Abstract
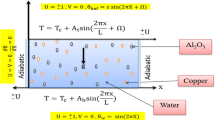
In the present study, a computational work has been done to see the heat transfer, fluid flow and temperature distribution in a lid-driven cavity due to an adiabatic rectangular bar with different dimensions and locations. The closed cavity is heated from the bottom wall and cooled from the top while, vertical walls are adiabatic and magnetic field is affected in horizontally. The governing partial differential equations are discretized via monolithic Galerkin finite element method of higher order. The resulting system of nonlinear algebraic equations are linearized at the discrete solution which have been computed utilizing the efficient geometric multigrid linear solver. The influences of various physical parameters on the flow, in specific ranges such as the nanoparticle volume fraction \(\phi = 0.04\), length and location of the insulated bar, Reynolds number \(1 \le Re \le 200\), Hartmann number \(0\le Ha \le 100\) and Richardson number, \(0\le Ri \le 10\) are investigated. It is found that the location of the bar is a good control parameter for heat and fluid flow inside the cavity. Vertical bar position becomes more effective on heat and fluid than that of horizontal bar position, and the presence of the bar becomes insignificant for the lower values of Richardson numbers.














Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(d_{\rm s}\) :
-
Diameter of nanoparticle (nm)
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity (\(\hbox {W\,m}^{-1}\,\hbox {K}^{-1}\))
- g :
-
Gravitational acceleration (\(\hbox {m\,s}^{-2}\))
- Gr :
-
Grashof number, \(\beta \hbox {g}\Delta \hbox {TL}^3/\nu ^2_{\rm f}\)
- \(C_{\rm p}\) :
-
Specific heat (\(\hbox {J\,kg}^{-1}\,\hbox {K}^{-1}\))
- L :
-
Length of closed cavity (m)
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number, \(\nu _{\rm f}/\alpha _{\rm f}\)
- Ha :
-
Hartmann number, \(B_{0}L\sqrt{\dfrac{\sigma _{\rm f}}{\mu _{\rm f}}}\),
- Ri :
-
Richardson number, \({Gr}/{Re}^2\)
- Re :
-
Reynolds number, \(\frac{U_0 L}{\nu _{\rm f}}\)
- Nu :
-
Nusselt number (local)
- \(Nu_{{\rm avg}}\) :
-
Average Nusselt number
- \(U_0\) :
-
Velocity of wall
- x, y :
-
Dimensional space coordinates (m)
- X, Y :
-
Dimensionless space coordinates
- p :
-
Pressure (\(\hbox {N\,m}^{-2}\))
- P :
-
Dimensionless pressure
- T :
-
Temperature in dimensional form (K)
- u, v :
-
Dimensional velocity components (\(\hbox {m s}^{-1}\))
- U, V :
-
Dimensionless velocity components
- \(T_{\rm h}\) :
-
Hot lower wall temperature (K)
- \(T_{\rm c}\) :
-
Cold upper moving wall temperature (K)
- \(\nu\) :
-
Kinematic viscosity (\(\hbox {m}^2\,\hbox {s}^{-1}\))
- \(\mu\) :
-
Dynamic viscosity (\(\hbox {kg\,m}^{-1}\,\hbox {s}^{-1}\))
- \(\beta\) :
-
Thermal expansion coefficient (\(\hbox {K}^{-1}\))
- \(\rho\) :
-
Density (\(\hbox {kg\,m}^{-3}\))
- \(\alpha\) :
-
Thermal diffusivity (\(\hbox {m}^2\,\hbox {s}^{-1}\))
- \(\theta\) :
-
Dimensionless temperature
- \(\phi\) :
-
Volume fraction of the nanoparticles
- c:
-
Cold
- h:
-
Hot
- f:
-
Fluid
- p:
-
Nanoparticles
- nf:
-
Nanofluid
References
Billah M, Rahman M, Sharif UM, Rahim N, Saidur R, Hasanuzzaman M. Numerical analysis of fluid flow due to mixed convection in a lid-driven cavity having a heated circular hollow cylinder. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2011;38(8):1093–103.
Öztop HF, Al-Salem K, Pop I. MHD mixed convection in a lid-driven cavity with corner heater. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2011;54(15):3494–504.
Khanafer K, Aithal S. Mixed convection heat transfer in a lid-driven cavity with a rotating circular cylinder. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2017;86(Supplement C):131–42.
Gangawane KM, Manikandan B. Mixed convection characteristics in lid-driven cavity containing heated triangular block. Chin J Chem Eng. 2017;25(10):1381–94.
Karbasifar B, Akbari M, Toghraie D. Mixed convection of water-aluminum oxide nanofluid in an inclined lid-driven cavity containing a hot elliptical centric cylinder. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2018;116(Supplement C):1237–49.
Hammami F, Souayeh B, Ben-Cheikh N, Ben-Beya B. Computational analysis of fluid flow due to a two-sided lid driven cavity with a circular cylinder. Comput Fluids. 2017;156(Supplement C):317–28 (Ninth International Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics (ICCFD9)).
Munshi MJH, Alim M, Bhuiyan A, Ali M. Hydrodynamic mixed convection in a lid-driven square cavity including elliptic shape heated block with corner heater. Procedia Eng. 2017;194(Supplement C):442–9 (10th International Conference on Marine Technology, MARTEC 2016).
Garoosi F, Jahanshaloo L, Rashidi MM, Badakhsh A, Ali ME. Numerical simulation of natural convection of the nanofluid in heat exchangers using a Buongiorno model. Appl Math Comput. 2015;254:183–203.
Hussain S, Öztop HF, Jamal M, Hamdeh N. Double diffusive nanofluid flow in a duct with cavity heated from below. Int J Mech Sci. 2017;131–132:535–45.
Selimefendigil F, Öztop HF. Analysis of MHD mixed convection in a flexible walled and nanofluids filled lid-driven cavity with volumetric heat generation. Int J Mech Sci. 2016;118:113–24.
Rashidi S, Mahian O, Languri EM. Applications of nanofluids in condensing and evaporating systems. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;131:2027–39.
Rashidi S, Eskandarian M, Mahian O, Poncet S. Combination of nanofluid and inserts for heat transfer enhancement. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7070-9.
Rashidi S, Karimi N, Mahian O, Abolfazli Esfahani J. A concise review on the role of nanoparticles upon the productivity of solar desalination systems. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7500-8.
Rashidi S, Javadi P, Esfahani JA. Second law of thermodynamics analysis for nanofluid turbulent flow inside a solar heater with the ribbed absorber plate. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018.
Laein RP, Rashidi S, Esfahani JA. Experimental investigation of nanofluid free convection over the vertical and horizontal flat plates with uniform heat flux by PIV. Adv Powder Technol. 2016;27(2):312–22.
Shirejini SZ, Rashidi S, Esfahani J. Recovery of drop in heat transfer rate for a rotating system by nanofluids. J Mol Liq. 2016;220:961–9.
Maskaniyan M, Rashidi S, Esfahani JA. A two-way couple of Eulerian–Lagrangian model for particle transport with different sizes in an obstructed channel. Powder Technol. 2017;312:260–9.
Rashidi S, Bovand M, Esfahani JA, Ahmadi G. Discrete particle model for convective \(\text{ Al }_{2}\text{ O }_{3}\) water nanofluid around a triangular obstacle. Appl Therm Eng. 2016;100:39–54.
Chamkha AJ, Abu-Nada E. Mixed convection flow in single- and double-lid driven square cavities filled with water \(\text{ Al }_{2}\text{ O }_{3}\) nanofluid: effect of viscosity models. Eur J Mech B/Fluids. 2012;36:82–96.
Abu-Nada E, Chamkha AJ. Mixed convection flow of a nanofluid in a lid-driven cavity with a wavy wall. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2014;57:36–47.
Chamkha AJ, Ismael MA. Natural convection in differentially heated partially porous layered cavities filled with a nanofluid. Numer Heat Transf A Appl. 2014;65(11):1089–113.
Parvin S, Nasrin R, Alim M, Hossain N, Chamkha AJ. Thermal conductivity variation on natural convection flow of water–alumina nano fluid in an annulus. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2012;55(19):5268–74.
Nasrin R, Alim M, Chamkha AJ. Combined convection flow in triangular wavy chamber filled with water CuO nanofluid: effect of viscosity models. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2012;39(8):1226–36.
Ismael MA, Armaghani T, Chamkha AJ. Conjugate heat transfer and entropy generation in a cavity filled with a nanofluid-saturated porous media and heated by a triangular solid. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng. 2016;59:138–51.
Ben-Nakhi A, Chamkha AJ. Effect of length and inclination of a thin fin on natural convection in a square enclosure. Numer Heat Transf A Appl. 2006;50(4):381–99.
Selimefendigil F, Öztop HF, Chamkha AJ. MHD mixed convection and entropy generation of nanofluid filled lid driven cavity under the influence of inclined magnetic fields imposed to its upper and lower diagonal triangular domains. J Magn Magn Mater. 2016;406(Supplement C):266–81.
Mamourian M, Shirvan KM, Ellahi R, Rahimi A. Optimization of mixed convection heat transfer with entropy generation in a wavy surface square lid-driven cavity by means of Taguchi approach. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2016;102(Supplement C):544–54.
Sheikholeslami M. Magnetohydrodynamic nanofluid forced convection in a porous lid driven cubic cavity using Lattice-Boltzmann method. J Mol Liq. 2017;231(Supplement C):555–65.
Khorasanizadeh H, Nikfar M, Amani J. Entropy generation of Cu water nanofluid mixed convection in a cavity. Eur J Mech B/Fluids. 2013;37(Supplement C):143–52.
Biswas N, Manna NK, Mahapatra PS. Enhanced thermal energy transport using adiabatic block inside lid-driven cavity. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2016;100(Supplement C):407–27.
Rashad A, Rashidi M, Lorenzini G, Ahmed SE, Aly AM. Magnetic field and internal heat generation effects on the free convection in a rectangular cavity filled with a porous medium saturated with \({Cu}\)water nanofluid. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;104:878–89.
Sheikholeslami M, Rashidi M, Ganji D. Effect of non-uniform magnetic field on forced convection heat transfer of \(\text{ Fe }_{3}\text{ O }_{4}\) water nanofluid. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 2015;294:299–312.
Sheikholeslami M, Vajravelu K, Rashidi MM. Forced convection heat transfer in a semi annulus under the influence of a variable magnetic field. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2016;92:339–48.
Rashidi S, Bovand M, Esfahani J. Opposition of magnetohydrodynamic and \(\text{ Al }_{2}\text{ O }_{3}\) water nanofluid flow around a vertex facing triangular obstacle. J Mol Liq. 2016;215:276–84.
bte Amir Hamzah NS, Kandasamy R, Muhammad R. Thermal radiation energy on squeezed MHD flow of Cu, Al\(_2\)O\(_3\) and CNTs-nanofluid over a sensor surface. Alex Eng J. 2016;55(3):2405–21.
Shirvan KM, Mamourian M, Mirzakhanlari S, Moghiman M. Investigation on effect of magnetic field on mixed convection heat transfer in a ventilated square cavity. Procedia Eng. 2015;127:1181–8.
Malleswaran A, Sivasankaran S, Bhuvaneswari M. Effect of heating location and size on MHD mixed convection in a lid-driven cavity. Int J Numer Methods Heat Fluid Flow. 2013;23:867–84.
Hussain S, ztop HF, Mehmood K, Abu-Hamdeh N. Effects of inclined magnetic field on mixed convection in a nanofluid filled double lid-driven cavity with volumetric heat generation or absorption using finite element method. Chin J Phys. 2018;56(2):484–501.
Sheikholeslami M, Bandpy MG, Ganji D. Numerical investigation of MHD effects on \(\text{ Al }_{2}\text{ O }_{3}\)-water nanofluid flow and heat transfer in a semi-annulus enclosure using LBM. Energy. 2013;60:501–10.
Karimipour A, Esfe MH, Safaei MR, Semiromi DT, Kazi SN. Mixed convection of copper-water nanofluid in a shallow inclined lid driven cavity using the Lattice Boltzmann Method. Physica A: Stat. Mech. Appl. 2014;402:150–68.
Abu-Nada E, Chamkha AJ. Mixed convection flow in a lid-driven inclined square enclosure filled with a nanofluid. Eur J Mech B/Fluids. 2010;29:472–82.
Alinia M, Ganji DD, Gorji-Bandpy M. Numerical study of mixed convection in an inclined two sided lid driven cavity filled with nanofluid using two-phase mixture model. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2011;38:1428–35.
Koo J, Kleinstreuer C. Viscous dissipation effects in microtubes and microchannels. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2004;47:3159–69.
Maxwell J C. A treatise on electricity and magnetism, vol. II. Cambridge: Oxford University Press; 1873.
Mehmood K, Hussain S, Sagheer M. Numerical simulation of MHD mixed convection in alumina-water nanofluid filled square porous cavity using KKL model: effects of non-linear thermal radiation and inclined magnetic field. J Mol Liq. 2017;238:485–98.
Hussain S, Ahmed S, Mehmood K, Sagheer M. Effects of inclination angle on mixed convective nanofluid flow in a double lid-driven cavity with discrete heat sources. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;106:847–60.
Mehmood K, Hussain S, Sagheer M. Mixed convection in alumina–water nanofluid filled lid-driven square cavity with an isothermally heated square blockage inside with magnetic field effect: introduction. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;109:397–409.
Koo J, Kleinstreuer C. Laminar nanofluid flow in microheat-sinks. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2005;48:2652–61.
Brinkman HC. The viscosity of concentrated suspensions and solutions. J Chem Phys. 1952;20:571–81.
Hussain S, Schieweck F, Turek S. Efficient Newton multigrid solution techniques for higher order space time Galerkin discretizations of incompressible flow. Appl Numer Math. 2014;83:51–71.
Sheremet MA, Pop I. Mixed convection in a lid-driven square cavity filled by a nanofluid: Buongiorno mathematical model. Appl Math Comput. 2015;266:792–808.
Saha LK, Somadder MC, Uddin MS. Mixed convection heat transfer in a lid driven cavity with wavy bottom surface. Am J Appl Math. 2014;1(5):92–101.
Iwatsu R, Hyun JM, Kuwahara K. Mixed convection in a driven cavity with a stable vertical temperature gradient. Int J Heat Mass transf. 1993;36:1601–8.
Zheng GF, Ha MY, Yoon HS, Park YG. A numerical study on mixed convection in a lid-driven cavity with a circular cylinder. J Mech Sci Technol. 2013;27(1):273–86.
Sharif MAR. Laminar mixed convection in shallow inclined driven cavities with hot moving lid on top and cooled from bottom. Appl Therm Eng. 2007;27:1036–42.
Malleswaran A, Sivasankaran S. A numerical simulation on MHD mixed convection in a lid-driven cavity with corner heaters. J Appl Fluid Mech. 2016;9:311–9.
Acknowledgements
Calculations have been carried out on the LiDOng cluster at Technische Universität, Dortmund, Germany. The support by the LiDOng team at the ITMC at TU Dortmund is gratefully acknowledged. We would like to thank the LiDOng cluster team for their help and support. We also used FeatFlow (www.featflow.de) solver package and would like to acknowledge the support by the FeatFlow team. Second and last authors extend their appreciation to the International Scientific Partnership Program (ISPP) at King Saud University for funding this research work through ISPP#131.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hussain, S., Öztop, H.F., Mehmood, K. et al. Control of combined convection in a nanofluid-filled lid-driven closed space via rectangular bar in the presence of magnetic field. J Therm Anal Calorim 137, 289–306 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7914-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7914-3