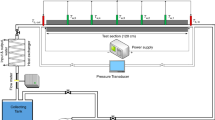
Abstract
A novel synthesis procedure is presented for preparing functionalized graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs). Using sonication method, the functionalized GNPs are dispersed in water-ethylene glycol to prepare water–ethylene glycol-based functionalized GNP nanofluids. Meanwhile, the thermophysical properties of the prepared nanofluids, i.e., thermal conductivity, specific heat capacity, and rheological properties are investigated. As the second phase of study, the heat transfer performance of an annular channel is simulated and measured in the presence of the prepared nanofluids. To this end, a computational fluid dynamics study has been carried out to calculate the heat transfer rate as well as pressure drop of the well-dispersed nanofluids. Meanwhile, the effects of concentration and Reynolds number on the convective heat transfer coefficient have been investigated at constant wall temperature boundary condition under turbulent flow regime. Consist with the results, the convective heat transfer coefficient of nanofluids are significantly higher than that of the base-fluid. The novel type of nanofluid reveals promising potential for use as an advanced working fluid in future heat transfer applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- c p :
-
Specific heat capacity at constant pressure (J kg−1 K−1)
- d p :
-
Nanoparticle diameter (m)
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity (W m−1 K−1)
- Nu :
-
Nusselt number (h D λ−1)
- p :
-
Static pressure (N m−2)
- Pr :
-
Liquid Prandtl number
- q″:
-
Heat flux (w m−2)
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- V :
-
Velocity (m s−1)
- u′:
-
Fluctuating part of velocity (m s−1)
- µ :
-
Dynamic viscosity (kg m−1 s−1)
- ρ :
-
Density (kg m−3)
- φ :
-
Particle volume fraction
- eff:
-
Effective
- f:
-
Fluid
- s:
-
Solid
- w:
-
Wall
- –:
-
Mean
- 0:
-
Initial
References
Mohammed HA. Laminar mixed convection heat transfer in a vertical circular tube under buoyancy-assisted and opposed flows. Energy Convers Manag. 2008;49(8):2006–15.
Abu-Nada E, Oztop HF. Effects of inclination angle on natural convection in enclosures filled with Cu–water nanofluid. Int J Heat Fluid Flow. 2009;30(4):669–78.
Duka B, Ferrario C, Passerini A, Piva S. Non-linear approximations for natural convection in a horizontal annulus. Int J Non-Linear Mech. 2007;42(9):1055–61.
Passerini A, Ferrario C, Thäter G. Natural convection in horizontal annuli: a lower bound for the energy. J Eng Math. 2008;62(3):247–59.
Kashani A, Jalali-vahid D, Hossainpour S. Numerical study of laminar forced convection of water/Al2O3 nanofluid in an annulus with constant wall temperature. IIUM Eng J. 2013;14(1).
Amiri A, Sadri R, Shanbedi M, Ahmadi G, Kazi S, Chew B, et al. Synthesis of ethylene glycol-treated graphene nanoplatelets with one-pot, microwave-assisted functionalization for use as a high performance engine coolant. Energy Convers Manag. 2015;101:767–77.
Heris SZ, Fallahi M, Shanbedi M, Amiri A. Heat transfer performance of two-phase closed thermosyphon with oxidized CNT/water nanofluids. Heat Mass Transf. 2016;52(1):85–93.
Shanbedi M, Heris SZ, Amiri A, Adyani S, Alizadeh M, Baniadam M. Optimization of the thermal efficiency of a two-phase closed thermosyphon using active learning on the human algorithm interaction. Numer Heat Transf Part A Appl. 2014;66(8):947–62.
Solangi K, Kazi S, Luhur M, Badarudin A, Amiri A, Sadri R, et al. A comprehensive review of thermo-physical properties and convective heat transfer to nanofluids. Energy. 2015;89:1065–86.
Toghraie D, Chaharsoghi VA, Afrand M. Measurement of thermal conductivity of ZnO–TiO2/EG hybrid nanofluid. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;125(1):527–35.
Mashaei PR, Shahryari M, Madani S. Numerical hydrothermal analysis of water–Al2O3 nanofluid forced convection in a narrow annulus filled by porous medium considering variable properties: application to cylindrical heat pipes. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016. doi:10.1007/s10973-016-5550-3.
Amiri A, Arzani HK, Kazi S, Chew B, Badarudin A. Backward-facing step heat transfer of the turbulent regime for functionalized graphene nanoplatelets based water–ethylene glycol nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2016;97:538–46.
Amiri A, Shanbedi M, Yarmand H, Arzani HK, Gharehkhani S, Montazer E, et al. Laminar convective heat transfer of hexylamine-treated MWCNTs-based turbine oil nanofluid. Energy Convers Manag. 2015;105:355–67.
Arzani HK, Amiri A, Kazi S, Chew B, Badarudin A. Experimental and numerical investigation of thermophysical properties, heat transfer and pressure drop of covalent and noncovalent functionalized graphene nanoplatelet-based water nanofluids in an annular heat exchanger. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2015;68:267–75.
Arzani HK, Amiri A, Kazi S, Chew B, Badarudin A. Experimental investigation of thermophysical properties and heat transfer rate of covalently functionalized MWCNT in an annular heat exchanger. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2016;75:67–77.
Zeinali S, Heris MN, Etemad SGh. Experimental investigation of convective heat transfer of Al2O3/water nanofluid in circular tube. Int J Heat Fluid Flow. 2007;28:203–10.
Heris SZ, Etemad SG, Esfahany MN. Experimental investigation of oxide nanofluids laminar flow convective heat transfer. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2006;33(4):529–35.
Shanbedi M, Amiri A, Rashidi S, Heris SZ, Baniadam M. Thermal performance prediction of two-phase closed thermosyphon using adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. Heat Transf Eng. 2015;36(3):315–24.
Amiri A, Shanbedi M, AliAkbarzade MJ. The specific heat capacity, effective thermal conductivity, density, and viscosity of coolants containing carboxylic acid functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J Dispersion Sci Technol. 2016;37(7):949–55.
Esfe MH, Saedodin S. Turbulent forced convection heat transfer and thermophysical properties of Mgo–water nanofluid with consideration of different nanoparticles diameter, an empirical study. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;119(2):1205–13.
Beheshti A, Shanbedi M, Heris SZ. Heat transfer and rheological properties of transformer oil-oxidized MWCNT nanofluid. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;118(3):1451–60.
Bahiraei M. A numerical study of heat transfer characteristics of CuO–water nanofluid by Euler–Lagrange approach. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;123(2):1591–9.
Kumar BR, Basheer NS, Jacob S, Kurian A, George SD. Thermal-lens probing of the enhanced thermal diffusivity of gold nanofluid-ethylene glycol mixture. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;119(1):453–60.
Ahammed N, Asirvatham LG, Wongwises S. Effect of volume concentration and temperature on viscosity and surface tension of graphene–water nanofluid for heat transfer applications. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;123(2):1399–409.
Hosseinzadeh M, Heris SZ, Beheshti A, Shanbedi M. Convective heat transfer and friction factor of aqueous Fe3O4 nanofluid flow under laminar regime. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;124(2):827–38.
Esfe MH, Ahangar MRH, Toghraie D, Hajmohammad MH, Rostamian H, Tourang H. Designing artificial neural network on thermal conductivity of Al2O3–water–EG (60–40 %) nanofluid using experimental data. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016. doi:10.1007/s10973-016-5469-8.
Chol S. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. ASME Publ Fed. 1995;231:99–106.
Barbés B, Páramo R, Blanco E, Casanova C. Thermal conductivity and specific heat capacity measurements of CuO nanofluids. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;115(2):1883–91.
Roy G, Nguyen CT, Lajoie P-R. Numerical investigation of laminar flow and heat transfer in a radial flow cooling system with the use of nanofluids. Superlattices Microstruct. 2004;35(3):497–511.
Khanafer K, Vafai K, Lightstone M. Buoyancy-driven heat transfer enhancement in a two-dimensional enclosure utilizing nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2003;46(19):3639–53.
Akbarinia A, Behzadmehr A. Numerical study of laminar mixed convection of a nanofluid in horizontal curved tubes. Appl Therm Eng. 2007;27(8):1327–37.
Akbarinia A, Laur R. Investigating the diameter of solid particles effects on a laminar nanofluid flow in a curved tube using a two phase approach. Int J Heat Fluid Flow. 2009;30(4):706–14.
Talebi F, Mahmoudi AH, Shahi M. Numerical study of mixed convection flows in a square lid-driven cavity utilizing nanofluid. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2010;37(1):79–90.
Shahi M, Mahmoudi AH, Talebi F. Numerical study of mixed convective cooling in a square cavity ventilated and partially heated from the below utilizing nanofluid. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2010;37(2):201–13.
Sundar LS, Sharma K. Turbulent heat transfer and friction factor of Al2O3 nanofluid in circular tube with twisted tape inserts. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2010;53(7):1409–16.
Amiri A, Shanbedi M, Chew B, Kazi S, Solangi K. Toward improved engine performance with crumpled nitrogen-doped graphene based water–ethylene glycol coolant. Chem Eng J. 2016;289:583–95.
Xuan Y, Li Q. Heat transfer enhancement of nanofluids. Int J Heat Fluid Flow. 2000;21(1):58–64.
Manninen M, Taivassalo V, Kallio S. On the mixture model for multiphase flow. Espoo: Technical Research Centre of Finland; 1996.
Crowe LM, Reid DS, Crowe JH. Is trehalose special for preserving dry biomaterials? Biophys J. 1996;71(4):2087.
Ishii M. Thermo-fluid dynamic theory of two-phase flow. NASA STI/Recon Tech Rep A. 1975;75:29657.
Xu H-K. Viscosity approximation methods for nonexpansive mappings. J Math Anal Appl. 2004;298(1):279–91.
Lotfi R, Saboohi Y, Rashidi A. Numerical study of forced convective heat transfer of nanofluids: comparison of different approaches. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2010;37(1):74–8.
Bianco V, Chiacchio F, Manca O, Nardini S. Numerical investigation of nanofluids forced convection in circular tubes. Appl Therm Eng. 2009;29(17):3632–42.
Mirmasoumi S, Behzadmehr A. Effect of nanoparticles mean diameter on mixed convection heat transfer of a nanofluid in a horizontal tube. Int J Heat Fluid Flow. 2008;29(2):557–66.
Mirmasoumi S, Behzadmehr A. Numerical study of laminar mixed convection of a nanofluid in a horizontal tube using two-phase mixture model. Appl Therm Eng. 2008;28(7):717–27.
Abu-Nada E, Masoud Z, Hijazi A. Natural convection heat transfer enhancement in horizontal concentric annuli using nanofluids. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2008;35(5):657–65.
Izadi M, Behzadmehr A, Jalali-Vahida D. Numerical study of developing laminar forced convection of a nanofluid in an annulus. Int J Therm Sci. 2009;48(11):2119–29.
Amiri A, Shanbedi M, Savari M, Chew B, Kazi S. Cadmium ion sorption from aqueous solutions by high surface area ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid- and diethylene triamine pentaacetic acid-treated carbon nanotubes. RSC Adv. 2015;5:71144–52.
Amiri A, Shanbedi M, Ahmadi G, Eshghi H, Chew BT, Kazi SN. Microwave-assisted direct coupling of graphene nanoplatelets with poly ethylene glycol and 4-phenylazophenol molecules for preparing stable-colloidal system. Colloids Surf A. 2015;487:131–41. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2015.09.032.
Behzadmehr A, Saffar-Avval M, Galanis N. Prediction of turbulent forced convection of a nanofluid in a tube with uniform heat flux using a two phase approach. Int J Heat Fluid Flow. 2007;28(2):211–9.
Shih TM. Numerical heat transfer. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 1984.
Launder BE, Spalding D. The numerical computation of turbulent flows. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 1974;3(2):269–89.
Aravind SJ, Baskar P, Baby TT, Sabareesh RK, Das S, Ramaprabhu S. Investigation of structural stability, dispersion, viscosity, and conductive heat transfer properties of functionalized carbon nanotube based nanofluids. J Phys Chem C. 2011;115(34):16737–44.
Ko GH, Heo K, Lee K, Kim DS, Kim C, Sohn Y, et al. An experimental study on the pressure drop of nanofluids containing carbon nanotubes in a horizontal tube. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2007;50(23):4749–53.
Aravind SJ, Ramaprabhu S. Graphene–multiwalled carbon nanotube-based nanofluids for improved heat dissipation. RSC Adv. 2013;3(13):4199–206.
Ding Y, Alias H, Wen D, Williams RA. Heat transfer of aqueous suspensions of carbon nanotubes (CNT nanofluids). Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2006;49(1):240–50.
Samira P, Saeed ZH, Motahare S, Mostafa K. Pressure drop and thermal performance of CuO/ethylene glycol (60%)–water (40%) nanofluid in car radiator. Korean J Chem Eng. 2015;32(4):609–16.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge University of Malaya Research Grants: RP012A-13AET, FP028-2014B, and High Impact Research Grant of UM.C/625/1/HIR/MOHE/ENG/45, as well as Faculty of Engineering, University of Malaya, Malaysia, for support to conduct this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khajeh Arzani, H., Amiri, A., Arzani, H.K. et al. Toward improved heat transfer performance of annular heat exchangers with water/ethylene glycol-based nanofluids containing graphene nanoplatelets. J Therm Anal Calorim 126, 1427–1436 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-016-5663-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-016-5663-8