Abstract
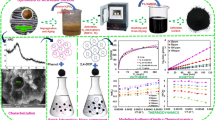
Catalytic co-pyrolysis of seaweed Enteromorpha clathrata (EN) and cellulose (CEL) with catalysts ZSM-5 and MCM-41 was investigated by TG, Py–GC/MS and fixed-bed experiments. The effects of temperature, catalysts, seaweed and cellulose ratio were examined on product yields distribution and bio-oil compositions by catalytic co-pyrolysis. The maximum bio-oil yield was recorded at the ratio of 1:1 (EN and CEL) with ZSM-5/MCM-41 at 500 °C on co-pyrolytic process. The interaction of radicals and faster heat transfer rate of EN/CEL induces the synergistic effects with catalysts. The advantage of mesoporous molecular sieve along with acidic microporous zeolite of ZSM-5/MCM-41 improved the cracking, dehydration, decarbonylation, decarboxylation, dealkylation, aromatization, oligomerization and deamination reactions. The overall study revealed that the amount of N-containing compounds were decreased and significantly elevated bio-oil production with increased furans and aromatics.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang SR, Dai GX, Yang HP, Luo ZY. Lignocellulosic biomass pyrolysis mechanism: a state-of-the-art review. Prog Energy Combust. 2017;62:33–86.
Sanchez-Silva L, López-González D, Garcia-Minguillan AM, Valverde JL. Pyrolysis, combustion and gasification characteristics of Nannochloropsis gaditana microalgae. Bioresour Technol. 2013;130:321–31.
Raheem A, Wan Azlina WAKG, Taufiq Yap YH, Danquah MK, Harun R. Thermochemical conversion of microalgal biomass for biofuel production. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2015;49:990–9.
Chen DY, Li YJ, Cen KH, Luo M, Li HY, Lu B. Pyrolysis polygeneration of poplar wood: effect of heating rate and pyrolysis temperature. Bioresour Technol. 2016;218:780–8.
Lu Q, Li WZ, Zhu XF. Overview of fuel properties of biomass fast pyrolysis oils. Energy Convers Manag. 2009;50:1376–83.
Wang S, Wang Q, Jiang XM, Han XX, Ji HS. Compositional analysis of bio-oil derived from pyrolysis of seaweed. Energy Convers Manag. 2013;68:273–80.
Hu Y, Wang S, Wang Q, et al. Influence of torrefaction pretreatment on the pyrolysis characteristics of seaweed biomass. Cellulose. 2019;26(15):8475–87.
Abnisa F, Daud WMAW. A review on co-pyrolysis of biomass: an optional technique to obtain a high-grade pyrolysis oil. Energy Convers Manag. 2014;87:71–85.
Chen W, Chen YQ, Yang HP, et al. Co-pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass and microalgae: products characteristics and interaction effect. Bioresour Technol. 2017;245:860–8.
Uzoejinwa BB, He X, Wang S, et al. Co-pyrolysis of biomass and waste plastics as a thermochemical conversion technology for high-grade biofuel production: recent progress and future directions elsewhere worldwide. Energy Convers Manag. 2018;163:468–92.
Zhao Y, Yang X, Fu Z, et al. Synergistic effect of catalytic co-pyrolysis of cellulose and polyethylene over HZSM-5. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08633-7.
Wang S, Wang Q, Hu YM, et al. Study on the synergistic co-pyrolysis behaviors of mixed rice husk and two types of seaweed by a combined TG-FTIR technique. J Anal Appl Pyrol. 2015;114:109–18.
Cao B, Sun Y, Guo J, et al. Synergistic effects of co-pyrolysis of macroalgae and polyvinyl chloride on bio-oil/bio-char properties and transferring regularity of chlorine. Fuel. 2019;246:319–29.
Uzoejinwa BB, He X, Wang S, et al. Co-pyrolysis of macroalgae and lignocellulosic biomass. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;136(5):2001–16.
Hu Y, Wang S, Li J, et al. Co-pyrolysis and co-hydrothermal liquefaction of seaweeds and rice husk: comparative study towards enhanced biofuel production. J Anal Appl Pyrol. 2018;129:162–70.
Zhang L, Liu R, Yin R, Mei Y. Upgrading of bio-oil from biomass fast pyrolysis in China: a review. Renew Sust Energy Rev. 2013;24:66–72.
Wang S, Cao B, Feng Y, et al. Co-pyrolysis and catalytic co-pyrolysis of Enteromorpha clathrata and rice husk. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;135(4):2613–23.
Fan Y, Cai Y, Li X, et al. Coking characteristics and deactivation mechanism of the HZSM-5 zeolite employed in the upgrading of biomass-derived vapors. J Ind Eng Chem. 2017;46:139–49.
Bao WR, Xue XL, Cao Q, Lu JJ, Lu YK. Study on biomass pyrolytic liquid products with MCM-41/SBA-15 as catalyst. J Fuel Chem Technol. 2006;34:675–9.
Sang Y, Liu HX, He SC, Li HS, Jiao QZ, Wu Q, Sun KN. Catalytic performance of hierarchical H-ZSM-5/MCM-41 for methanol dehydration to dimethyl ether. J Energy Chem. 2013;22:769–77.
Ma W, Liu B, Ji X, Li X, Yan B, Cheng Z. Catalytic co-cracking of distilled bio-oil and ethanol over Ni-ZSM-5/MCM-41 in a fixed-bed. Biomass Bioenergy. 2017;102:31–6.
Di ZX, Yang C, Jiao XJ, Li JQ, Wu JH, Zhang DK. A ZSM-5/MCM-48 based catalyst for methanol to gasoline conversion. Fuel. 2013;104:878–81.
Wang J, Wang GC, Zhang MX, Chen MQ, Li DM, et al. A comparative study of thermolysis characteristics and kinetics of seaweeds and fir wood. Process Biochem. 2006;41:1883–6.
Zhao CH, Zhang XP, Shi L. Catalytic pyrolysis characteristics of scrap printed circuit boards by TG-FTIR. Waste Manag. 2017;61:354–61.
Liu GY, Wright MM, Zhao QL, Brown RC, Wang KG, Xue Y. Catalytic pyrolysis of amino acids: comparison of aliphatic amino acid and cyclic amino acid. Energy Convers Manag. 2016;112:220–5.
Gopakumar ST, Adhikari S, Chattanathan SA, et al. Catalytic pyrolysis of green algae for hydrocarbon production using H+ZSM-5 catalyst. Bioresour Technol. 2012;118:150–7.
Gayubo AG, Aguayo AT, Atutxa A, et al. Transformation of oxygenate components of biomass pyrolysis oil on a ZSM-5 zeolite. I. Alcohols and phenols. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2004;43:2610–8.
Maher KD, Bressler DC. Pyrolysis of triglyceride materials for the production of renewable fuels and chemicals. Bioresour Technol. 2007;98:2351–68.
Du ZY, Hu B, Ma XC, et al. Catalytic pyrolysis of microalgae and their three major components: carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Bioresour Technol. 2013;130:777–82.
Wang KG, Kim KH, Brown RC. Catalytic pyrolysis of individual components of lignocellulosic biomass. Green Chem. 2014;16:727–35.
Du ZY, Ma XC, Li Y, et al. Production of aromatic hydrocarbons by catalytic pyrolysis of microalgae with zeolites: catalyst screening in a pyroprobe. Bioresour Technol. 2013;139:397–401.
Adjaye JD, Bakhshi NN. Production of hydrocarbons by catalytic upgrading of a fast pyrolysis bio-oil. Part I: conversion over various catalysts. Fuel Process Technol. 1995;45:161–83.
Wang K, Brown RC. Catalytic pyrolysis of corn dried distillers grains with solubles to produce hydrocarbons. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2014;2:2142–8.
Bradbury AG, Sakai Y, Shafizadeh F. A kinetic model for pyrolysis of cellulose. J Appl Polym Sci. 1979;23(11):3271–80.
Dickerson T, Soria J. Catalytic fast pyrolysis: a review. Energies. 2013;6(1):514–38.
Lorenzetti C, Roberto C, Daniele F, et al. A comparative study on the catalytic effect of H-ZSM5 on upgrading of pyrolysis vapors derived from lignocellulosic and proteinaceous biomass. Fuel. 2016;166:446–52.
Fan LL, Chen P, Zhang YN, et al. Fast microwave-assisted catalytic co-pyrolysis of lignin and low-density polyethylene with HZSM-5 and MgO for improved bio-oil yield and quality. Bioresour Technol. 2017;225:199–205.
Zhang X, Zhang S, Yang H, Shi T, Chen Y, Chen H. Influence of NH3/CO2 modification on the characteristic of biochar and the CO2 capture. Bioenergy Res. 2013;6:1147–53.
Xie QL, Peng P, Liu SY, Min M, Cheng YL, Wan YQ. Fast microwave-assisted catalytic pyrolysis of sewage sludge for bio-oil production. Bioresour Technol. 2014;172:162–8.
Dong Q, Zhang S, Zhang L, Ding K, Xiong Y. Effects of four types of dilute acid washing on moso bamboo pyrolysis using Py–GC/MS. Bioresour Technol. 2015;185:62–9.
Xin S, Yang H, Chen Y, Wang X, Chen H. Assessment of pyrolysis polygeneration of biomass based on major components: product characterization and elucidation of degradation pathways. Fuel. 2013;113:266–73.
Cheng YT, George WH. Chemistry of furan conversion into aromatics and olefins over ZSM-5: a model biomass conversion reaction. ACS Catal. 2011;1:611–28.
Vollhardt KPC, Schore NE. Organic chemistry: structure and function. 5th ed. New York: Freeman WH; 2005.
Joshua KK, Lavrent K, Barry D. Phenols from pyrolysis and co-pyrolysis of tobacco biomass components. Chemosphere. 2015;138:259–65.
Xiao R, Zhang HY, Shen DK. Selective pyrolysis of biomass to liquid fuels and chemicals. Beijing: Science Press; 2015. p. 46.
Serrano VG, Villegas JP, Florindo AP, Valle CD, Calahorro CV. FT-IR study of rockrose and of char and activated carbon. J Anal Appl Pyrol. 1996;36:71–80.
Meesuk S, Cao JP, Sato K, Ogawa Y, Takarada T. The effects of temperature on product yields and composition of bio-oils in hydropyrolysis of rice husk using nickel-loaded brown coal char catalyst. J Anal Appl Pyrol. 2012;94:238–45.
Ponder GR, Richards GN. Thermal synthesis and pyrolysis of xylan. Carbohydr Res. 1991;218:143–55.
Wang S, Xia Z, Hu YM, et al. Co-pyrolysis mechanism of seaweed polysaccharides and cellulose based on macroscopic experiments and molecular simulations. Bioresour Technol. 2017;228:305–14.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51676091), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2019T120408, 2019TQ0125) and the “333 Project” in Jiangsu Province (No. BRA2019277).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Y., Wang, H., Lakshmikandan, M. et al. Catalytic co-pyrolysis of seaweeds and cellulose using mixed ZSM-5 and MCM-41 for enhanced crude bio-oil production. J Therm Anal Calorim 143, 827–842 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09291-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09291-w