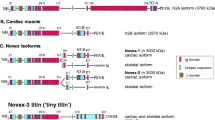
Abstract
Rat cardiac titin undergoes developmental changes in isoform expression during the period from late embryonic through the first 20–25 days of life. At least five size classes of titin isoforms have been identified using SDS agarose gel electrophoresis. The longest normal isoform is expressed in the embryonic stages, and it is progressively replaced with increasingly smaller versions. The isoform switching is consistent with changes in resting tension from lower values in one-day neonates to higher levels in adult myocytes. Considerable micro-heterogeneity in alternative splicing patterns also was found, particularly in the N2BA PEVK region of human, rat, and dog ventricle. A rat mutation has been identified in which the embryonic-neonatal titin isoform transitions are markedly delayed. These mutant animals may prove useful for examining the role of titin in stretch-activated signal transduction and in the Frank–Starling relationship.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bang ML, Centner T, Fornoff F, Geach AJ, Gotthardt M, McNabb M, Witt CC, Labeit D, Gregorio CC, Granzier H, Labeit S (2001) The complete gene sequence of titin, expression of an unusual approximately 700-kDa titin isoform, and its interaction with obscurin identify a novel Z-line to I-band linking system. Circ Res 89:1065–1072
Campbell KS, Moss RL 2003. SLControl: PC-based data acquisition and analysis for muscle mechanics. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 285:H2857–H2864
Cazorla O, Freiburg A, Helmes M, Centner T, McNabb M, Wu Y, Trombitas K, Labeit S, Granzier H (2000) Differential expression of cardiac titin isoforms and modulation of cellular stiffness. Circ Res 86:59–67
Cooper TA, Ordahl CP (1985) A single cardiac troponin T gene generates embryonic and adult isoforms via developmentally regulated alternate splicing. J Biol Chem 260:11140–11148
Epstein ND, Davis JS (2003) Sensing stretch is fundamental. Cell 112:147–150
Freiburg A, Trombitas K, Hell W, Cazorla O, Fougerousse F, Centner T, Kolmerer B, Witt C, Beckmann JS, Gregorio CC, Granzier H, Labeit S (2000) Series of exon-skipping events in the elastic spring region of titin as the structural basis for myofibrillar elastic diversity. Circ Res 86:1114–1121
Fukuda N, Granzier H (2004) Role of the giant elastic protein titin in the Frank–Starling mechanism of the heart. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 2:135–139
Fukuda N, Wu Y, Farman G, Irving TC, Granzier H (2003) Titin isoform variance and length dependence of activation in skinned bovine cardiac muscle. J Physiol 553:147–154
Furst DO, Osborn M, Nave R, Weber K (1988) The organization of the titin filaments in the half-sarcomere revealed by monoclonal antibodies in immunoelectron microscopy: a map of ten nonrepetitive epitopes starting at the Z-line extends close to the M-line. J Cell Biol 106:1563–1572
Granzier H, Labeit S (2002) Cardiac titin: an adjustable multi-functional spring. J Physiol (Lond) 541:335–342
Granzier HL, Labeit S (2004) The giant protein titin: a major player in myocardial mechanics, signaling, and disease. Circ Res 94:284–295
Greaser M (2001) Identification of new repeating motifs in titin. Proteins 43:145–149
Greaser ML, Berri M, Warren CM, Mozdziak PE (2002) Species variations in cDNA sequence and exon splicing patterns in the extensible I-band region of cardiac titin: relation to passive tension. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 23:471–480
Gregorio CC, Granzier H, Sorimachi H, Labeit S (1999) Muscle assembly: a titanic achievement? Curr Opin Cell Biol 11:18–25
Gutierrez-Cruz G, Van Heerden AH, Wang K (2001) Modular motif, structural folds and affinity profiles of the PEVK segment of human fetal skeletal muscle titin. J Biol Chem 276:7442–7449
Helmes M, Trombitas K, Centner T, Kellermayer M, Labeit S, Linke WA, Granzier H (1999) Mechanically driven contour-length adjustment in rat cardiac titin’s unique N2B sequence: titin is an adjustable spring. Circ Res 84:1339–1352
Jin JP, Lin JJ (1989) Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones encoding embryonic and adult isoforms of rat cardiac troponin T. J Biol Chem 264:14471–14477
Labeit S, Kolmerer B (1995) Titins: giant proteins in charge of muscle ultrastructure and elasticity. Science 270:293–296
Lahmers S, Wu Y, Call DR, Labeit S, Granzier H (2004) Developmental control of titin isoform expression and passive stiffness in fetal and neonatal myocardium. Circ Res 94:505–513
Linke WA, Rudy DE, Centner T, Gautel M, Witt C, Labeit S, Gregorio CC (1999) I-band titin in cardiac muscle is a three-element molecular spring and is critical for maintaining thin filament structure. J Cell Biol 146:631–644
Lompre AM, Mercadier JJ, Wisnewsky C, Bouveret P, Pantaloni C, D’Albis A, Schwartz K (1981) Species- and age-dependent changes in the relative amounts of cardiac myosin isozymes in mammals. Dev Biol 84: 286–290
Lompre AM, Nadel-Ginard B, Mahdavi V (1984) Expression of the cardiac ventricular alpha- and beta-myosin heavy chain gene is developmentally and hormonally regulated. J Biol Chem 259: 6437–6446
Makarenko I, Opitz CA, Leake MC, Neagoe C, Kulke M, Gwathmey JK, del Monte F, Hajjar RJ, Linke WA (2004) Passive stiffness changes caused by upregulation of compliant titin isoforms in human dilated cardiomyopathy hearts. Circ Res 95:708–716
Maruyama K (1976) Connectin, an elastic protein from myofibrils. J Biochem (Tokyo) 80:405–407
Maruyama K (1997) Connectin/titin, a giant elastic protein of muscle. FASEB J 11:341–345
Miller MK, Granzier H, Ehler E, Gregorio CC (2004) The sensitive giant: the role of titin-based stretch sensing complexes in the heart. Trends Cell Biol 14:119–126
Nagueh SF, Shah G, Wu Y, Torre-Amione G, King NM, Lahmers S, Witt CC, Becker K, Labeit S, Granzier HL (2004) Altered titin expression, myocardial stiffness, and left ventricular function in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Circulation 110:155–162
Opitz CA, Leake MC, Makarenko I, Benes V, Linke WA (2004) Developmentally regulated switching of titin size alters myofibrillar stiffness in the perinatal heart. Circ Res 94:967–975
Reiser PJ, Westfall MV, Schiaffino S, Solaro JR (1994) Tension production and thin-filament protein isoforms in developing rat myocardium. Am J Physiol 267: H1589–H1596
Strang KT, Sweitzer NK, Greaser ML, Moss RL (1994) Beta-adrenergic receptor stimulation increases unloaded shortening velocity of skinned single ventricular myocytes from rats. Circ Res 74: 542–549
Saggin L, Ausoni S, Gorza L, Sartore S, Schiaffino S (1988) Troponin T switching in the developing rat heart. J Biol Chem 263:18488–18492
Schmucker D, Clemens JC, Shu H, Worby CA, Xiao J, Muda M, Dixon JE, Zipursky SL (2000) Drosophila Dscam is an axon guidance receptor exhibiting extraordinary molecular diversity. Cell 101:671–684
Tskhovrebova L, Trinick J (2003) Titin: properties and family relationships. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:679–689
Trombitas K, Freiburg A, Centner T, Labeit S, Granzier H (1999) Molecular dissection of N2B cardiac titin’s extensibility. Biophys J 77:3189–3196
Trombitas K, Redkar A, Centner T, Wu Y, Labeit S, Granzier H (2000) Extensibility of isoforms of cardiac titin: variation in contour length of molecular subsegments provides a basis for cellular passive stiffness diversity. Biophys J 79:3226–3234
Trombitas K, Wu Y, Labeit D, Labeit S, Granzier H (2001) Cardiac titin isoforms are coexpressed in the half-sarcomere and extend independently. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 281:H1793–H1799
Wang K, McClure J, Tu A (1979) Titin: major myofibrillar components of striated muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:3698–3702
Wang K, McCarter R, Wright J, Beverly J, Ramirez-Mitchell R (1991) Regulation of skeletal muscle stiffness and elasticity by titin isoforms: A test of the segmental extension model of resting tension. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:7101–7105
Warren CM, Krzesinski PR, Greaser ML (2003a) Vertical agarose gel electrophoresis and electroblotting of high molecular weight proteins. Electrophoresis 24:1695–1702
Warren CM, Jordan MC, Roos KP, Krzesinski PR, Greaser ML (2003b) Titin isoform expression in normal and hypertensive myocardium. Cardiovasc Res 59:86–94
Warren CM, Krzesinski PR, Campbell KS, Moss RL, Greaser ML (2004) Titin isoform changes in rat myocardium during development. Mech Dev 121:1301–1312
Watanabe K, Nair P, Labeit D, Kellermayer MS, Greaser M, Labeit S, Granzier H (2002) Molecular mechanics of cardiac titin’s PEVK and N2B spring elements. J Biol Chem 277:11549–11548
Wu Y, Cazorla O, Labeit D, Labeit S, Granzier H (2000) Changes in titin and collagen underlie diastolic stiffness diversity of cardiac muscle. J Mol Cell Cardiol 32:2151–2162
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the College of Agricultural and Life Sciences, University of Wisconsin-Madison and by grants from the National Institutes of Health (HL47053; HL62466; HL77196).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Greaser, M.L., Krzesinski, P.R., Warren, C.M. et al. Developmental changes in rat cardiac titin/connectin: transitions in normal animals and in mutants with a delayed pattern of isoform transition. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 26, 325–332 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10974-005-9039-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10974-005-9039-0