2009) Central nesfatin-1 reduces dark-phase food intake and gastric emptying in rats: differential role of corticotropin-releasing factor2 receptor. Endocrinology. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2009-0578
Strader AD, Schiöth HB, Buntin JD (2003) The role of the melanocortin system and the melanocortin-4 receptor in ring dove (Streptopelia risoria) feeding behavior. Brain Res 960:112–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-8993(02)03799-X
Tachibana T, Sato M, Takahashi H, Ukena K, Tsutsui K, Furuse M (2005) Gonadotrophin-inhibiting hormone stimulates feeding behavior in chicks. Brain Res 1050:94–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2005.05.035
Tachibana T, Sato M, Oikawa D, Takahashi H, Boswell T, Furuse M (2007) The anorexic effect of a-melanocyte-stimulating hormone is mediated by corticotrophin releasing factor in chicks. Comp Biochem Physiol A 147:173–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2006.12.044
Tachibana T, Masuda N, Tsutsui K, Ukena K, Ueda H (2008) The orexigenic effect of GnIH is mediated by central opioid receptors in chicks. Comp Biochem Physiol A 150:21–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2008.02.018
Tsutsui K, Bentley GE, Kriegsfeld LJ, Osugi T, Seong JY, Vaudry H (2010) Discovery and evolutionary history of gonadotrophin-inhibitory hormone and kisspeptin: new key neuropeptides controlling reproduction. J Neuroendocrinol 22(7):716–727. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2826.2010.02018.x
Van Tienhoven A, Juhasz LP (1962) The chicken telencephalon, diencephalon and mesencephalon in sterotaxic coordinates. J Comp Neurol 118:185–197. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.901180205
Yamada H, Bruijnzeel AW (2011) Stimulation of alpha2-adrenergic receptors in the central nucleus of the amygdala attenuates stress-induced reinstatement of nicotine seeking in rats. Neuropharmacology 60:303–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.09.013
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the central laboratory (Dr. Rastegar Lab.) of the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, the University of Tehran for cooperation. This research is conducted as a part of the Ph.D. thesis of the first author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have no potential conflicts of interest.
Informed Consent
There is no informed consent in this study.
Research Involving Human and/or Animals Rights
This manuscript does not contain any studies with human subjects performed by any of the authors. All experiments were executed according to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and were approved by the institutional animal ethics committee.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moosadoost, Y., Zendehdel, M. & Khodadadi, M. The Effect of RFamide-Related Peptide-3 (RFRP-3 or NPVF) on Food Intake in Neonatal Chickens: The Role of MC3/MC4 and CRF1/CRF2 Receptors. Int J Pept Res Ther 27, 253–262 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-020-10081-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-020-10081-z