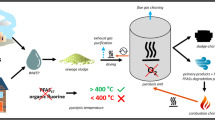
Abstract
Co-combustion of sewage sludge and bituminous coal in O2/CO2 atmosphere was carried out in a horizontal electric heating tube furnace. The effects of incineration temperature, mass ratio of sewage sludge to coal (Xs) and incineration atmosphere on the release characteristics of heavy metals (HMs, such as As, Cr, Ni and Pb) were investigated. The results indicated that incineration temperature can promote the release of As and Pb significantly, but it has little effect on the release of Cr and Ni. The release fractions of As, Cr, Ni and Pb in 21%O2/79%CO2 atmosphere are less than that in air atmosphere due to higher specific heat of CO2. With increasing O2 content in O2/CO2 atmosphere, the release fractions of Cr, Ni and Pb increase, but As release fraction decreases. With the increase in Xs, the release fractions of As and Pb increase, Cr release fraction decreases, but Ni release fraction is almost stable. It is infeasible to predict the release fractions of different HMs under co-combustion based on sewage sludge addition and their release fractions of mono-combustion. The co-combustion condition of sewage sludge with coal is suggested as: temperature of 800–900 °C, 30%O2 in O2/CO2 atmosphere, and about 30% sludge addition.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen H, Yan SH, Ye ZL, Meng HJ, Zhu YG. Utilization of urban sewage sludge: Chinese perspectives. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2012;19(5):1454–63.
Werthera J, Ogada T. Sewage sludge combustion. Prog Energy Combust Sci. 1999;25(1):55–116.
Tyagi VK, Lo SL. Sludge: a waste or renewable source for energy and resources recovery? Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2013;25(5):708–28.
Chen T, Yan B. Fixation and partitioning of heavy metals in slag after incineration of sewage sludge. Waste Manag. 2012;32(5):957–64.
Niu S, Chen M, Li Y, Lu T. Combustion characteristics of municipal sewage sludge with different initial moisture contents. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;129(2):1189–99.
Jang HN, Kim JH, Back SK, Sung JH, Yoo HM, Choi HS, Seo YC. Combustion characteristics of waste sludge at air and oxy-fuel combustion conditions in a circulating fluidized bed reactor. Fuel. 2016;170(5):92–9.
Åmand LE, Leckner B. Metal emissions from co-combustion of sewage sludge and coal/wood in fluidized bed. Fuel. 2004;83(13):1803–21.
Zhang Y, Zhang L, Duan F, Jiang X, Sun X, Chyang C. Co-combustion characteristics of sewage sludge with different rank bituminous coals under the O2/CO2 atmosphere. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;121(2):729–36.
Niu S, Chen M, Li Y, Song J. Co-combustion characteristics of municipal sewage sludge and bituminous coal. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6716-3.
Li L, Zhao N, Wei W, Sun Y. A review of research progress on CO2 capture, storage, and utilization in Chinese Academy of Sciences. Fuel. 2013;108(11):112–30.
Buhre BJP, Elliott LK, Sheng CD, Gupta RP, Wall TF. Oxy-fuel combustion technology for coal-fired power generation. Prog Energy Combust Sci. 2005;31(4):283–307.
Scheffknecht G, Al-Makhadmeh L, Schnell U, Maier J. Oxy-fuel coal combustion—a review of the current state-of-the-art. Int J Greenhouse Gas Control. 2011;5(S1):S16–35.
Font O, Córdoba P, Leiva C, Romeo LM, Bolea I, Guedea I, Moreno N, Querol X, Fernandez C, Díez LI. Fate and abatement of mercury and other trace elements in a coal fluidised bed oxy combustion pilot plant. Fuel. 2012;95(95):272–81.
Zhou Z, Hu X, You Z, Wang Z, Zhou J, Cen K. Oxy-fuel combustion characteristics and kinetic parameters of lignite coal from thermo-gravimetric data. Thermochim Acta. 2013;553(553):54–9.
Contreras ML, García-Frutos FJ, Bahillo A. Oxy-fuel combustion effects on trace metals behaviour by equilibrium calculations. Fuel. 2013;108:474–83.
Vejahati F, Xu Z, Gupta R. Trace elements in coal: associations with coal and minerals and their behavior during coal utilization—a review. Fuel. 2010;89(4):904–11.
Corella J, Toledo JM. Incineration of doped sludges in fluidized bed. Fate and partitioning of six targeted heavy metals. I. Pilot plant used and results. J Hazard Mater. 2000;80(1–3):81–105.
Fytili D, Zabaniotou A. Utilization of sewage sludge in EU application of old and new methods—a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2008;12(1):116–40.
Xu M, Yan R, Zheng C, Qiao Y, Han J, Sheng C. Status of trace element emission in a coal combustion process: a review. Fuel Process Technol. 2003;85(2–3):215–37.
Clarke LB. The fate of trace elements during coal combustion and gasification: an overview. Fuel. 1993;72(6):731–6.
Zhuang Y, Pavlish JH. Fate of hazardous air pollutants in oxygen-fired coal combustion with different flue gas recycling. Environ Sci Technol. 2012;46(8):4657–65.
Zhang R, Jiang X, Chi Y, Yan J. Experimental and thermodynamic study of the partition of Cr, Ni, Cu, Pb and Mn during co-combustion of pickling sludge and bituminous coal. Energy Fuels. 2016;30(1):690–7.
Miller BB, Kandiyoti R, Dugwell DR. Trace element behavior during co-combustion of sewage sludge with Polish coal. Energy Fuels. 2004;18(4):1093–103.
Folgueras MB, DÌAz RM, Xiberta J, Prieto I. Volatilisation of trace elements for coal-sewage sludge blends during their combustion. Fuel. 2003;82(15):1939–48.
Zhang G, Hai J, Cheng J, Cai Z, Ren M, Zhang S, Zhang J. Evaluation of PCDD/Fs and metals emission from a circulating fluidized bed incinerator co-combusting sewage sludge with coal. J Environ Sci. 2013;25(1):231–5.
Liu J, Fu J, Ning X, Sun S, Wang Y, Xie W, Huang S, Zhong S. An experimental and thermodynamic equilibrium investigation of the Pb, Zn, Cr, Cu, Mn and Ni partitioning during sewage sludge incineration. J Environ Sci. 2015;35(9):43–54.
Lin M, Ning X, Liang X, Wei P, Wang Y, Liu J. Study of the heavy metals residual in the incineration slag of textile dyeing sludge. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng. 2014;45(4):1814–20.
Opila EJ, Myers DL, Jacobson NS, Nielsen IMB, Johnson DF, Olminsky JK, Allendorf MD. Theoretical and experimental investigation of the thermochemistry of CrO2(OH)2(g). J Phys Chem A. 2007;111(23):1971–80.
Contreras ML, Arostegui JM, Armesto L. Arsenic interactions during co-combustion processes based on thermodynamic equilibrium calculations. Fuel. 2009;88(3):539–46.
Acknowledgements
The financial supports of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51476079), Jiangsu Province Prospective Cooperation Research Project of China (BY2015001-01) and Jiangsu Province Major Project of University Natural Science Research of China (15KJA610002) are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bu, Y., Dai, X. & Lu, P. Release characteristics of semi-volatile heavy metals during co-combustion of sewage sludge and coal under the O2/CO2 atmosphere. J Therm Anal Calorim 133, 1041–1047 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7170-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7170-6