Abstract
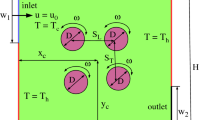
Forced convection of hybrid Ag–MgO/water nanofluid in a three-dimensional T-shaped vented cavity with multiple ports under the effects of a inner rotating cone and magnetic field is numerically studied with finite volume method. The simulation is performed for various values of parameters such as: Reynolds number (between 100 and 1000), Hartmann number (between 0 and 60), angular velocity of the rotating cone (between − 200 rad/s and 0), aspect ratio of the circular cylinders of the base of the cone (between 0.5 and 2) and nanoparticle solid volume fraction of the hybrid nanofluid (\(\phi _1\) between 0 and 0.01, \(\phi _2\) between 0 and 0.01). It was observed that the average heat transfer rate rises with higher values of Reynolds number, Hartmann number above a specified value, angular rotational speed of the cone, aspect ratio of the cone for values above 1 and solid nanoparticle volume fractions of the hybrid particles. In total, 61% of average heat transfer enhancement for left horizontal upper surface is achieved with the imposed magnetic field. The enhancement in the average Nusselt numbers is 25.6% for the rotating cone at the highest angular velocity as compared to a motionless one. The average heat transfer increases almost linearly with hybrid solid nanoparticle volume fraction, while 8.96% and 15.52% enhancements are obtained for varying the solid volume fraction of the particles with the lower and higher thermal conductivity up to 0.01.















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ha:
-
Hartmann number
- H :
-
Size of the cavity
- h :
-
Local heat transfer coefficient
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity
- n :
-
Unit normal vector
- \(\hbox {Nu}_\mathrm{s}\) :
-
Local Nusselt number
- \(\hbox {Nu}_\mathrm{m}\) :
-
Average Nusselt number
- p :
-
Pressure
- Pr:
-
Prandtl number
- R :
-
Normalized residual
- Pr:
-
Reynolds number
- T :
-
Temperature
- u, v :
-
x–y velocity components
- x, y :
-
Cartesian coordinates
- \(\alpha\) :
-
Thermal diffusivity
- \(\beta\) :
-
Expansion coefficient
- \(\phi\) :
-
Solid volume fraction
- \(\nu\) :
-
Kinematic viscosity
- \(\theta\) :
-
Non-dimensional temperature
- \(\rho\) :
-
Density of the fluid
- c:
-
Cold
- h:
-
Hot
- m:
-
Average
- nf:
-
Nanofluid
- p:
-
Solid particle
References
Saeidi S, Khodadadi J. Forced convection in a square cavity with inlet and outlet ports. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2006;49:1896–906.
Shahi M, Mahmoudi AH, Talebi F. Numerical study of mixed convective cooling in a square cavity ventilated and partially heated from the below utilizing nanofluid. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2010;37:201–13.
Sourtiji E, Hosseinizadeh S, Gorji-Bandpy M, Ganji D. Heat transfer enhancement of mixed convection in a square cavity with inlet and outlet ports due to oscillation of incoming flow. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2011;8:806–14.
Zhao M, Yang M, Lu M, Zhang Y. Evolution to chaotic mixed convection in a multiple ventilated cavity. Int J Therm Sci. 2011;50:2464–72.
Angirasa D. Mixed convection in a vented enclosure with an isothermal vertical surface. Fluid Dyn Res. 2000;26:219–33.
Selimefendigil F, Ismael MA, Chamkha AJ. Mixed convection in superposed nanofluid and porous layers in square enclosure with inner rotating cylinder. Int J Mech Sci. 2017;124–125:95–108.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF. Influence of inclination angle of magnetic field on mixed convection of nanofluid flow over a backward facing step and entropy generation. Adv Powder Technol. 2015;26:1663–75.
Abbassi H, Nassrallah SB. MHD flow and heat transfer in a backward-facing step. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2007;34:231–7.
Saeidi S, Khodadadi J. Transient flow and heat transfer leading to periodic state in a cavity with inlet and outlet ports due to incoming flow oscillation. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2007;50:530–8.
Ismael MA, Jasim HF. Role of the fluid-structure interaction in mixed convection in a vented cavity. Int J Mech Sci. 2018;135:190–202.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF. Effects of an inner stationary cylinder having an elastic rod-like extension on the mixed convection of cnt-water nanofluid in a three dimensional vented cavity. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2019;137:650–68.
Gowda BMK, Rajagopal MS, Seetharam Aswatha KN. Heat transfer in a side heated trapezoidal cavity with openings. Eng Sci Technol Int J. 2019;22:153–67.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF. Fluid-solid interaction of elastic-step type corrugation effects on the mixed convection of nanofluid in a vented cavity with magnetic field. Int J Mech Sci. 2019;152:185–97.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF. Fuzzy-based estimation of mixed convection heat transfer in a square cavity in the presence of an adiabatic inclined fin. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2012;39:1639–46.
Islam A, Sharif M, Carlson E. Mixed convection in a lid driven square cavity with an isothermally heated square blockage inside. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2012;55:5244–55.
Shi X, Khodadadi J. Laminar fluid flow and heat transfer in a lid-driven cavity due to a thin fin. J Heat Transf. 2002;124:1056–63.
Kumar A, Dhiman AK. Effect of a circular cylinder on separated forced convection at a backward-facing step. Int J Therm Sci. 2012;52:176–85.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF. Control of laminar pulsating flow and heat transfer in backward-facing step by using a square obstacle. J Heat Transf. 2014;136:081701.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF. Mixed convection of nanofluids in a three dimensional cavity with two adiabatic inner rotating cylinders. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2018;117:331–43.
Shih Y, Khodadadi J, Weng K, Ahmed A. Periodic fluid flow and heat transfer in a square cavity due to an insulated or isothermal rotating cylinder. J Heat Transf. 2009;131:1–11.
Hussain SH, Hussein AK. Mixed convection heat transfer in a differentially heated square enclosure with a conductive rotating circular cylinder at different vertical locations. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2011;38:263–74.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF. Numerical study of MHD mixed convection in a nanofluid filled lid driven square enclosure with a rotating cylinder. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2014;78:741–54.
Roslan R, Saleh H, Hashim I. Effect of rotating cylinder on heat transfer in a square enclosure filled with nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2012;55:7247–56.
Costa VAF, Raimundo AM. Steady mixed convection in a differentially heated square enclosure with an active rotating circular cylinder. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2010;53:1208–19.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF. Conjugate mixed convection of nanofluid in a cubic enclosure separated with a conductive plate and having an inner rotating cylinder. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2019;139:1000–17.
Kareem AK, Gao S. Mixed convection heat transfer of turbulent flow in a three-dimensional lid-driven cavity with a rotating cylinder. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;112:185–200.
Spizzichino A, Zemach E, Feldman Y. Oscillatory instability of a 3d natural convection flow around a tandem of cold and hot vertically aligned cylinders placed inside a cold cubic enclosure. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2019;141:327–45.
Nkurikiyimfura I, Wang Y, Pan Z. Heat transfer enhancement by magnetic nanofluids—a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2013;21:548–61.
Oztop HF, Al-Salem K, Pop I. MHD mixed convection in a lid-driven cavity with corner heater. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2011;54:494–3504.
Mehryan SAM, Ghalambaz M, Ismael MA, Chamkha AJ. Analysis of fluid-solid interaction in MHD natural convection in a square cavity equally partitioned by a vertical flexible membrane. J Magn Magn Mater. 2017;424:161–73.
Hossain MS, Alim MA. MHD free convection within trapezoidal cavity with non-uniformly heated bottom wall. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2014;69:327–36.
Pekmen B, Sezgin MT. MHD flow and heat transfer in a lid-driven porous enclosure. Comput Fluids. 2014;89:191–9.
Sheikholeslami M, Bandpy MG, Ellahi R, Zeeshan A. Simulation of MHD cuo–water nanofluid flow and convective heat transfer considering lorentz forces. J Magn Magn Mater. 2014;369:69–80.
Guedda M, Ouahsine A. Similarity solutions of MHD flows in a saturated porous medium. Eur J Mech B Fluids. 2012;33:87–94.
Khan M, Fetecau C, Hayat T. MHD transient flows in a channel of rectangular cross-section with porous medium. Phys Lett A. 2007;369:44–54.
Aydin O, Kaya A. MHD-mixed convection from a vertical slender cylinder. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul. 2011;16:1863–73.
Rahman M, Oztop HF, Saidur R, Mekhilef S, Al-Salem K. Finite element solution of MHD mixed convection in a channel with a fully or partially heated cavity. Comput Fluids. 2013;79:53–64.
Sheikholeslami M, Bandpy MG, Ganji D. Numerical investigation of MHD effects on \(\text{ Al }_{2}\text{ O }_{3}\)-water nanofluid flow and heat transfer in a semi-annulus enclosure using LBM. Energy. 2013;60:501–10.
Oztop HF, Rahman M, Ahsan A, Hasanuzzaman M, Saidur R, Al-Salem K, Rahim N. MHD natural convection in an enclosure from two semi-circular heaters on the bottom wall. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2012;55:1844–54.
Mahmoudi A, Mejri I, Abbassi MA, Omri A. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of MHD natural convection in a nanofluid-filled cavity with linear temperature distribution. Powder Technol. 2014;256:257–71.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF, Chamkha AJ. Fluid-structure-magnetic field interaction in a nanofluid filled lid-driven cavity with flexible side wall. Eur J Mech B Fluids. 2017;61:77–85.
Kefayati G. Effect of a magnetic field on natural convection in an open cavity subjugated to water/alumina nanofluid using lattice Boltzmann method. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2013;40:67–77.
Sheikholeslami M, Gorji-Bandpy M, Ganji D, Soleimani S, Seyyedi S. Natural convection of nanofluids in an enclosure between a circular and a sinusoidal cylinder in the presence of magnetic field. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2012;39:1435–43.
Ghasemi B, Aminossadati S, Raisi A. Magnetic field effect on natural convection in a nanofluid-filled square enclosure. Int J Therm Sci. 2011;50:1748–56.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF. Forced convection and thermal predictions of pulsating nanofluid flow over a backward facing step with a corrugated bottom wall. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;110:231–47.
Sajid MU, Ali HM. Recent advances in application of nanofluids in heat transfer devices: a critical review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2019;103:556–92.
Gholamalipour P, Siavashi M, Doranehgard MH. Eccentricity effects of heat source inside a porous annulus on the natural convection heat transfer and entropy generation of Cu–water nanofluid. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2019;109:104367.
Miroshnichenko IV, Sheremet MA, Oztop HF, Abu-Hamdeh N. Natural convection of alumina-water nanofluid in an open cavity having multiple porous layers. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;125:648–57.
Murshed S, de Castro CAN. Superior thermal features of carbon nanotubes-based nanofluids—a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2014;37:155–67.
Siavashi M, Kimia Karimi QX, Doranehgard MH. Numerical analysis of mixed convection of two-phase non-newtonian nanofluid flow inside a partially porous square enclosure with a rotating cylinder. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;137:267–87.
Abu-Nada E, Chamkha AJ. Mixed convection flow of a nanofluid in a lid-driven cavity with a wavy wall. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2014;57:36–47.
Manca O, Mesolella P, Nardini S, Ricci D. Numerical study of a confined slot impinging jet with nanofluids. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2011;6:188.
Astanina MS, Sheremet MA, Oztop HF, Abu-Hamdeh N. Mixed convection of \(\text{ Al }_{2}\text{ O }_{3}\)-water nanofluid in a lid-driven cavity having two porous layers. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;118:527–37.
Saffarian MR, Moravej M, Doranehgard MH. Heat transfer enhancement in a flat plate solar collector with different flow path shapes using nanofluid. Renew Energy. 2020;146:2316–29.
Koo J, Kleinstreuer C. Laminar nanofluid flow in microheat-sinks. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2005;48:2652–61.
Tiwari R, Das MK. Heat transfer augmentation in a two-sided lid-driven differentially heated square cavity utilizing nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2007;50:2002–18.
Xue Q. Model for thermal conductivity of carbon nanotube—based composites. Physica B. 2005;368:302–7.
Wang X, Xu X, Choi S. Thermal conductivity of nanoparticles-fluid mixture. J Thermophys Heat Transf. 1999;13:474–80.
Kakac S, Pramuanjaroenkij A. Review of convective heat transfer enhancement with nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2009;52:3187–96.
Arshad W, Ali HM. Experimental investigation of heat transfer and pressure drop in a straight minichannel heat sink using \(\text{ TiO }_{2}\) nanofluid. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;110:248–56.
Oztop HF, Abu-Nada E. Numerical study of natural convection in partially heated rectangular enclosures filled with nanofluids. Int J Heat Fluid Flow. 2008;29:1326–36.
Wongcharee K, Chuwattanakul V, Eiamsaard S. Heat transfer of swirling impinging jets with \(\text{ TiO }_{2}\)-water nanofluids. Chem Eng Process Process Intensification. 2017;114:16–23.
Ali HM, Ali H, Liaquat H, Maqsood HTB, Nadir MA. Experimental investigation of convective heat transfer augmentation for car radiator using ZnO–water nanofluids. Energy. 2015;84:317–24.
Cho CC. Heat transfer and entropy generation of natural convection in nanofluid-filled square cavity with partially-heated wavy surface. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2014;77:818–27.
Ma Y, Mohebbi R, Rashidi MM, Yang Z. MHD convective heat transfer of Ag–MgO/water hybrid nanofluid in a channel with active heaters and coolers. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2019;137:714–26.
Esfe MH, Arani AAA, Rezaie M, Yan W, Karimipour A. Experimental determination of thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity of Ag–MgO/water hybrid nanofluid. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2015;66:189–95.
Maxwell JC. A treatise on electricity and magnetism. Oxford: Clarendon Press; 1881.
Tayebi T, Chamkha AJ. Entropy generation analysis due to MHD natural convection flow in a cavity occupied with hybrid nanofluid and equipped with a conducting hollow cylinder. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08651-5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Selimefendigil, F., Öztop, H.F. Impact of a rotating cone on forced convection of Ag–MgO/water hybrid nanofluid in a 3D multiple vented T-shaped cavity considering magnetic field effects. J Therm Anal Calorim 143, 1485–1501 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09348-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09348-w