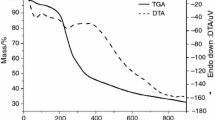
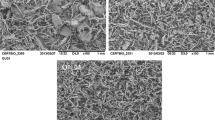
Abstract
The aim of this study was to evaluate the physical quality of Tabebuia caraiba (Mart.) Bur. powder, separately in three batches of different particle sizes, through the adapted Ozawa method. The Ozawa model was used for thermogravimetry (TG) data analysis in dynamic synthetic air and nitrogen atmospheres in different heating rates (5, 10, 20 and 40 °C min−1). The software TA-50 was used to data treatment. Kinetic data showed different values of activation energy and same reaction order according to the particle powder sample size in a specific model (derivative or tangent) of data treatment. The difference factor (F 1) was used to compare the parallelism line of the samples constructed by Ozawa graphs. Different kinetic results discriminate the particles size of the samples. TG technique allowed discriminating different particle sizes of herbal medicine powder.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lemos OA, Sanches JCM, Silva IEF, Silva MLA, Vinhólis AHC, Felix MAP, Santos RA, Cecchi AO. Genotoxic effects of Tabebuia impetiginosa (Mart. Ex DC.) Standl. (Lamiales, Bignoniaceae) extract in Wistar rats. Genet Mol Biol. 2012;35:498–502.
Lorenzi H, Matos FJA. Plantas Medicinais no Brasil: Nativas e Exóticas Cultivadas. Vol II. Nova Odessa, SP: Instituto Plantarum, 2002.
Coelho AAM, Paula JE, Espíndola LS. Efeito de extratos de plantas do Cerrado em Dipetalogaster máxima. Rev Bras Entomol. 2009;3:444–51.
Carvalho ACB, Santos LA, Silveira D. La regulación de los medicamentos herbarios en Brasil. Boletín Latinoamericano y del Caribe de Plantas Medicinales y Aromáticas. Bol Latinoam Caribe Plant Med Arom. 2008;8:7–11.
Nakazawa TA. Particularidades de formulações para fitoterápicos. Rev Racine. 1999;53:38–41.
Calixto JB. Efficacy, safety, quality control, marketing and regulatory guidelines for herbal medicines (phytotherapeutic agents). Braz J Med Biol Res. 2000;2:179–89.
Júnior Silva. JOC. Brazil: Universidade de São Paulo; 2006. p. 120.
Skoog DA, Holler FJ, Nienman TA. Principles of instrumental analysis. 5th ed. USA: Harcourt Brace & Company Philadelphia; 1998.
Silva EC, Paola MVRV, Matos JR. Análise Térmica Aplicada à Cosmetologia. Rev Bras Ciên Farm. 2007;47:347–56.
Boer TM, Procópio JVV, Nascimento TG, Macêdo RO. Correlation of thermal analysis and pyrolysis coupled to GC–MS in the characterization of tacrolimus. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013;73:18–23.
Santos AFO, Procópio JVV, Moura EA, Correia LP, Pinto MF, Macêdo RO. Ozawa kinetic model application for physical quality differentiation of simvastatin raw material. Lat Am J Pharm. 2013;32:927–30.
Wang C, Wang Z, Pan Y, Sun XZ. Application of pyrolysis-gas chromatography and hierarchical cluster analysis to the discrimination of the Chinese traditional medicine Dendrobium candidum Wall. ex Lindl. J Anal Appl Pyrol. 2011;90:13–7.
Yuan M, Zhang MG, Yuan P, Zeng Z, Yan CL. Pyrolysis-gas chromatography fingerprint with fuzzy cluster analysis for Curcuma aromatica Salisb., Chinese. J Chromatogr. 2003;21:469–71.
Procópio JVV, Souza VG, Costa RA, Correia LP, Souza FS, Macêdo RO. Application of thermal analysis and pyrolysis coupled to GC/MS in the qualification of simvastatin pharmaceutical raw material. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2011. doi:10.1007/s10973-010-1274-y.
Moura EA, Correia LP, Pinto MF, Procópio JVV, Souza FS, Macêdo RO. Thermal characterization of the solid state and raw material fluconazole by thermal analysis and pyrolysis coupled to GC/MS. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2010;100:289–93.
Fernandes FHA, Santana CP, Santos RL, Correia LP, Conceição MM, Macêdo RO, Medeiros ACD. Thermal characterization of dried extract of medicinal plant by DSC and analytical techniques. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;113–2:443–7.
Macêdo RO, Tecnologia analítica baseada na pirólise acoplada à cromatografia gasosa/espectrometria de massa para caracterização e obtenção de compostos químicos a partir de extratos de Erythrina mulungu Linné secos por nebulização, PI0800530-3 A2, 2010.
Oliveira EJ, Alvarez EDA, Lima NGPB, Macêdo RO. Usefulness of pyrolysis coupled to gas chromatography/mass spectrometry for evaluating the reproducibility of commercial samples of Cymbopogon citratus Stapf. Poaceae. Braz J Pharmacogn. 2010;20:93–9.
Correia LP, Procopio JVV, Santana CP, Santos AFO, Cavalcante HMM, Macedo RO. Characterization of herbal medicine with different particle sizes using pyrolysis GC/MS, SEM and thermal techniques. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;111:1691–8.
Acknowledgements
To CNPq, for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Correia, L.P., Procópio, J.V.V., Santana, C.P. et al. Herbal medicine physical quality evaluation by thermal analysis using adapted Ozawa method. J Therm Anal Calorim 122, 207–214 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4638-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4638-5