Abstract
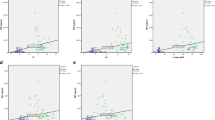
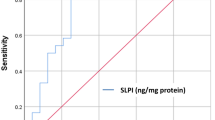
Antimicrobial peptide LL37, present in the saliva, has an important role in oral health maintenance, and many studies have shown that this peptide can modulate pro-inflammatory cytokine expression. The study of salivary cytokine expression helps shed further light on the salivary immune system and can predict or monitor periodontal disease. The aim of this study was to determine LL37 levels, comparing them with the levels of salivary TNF-α, IL6, and IL-1β of patients with different treatment needs. A total of 120 patients, classified by periodontal treatment needs according to the PSR/CPITN index, participated in this study. Group 1 included periodontally healthy patients (index 0), whereas groups 2 and 3 consisted of patients with periodontal disease—group 2 with at least one sextant classified as index 1 or 2 and group 3 with at least one sextant presenting index 3 or 4. Salivary samples were collected from all patients and TNF-α, IL6, IL-1β, and LL37 antimicrobial peptide were determined by ELISA. Patients without periodontal treatment needs showed higher salivary levels of LL37 when compared to those with any periodontal involvement. Low salivary LL37 levels in patients with periodontal disease were associated with the increase of TNF-α and IL6 expressions. No relationship between salivary IL-1β levels and different PSR/CPTIN indices, nor any correlation of IL-1β with salivary LL37 concentration, was observed. Results of the present study support the hypothesis that low levels of LL37 can modulate the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL6.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agerberth B, Gunne H, Odeberg J, Kogner P, Boman HG, Gudmundsson GH (1995) FALL-39, a putative human peptide antibiotic, is cysteine-free and expressed in bone marrow and testis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92(1):195–199. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.92.1.195
Ainamo J, Barmes D, Beagrie G, Cutress T, Martin J, Sardo-Infirri J (1982) Development of the World Health Organization (WHO) community periodontal index of treatment needs (CPITN). Int Dent J 32(3):281–291
American Dental Association and American Academy of Periodontics (1992) Periodontal screening and recording training program kit, Chicago
Bals R (2000) Epithelial antimicrobial peptides in host defense against infection. Respir Res 1(3):141–150. https://doi.org/10.1186/rr25
Beklen A, Hukkanen M, Richardson R, Konttinen YT (2008) Immunohistochemical localization of toll-like receptors 1–10 in periodontitis. Oral Microbiol Immunol 23(5):425–431. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-302X.2008.00448.x
Bowdish DM, Davidson DJ, Hancock RE (2005) A re-evaluation of the role of host defence peptides in mammalian immunity. Curr Protein Pept Sci 6(1):35–51. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389203053027494
Braff MH, Hawkins MA, Di Nardo A, Lopez-Garcia B, Howell MD, Wong C, Lin K, Streib JE, Dorschner R, Leung DY, Gallo RL (2005) Structure-function relationships among human cathelicidin peptides: dissociation of antimicrobial properties from host immunostimulatory activities. J Immunol 174(7):4271–4278. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.174.7.4271
Castañeda-Delgado JE, Frausto-Lujan I, González-Curiel I, Montoya-Rosales A, Serrano CJ, Torres-Juarez F, Enciso-Moreno JA, Rivas-Santiago B (2017) Differences in cytokine production during aging and its relationship with antimicrobial peptides production. Immunol Invest 46(1):48–58. https://doi.org/10.1080/08820139.2016.1212873
Dale BA, Kimball JR, Krisanaprakornkit S, Roberts F, Robinovitch M, O’Neal R, Valore EV, Ganz T, Anderson GM, Weinberg A (2001) Localized antimicrobial peptide expression in human gingiva. J Periodontal Res 36(5):285–294. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0765.2001.360503.x
Davidson DJ, Currie AJ, Reid GS, Bowdish DM, MacDonald KL, Ma RC, Hancock RE, Speert DP (2004) The cationic antimicrobial peptide LL-37 modulates dendritic cell differentiation and dendritic cell-induced T cell polarization. J Immunol 172(2):1146–1156. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.172.2.1146
De Smet K, Contreras R (2005) Human antimicrobial peptides: defensins, cathelicidins and histatins. Biotechnol Lett 27:1337–1347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-005-0936-5
Dürr UH, Sudheendra US, Ramamoorthy A (2006) LL-37, the only human member of the cathelicidin family of antimicrobial peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta 1758(9):1408–1425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.03.030
Ebersole JL, Nagarajan R, Akers D, Miller CS (2015) Targeted salivary biomarkers for discrimination of periodontal health and disease(s). Front Cell Infect Microbiol 19:62. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2015.00062
Eckmann L (2005) Defence molecules in intestinal innate immunity against bacterial infections. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 21(2):147–151. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mog.0000153311.97832.8c
Feldmann M, Maini RN (2001) Anti-TNF alpha therapy of rheumatoid arthritis: what have we learned? Annu Rev Immunol 19(1):163–96. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.19.1.163
Frohm M, Agerberth B, Ahangari G, Stâhle-Bäckdahl M, Lidén S, Wigzell H, Gudmundsson GH (1997) The expression of the gene coding for the antibacterial peptide LL-37 is induced in human keratinocytes during inflammatory disorders. J Biol Chem 272(24):15258–15263. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.24.15258
Goodson JM (2003) Gingival crevice fluid flow. Periodontology 31(1):43–54. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0757.2003.03104.x
Gorr SU (2012) Antimicrobial peptides in periodontal innate defense. Front Oral Biol 15:84–98. https://doi.org/10.1159/000329673
Hase K, Murakami M, Iimura M, Cole SP, Horibe Y, Ohtake T, Obonyo M, Gallo RL, Eckmann L, Kagnoff MF (2003) Expression of LL-37 by human gastric epithelial cells as a potential host defense mechanism against Helicobacter pylori. Gastroenterology 125(6):1613–1625. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2003.08.028
Kc S, Wang XZ, Gallagher JE (2019) Diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of host-derived salivary biomarkers in periodontal disease amongst adults: systematic review. J Clin Periodontol.https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.13218
Khosravi R, Ka K, Huang T, Khalili S, Nguyen BH, Nicolau B, Khosravi Tran SD (2013) Tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-6: potential interorgan inflammatory mediators contributing to destructive periodontal disease in obesity or metabolic syndrome. Mediat Inflamm 2013:728987. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/728987
Kim JJ, Kim CJ, Camargo PM (2013) Salivary biomarkers in the diagnosis of periodontal diseases. J Calif Dent Assoc 41(2):119–124
Kjeldsen M, Holmstrup P, Lindemann RA, Bendtzen K (1995) Bacterial-stimulated cytokine production of peripheral mononuclear cells from patients of various periodontitis categories. J Periodontol 66:139–144. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.1995.66.2.139
Koski H, Janin A, Humphreys-Beher MG, Sorsa T, Malmström M, Konttinen YT (2001) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and receptors for it in labial salivary glands in Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin Exp Rheumatol 19(2):131–137
Lee JM, Garon E, Wong DT (2009) Salivary diagnostics. Orthod Craniofac Res 12(3):206–211. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1601-6343.2009.01454.x
Lehrer RI (2004) Primate defensins. Nat Rev Microbiol 2(9):727–738. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro976
Machado PR, Araújo MIAS, Carvalho L, Carvalho EM (2004) Immune response mechanisms to infections. An bras Dermatol 79(6):647–664. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0365-05962004000600002
Méndez-Samperio P (2013) Recent advances in the field of antimicrobial peptides in inflammatory diseases. Adv Biomed Res 29:50. https://doi.org/10.4103/2277-9175.114192
Nazar Majeed Z, Philip K, Alabsi AM, Pushparajan S, Swaminathan D (2016) Identification of gingival crevicular fluid sampling, analytical methods, and oral biomarkers for the diagnosis and monitoring of periodontal diseases: a systematic review. Dis Markers 2016:1804727. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/1804727
Özcan E, Saygun NI, Serdar MA, Kurt N (2015) Evaluation of the salivary levels of visfatin, chemerin, and progranulin in periodontal inflammation. Clin Oral Investig 19(4):921–928. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-014-1308-0
Pinheiro da Silva F, Machado MC (2017) The dual role of cathelicidins in systemic inflammation. Immunol Lett 182:57–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2017.01.004
Podzimek S, Vondrackova L, Duskova J, Janatova T, Broukal Z (2016) Salivary markers for periodontal and general diseases. Dis Markers 2016:9179632. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/9179632
Rams TE, Loesche WJ (2017) Relationship between periodontal screening and recording index scores and need for periodontal access surgery. J Periodontol 88(10):1042–1050. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2017.170070
Schicht M, Stengl C, Sel S, Heinemann F, Götz W, Petschelt A, Pelka M, Scholz M, Rausch F, Paulsen F, Bräuer L (2015) The distribution of human surfactant proteins within the oral cavity and their role during infectious diseases of the gingiva. Ann Anat 199:92–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aanat.2014.05.040
Sternlicht MD, Werb Z (2001) How matrix metalloproteinases regulate cell behavior. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 17:463–516. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.cellbio.17.1.463
Syndergaard B, Al-Sabbagh M, Kryscio RJ, Xi J, Ding X, Ebersole JL, Miller CS (2014) Salivary biomarkers associated with gingivitis and response to therapy. J Periodontol 85(8):e295–e303. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2014.130696
Tada H, Shimizu T, Matsushita K, Takada H (2017) Porphyromonas gingivalis-induced IL-33 down-regulates hCAP-18/LL-37 production in human gingival epithelial cells. Biomed Res 38(3):167–173. https://doi.org/10.2220/biomedres.38.167
Thomas MV, Branscum A, Miller CS, Ebersole J, Al-Sabbagh M, Schuster JL (2009) Within-subject variability in repeated measures of salivary analytes in healthy adults. J Periodontol 80(7):1146–1153. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2009.080654
Woo JS, Jeong JY, Hwang YJ, Chae SW, Hwang SJ, Lee HM (2003) Expression of cathelicidin in human salivary glands. Arch Otolaryngol 129(2):211–214. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.129.2.211
Yucel-Lindberg T, Båge T (2013) Inflammatory mediators in the pathogenesis of periodontitis. Expert Rev Mol Med 15:e7. https://doi.org/10.1017/erm.2013.8
Acknowledgements
This study was developed at the Department of Basic and Oral Biology of the School of Dentistry of Ribeirão Preto, University of São Paulo. Dr. Ribeiro was granted a graduate fellowship from the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This study involves human participants, so it was performed in accordance with the ethical standards established in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. It was approved by the Research Ethics Committee (Process No. 0003.0.138.000–10), and all patients signed an informed consent form before their participation.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ribeiro, A.E.R.A., Lourenço, A.G., Motta, A.C.F. et al. Salivary Expression of Antimicrobial Peptide LL37 and Its Correlation with Pro-inflammatory Cytokines in Patients with Different Periodontal Treatment Needs. Int J Pept Res Ther 26, 2547–2553 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-020-10047-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-020-10047-1