Abstract
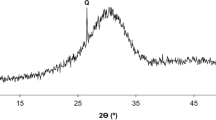
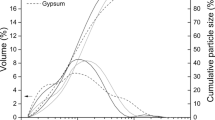
In order to evaluate the pozzolanic activity of a natural pozzolan (NP) of rhyolitic composition, several pastes were prepared by mixing the pozzolan with hydrated lime, in different ratios. The pastes were stored in standard conditions (RH = 99 ± 1%, T = 25 ± 1 °C) and evaluated using thermal analysis (TG-DTA), X-ray diffraction, compressive strength tests and mercury intrusion porosimetry, up to 270 days of curing. The obtained results showed that the compounds formed are CSH and C4ACH11 (monocarboaluminate). The calcium hydroxide consumption increases as the initial amount of the natural pozzolan in the paste augments. As the NP/lime ratio increases, the open total porosity and total cumulative volume decrease, while the bulk density increases. The maximum strength development is obtained for NP/lime ratio of 2.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vitruvius M. Ten books on architecture. New York: Dover Publication; 1960.
Lugli G. La tecnica edilizia romana. Roma: Bardi Editore; 1957.
Malinowski R, Frifelt K. Prehistoric hydraulic mortar: the Ubaid period 5–4000 years BC: technical properties, Document D12. Swedish Council for Building Research, Stockholm, Sweden; 1993. p. 16.
Pavlidou E. Systematic analysis of natural pozzolans from Greece suitable for repair mortars. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;108:671–5.
Massazza F. Pozzolanic cements. Cem Concr Compos. 1993;15:185–214.
Walker R, Pavia S. Physical properties and reactivity of pozzolans, and their influence on the properties of lime–pozzolan pastes. Mater Struct. 2011;44:1139–50.
Parhizkar T, Najimi M, Pourkhorshidi AR, Jafarpour F, Hillemeier B, Herr R. Proposing a new approach for qualification of natural pozzolans. Trans A Civil Eng. 2010;17(6):450–6.
Carr JG. An investigation on the effect of brick dust on lime-based mortars. Masters dissertation, University of Pennsylvania; 1995.
Efstathiades E. Worldwide pioneering the ancient Greek construction materials technology and its applications in civil engineering work. Technical Times. May–June 2004 (in greek).
Koui M, Ftikos CH. The ancient Kamirian water storage tank: a proof of concrete technology and durability for three millenniums. Mater Struct. 1998;31:623–6.
Costa U, Massazza F. Factors affecting the reaction with lime of pozzolana. Il Cemento. 1974;3:131–40.
Donatello S, Tyrer M, Cheeseman CR. Comparison of test methods to assess pozzolanic activity. Cem Concr Compos. 2010;32:121–7.
Frias M, Cabrera J. Influence of MK on the reaction kinetics in MK/lime and MK-blended cement systems at 20 °C. Cem Concr Res. 2001;31:519–27.
Frias Rojas M, Sanchez de Rojas MI. The effect of high curing temperature on the reaction kinetics in MK/lime and MK-blended cement matrices at 60 °C. Cem Concr Res. 2003;33:643–9.
Bakolas A, Aggelakopoulou E, Anagnostopoulou S, Moropoulou A. Evaluation of pozzolanic activity and physico-chemical characteristics in metakaolin-lime pastes. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2006;84(1):157–63.
Bakolas A, Aggelakopoulou E, Moropoulou A. Evaluation of pozzolanic activity and physicomechanical characteristics in ceramic powder-lime pastes. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;92(1):345–51.
Uzal B, Turanli L, Yücel H, Göncüoğlu MC, Çulfaz A. Pozzolanic activity of clinoptilolite: a comparative study with silica fume, fly ash and a non-zeolitic natural pozzolan. Cem Concr Res. 2010;40:398–404.
Nežerka V, Slížková Z, Tesárek P, Plachý T, Frankeová D, Petráňová V. Comprehensive study on mechanical properties of lime-based pastes with additions of metakaolin and brick dust. Cem Concr Res. 2014;64:17–29.
Ubbriaco P, Tasseli F. A study of the hydration of lime-pozzolan binders. J Therm Anal. 1998;52:1047–54.
Salvador S. Pozzolanic properties of flash-calcined kaolinite: a comparative study with soak-calcined products. Cem Concr Res. 1995;25:102–12.
Massazza F. Pozzolana and pozzolanic cements. In: Hewlett PC, editor. Lea’s chemistry of cement and concrete. 4th ed. Oxford: Elsevier; 2004. p. 471–634.
Klimesch DS, Ray A. Use of the second-derivative differential thermal curve in the evaluation of cement-quartz pastes with metakaolin addition autoclaved at 180 °C. Thermochim Acta. 1997;307:167–76.
Klimesch DS, Ray A. The use of TG-DTA to study the effects of ground quartz with different surface areas in autoclaved cement: quartz pastes. Use of the semi-isothermal thermogravimetric technique. Thermochim Acta. 1997;306:159–65.
Paya J, Monzo J, Borrachero MV, Velazquez S, Bonilla M. Determination of the pozzolanic activity of fluid catalytic cracking residue. Thermogravimetric analysis studies on FC3R–lime pastes. Cem Concr Res. 2003;33:1085–91.
Ubbriaco P, Bruno P, Traini A, Calabrese D. Fly ASH reactivity. Formation of hydrate phases. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2001;66:293–305.
Pera J, Amrouz A. Development of highly reactive metakaolin from paper sludge. Adv Cem Based Mater. 1998;7:49–56.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bakolas, A., Aggelakopoulou, E. Pozzolanic activity of natural pozzolan–lime pastes and physicomechanical characteristics. J Therm Anal Calorim 135, 2953–2961 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7612-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7612-1