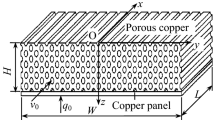
Abstract
Extended surfaces represent one of practical approaches to enhance heat transfer. Based on the laws of conductive and convective heat transfer, an increase in the area across which the object is in contact with the fluid can increase heat transfer. Due to its special structure, porous media can be seen as suitable alternatives for extended surface applications. On this basis, this research investigates the effect of connection type of sintered porous fins on heat transfer and pressure drop in the fluid flow. Connection model of four- and six-contact sintered balls of constant dimensions was evaluated by means of CFD simulation in this research. To describe the problem further, surface analysis on the reference cube is presented. The results indicate that the six-contact model has more porosity than the four-contact in reference cube by 29.45%. It was further found that the six-contact model tends to increase convective heat transfer by 33%. Results of surface analysis show that the main reasons for the difference in heat transfer between the four- and six-contact models are porosity and the angle at which balls are arranged with another.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Surface area (m2)
- C p :
-
Specific heat (J kg K−1)
- d p :
-
Ball diameter (m)
- D h,ch :
-
The hydraulic diameter of the channel
- G k :
-
Turbulence kinetic energy generated due to velocity (W)
- G B :
-
Turbulence kinetic energy generated due to body force (W)
- h :
-
Heat transfer coefficient (W m−2 K)
- H :
-
Enthalpy (J)
- K :
-
Thermal conductivity (W m k−1)
- k :
-
Kinetic energy (J kg−1)
- L :
-
Fin length (m)
- \(\dot{m}\) :
-
Mass flow rate (kg s−1)
- Nu :
-
Nusselt number
- P :
-
Pressure (pa)
- ΔP :
-
Pressure drop (Pa)
- \(\dot{Q}\) :
-
Heat transfer (w)
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- S :
-
Source term
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- U :
-
Fluid velocity (m s−1)
- Y M :
-
Turbulence density
- ε :
-
Energy dissipation (J kg−1)
- μ :
-
Absolute viscosity (N s m−2)
- η :
-
Thermal efficiency
- ρ :
-
Density (kg m−3)
- σ :
-
Turbulent Prandtl number
- θ :
-
Dimensionless temperature
- f :
-
Fluid
- s :
-
Solid surface
- w :
-
Wall
- cond :
-
Conduction
- conv :
-
Convection
- total :
-
Total
- LMTD :
-
Logarithmic average of the temperature difference
- in :
-
Inlet
- out :
-
Outlet
- fin :
-
Related to fin
- ave :
-
Average
- b :
-
Base
- i :
-
Interface of solid and liquid
References
Arpaci VS, Larsen PS. Convection heat transfer. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall; 1984.
Ye W-B. Enhanced latent heat thermal energy storage in the double tubes using fins. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;128(1):533–40.
Ben-Nakhi A, Chamkha AJ. Effect of length and inclination of a thin fin on natural convection in a square enclosure. Numer Heat Transf A. 2006;50:381–99.
Ben-Nakhi A, Chamkha AJ. Conjugate natural convection around a finned pipe in a square enclosure with internal heat generation. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2007;50:2260–71.
Ben-Nakhi A, Chamkha AJ. Conjugate natural convection in a square enclosure with inclined thin fin of arbitrary length. Int J Therm Sci. 2007;46:467–78.
Ben-Nakhi A, Chamkha AJ, Ben Beya B. Effect of inclination on heat transfer and fluid flow in a finned enclosure filled with a dielectric liquid. Numer Heat Transfer, Part A. 2009;56:286–300.
Chamkha AJ, Mansour MA, Ahmad SE. Double-diffusive natural convection in inclined finned triangular porous enclosures in the presence of heat generation/absorption effects. Heat Mass Transf. 2010;46:757–68.
Ghalambaz M, Jamesahar E, Ismael MA, Chamkha AJ. Fluid-structure interaction study of natural convection heat transfer over a flexible oscillating fin in a square cavity. Int J Therm Sci. 2017;111:256–73.
Morega A. Optimal arrays of pin fins and plate fins in laminar forced convection. J Heat Transf. 1993;115:75.
Wirtz RA. A semi-empirical model for porous media heat exchanger design. ASME-Publications-Htd. 1997;349:155–62.
Jeng T-M, Tzeng S-C. Numerical study of confined slot jet impinging on porous metallic foam heat sink. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2005;48(23):4685–94.
Hamdan M, Al-Nimr MA. The use of porous fins for heat transfer augmentation in parallel-plate channels. Transp Porous Media. 2010;84(2):409–20.
Lindstedt M, Karvinen R. Conjugated heat transfer from a uniformly heated plate and a plate fin with uniform base heat flux. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;107:89–95.
Bejan A. Entropy generation minimization: the new thermodynamics of finite-size devices and finite-time processes. J Appl Phys. 1996;79(3):1191–218.
Chen L, Yang A, Xie Z, Sun F. Constructal entropy generation rate minimization for cylindrical pin-fin heat sinks. Int J Therm Sci. 2017;111:168–74.
Alshuraiaan B, Khanafer K. The effect of the position of the heated thin porous fin on the laminar natural convection heat transfer in a differentially heated cavity. Int Commun Heat Mass Transfer. 2016;78:190–9.
Bilen K, Gok S, Olcay A, Solmus I. Investigation of the effect of aluminum porous fins on heat transfer. Energy. 2017;138:1187–98.
Kundu B, Lee K-S. A proper analytical analysis of annular step porous fins for determining maximum heat transfer. Energy Convers Manag. 2016;110:469–80.
Siavashi M, Bahrami HRT, Saffari H. Numerical investigation of flow characteristics, heat transfer and entropy generation of nanofluid flow inside an annular pipe partially or completely filled with porous media using two-phase mixture model. Energy. 2015;93:2451–66.
Zargartalebi H, Ghalambaz M, Noghrehabadi A, Chamkha AJ. Natural convection of a nanofluid in an enclosure with inclined local thermal nonequilibrium porous fin considering Buongiorno’s model. Numer Heat Transf A. 2016;70:432–45.
Vafai K. Handbook of porous media. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2009.
Jiang PX, Li M, Lu TJ, Yu L, Ren ZP. Experimental research on convection heat transfer in sintered porous plate channels. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2004;47:2085–96.
Jiang P-X, Lu X-C. Numerical simulation of fluid flow and convection heat transfer in sintered porous plate channels. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2006;49(9):1685–95.
Chuan L, Wang X-D, Wang T-H, Yan W-M. Fluid flow and heat transfer in microchannel heat sink based on porous fin design concept. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2015;65:52–7.
Zhong W, Xu K, Li X, Liao Y, Tao G, Kagawa T. Determination of pressure drop for air flow through sintered metal porous media using a modified Ergun equation. Adv Powder Technol. 2016;27(4):1134–40.
Huang G, Zhu Y, Liao Z, Ouyang X-L, Jiang P-X. Experimental investigation of transpiration cooling with phase change for sintered porous plates. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;114:1201–13.
Versteeg H-K, Malalasekera W. An introduction to computational Fluid Dynamics: The Finite, vol. Method. London: Pearson Education; 2007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mesgarpour, M., Heydari, A. & Saddodin, S. Investigating the effect of connection type of a sintered porous fin through a channel on heat transfer and fluid flow. J Therm Anal Calorim 135, 461–474 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7356-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7356-y