Abstract
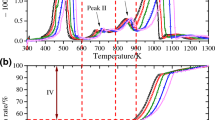
Pyrotechnic mixtures are susceptible to explosive decompositions. The aim of this paper is to generate thermal decomposition data under adiabatic conditions for fireworks mixtures containing potassium nitrate, barium nitrate, sulfur, and aluminum which are manufactured on a commercial scale. Differential scanning calorimeter is used for screening tests and accelerating rate calorimeter is used for other studies. The self heat rate data obtained showed onset temperature in the range of 275–295 °C for the fireworks atom bomb, Chinese cracker and palm leaf cracker. Of the three mixtures studied, atom bomb mixture had an early onset at 275 °C. The mixtures in general showed vigor exothermic decompositions. Palm leaf mixture exhibits multiple exotherm and reached a final temperature of 414 °C. The thermal decomposition contributes to substantial rise in system pressure. The heats of exothermic decomposition and Arrhenius kinetics were computed. The kinetic data are validated by comparing the predicted self heat rates with the experimental data.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- KNO3 :
-
Potassium nitrate
- S:
-
Sulfur
- BaNO3 :
-
Barium nitrate
- Al:
-
Aluminum
- C :
-
Concentration
- T :
-
Temperature (°C)
- T 0 :
-
Initial temperature (°C)
- T F :
-
Final temperature (°C)
- ∆H :
-
Heat of reaction (Cal g−1)
- ϕ:
-
Thermal inertia
- m S :
-
Mass of sample (g)
- m B :
-
Mass of bomb (g)
- k :
-
Rate coefficient
- m T :
-
Rate of temperature increase (°C min−1)
- k*:
-
Pseudo rate constant
- E :
-
Activation energy (kJ mol−1)
- R :
-
Universal gas constant
- A:
-
Pre-exponential factor (s−1)
- ΔE :
-
Threshold energy (Cal g−1)
- \( \overline{C}_{\text{P}} \) :
-
Average heat capacity (J g−1 K−1)
- \( \overline{C}_{\text{ps}} \) :
-
Average heat capacity of sample (J g−1 K−1)
- \( \overline{C}_{\text{pB}} \) :
-
Average heat capacity of bomb (J g−1 K−1)
References
Sivapirakasam SP, Surianarayanan M, Venkataratnam GS and Nagaraj P. Hazard evaluation technique for Firework compositions. In: Indian Chemical Engineering Congress; 2003, p. 126.
Sivapirakasam SP, Surianarayanan M, Venkataratnam GS, Nagaraj P. Impact sensitiveness analysis of pyrotechnic flash compositions. J Pyrotech. 2005;21:52.
Ramu S. Hazard evaluation techniques and hazard evaluation criteria for composite propellants and explosives. In: Vikram Sarabhai Space Safety Symposium 1999, pp. 133–134.
Bowes R. Hazard analysis of pyrotechnic composition. In: Proceedings of 2nd international symposium on fireworks, Vancouver, Canada; 1994.
Herder G, Weterings FP, de Klerk WPC. Mechanical analysis on rocket propellants. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2003;72:921–929.
Sivapirakasam SP, Surianarayanan M, Chandrasekran F. Thermal characterization of pyrotechnic flash compositions. Sci Tech Energetic Mater. 2010;71:1.
Sivapirakasam SP, Surianarayanan M, Vijayaraghavan R. Thermal characterization and kinetic modeling of a pyrotechnic flash composition under adiabatic conditions. J Pyrotech. 2006;23:61–66.
Lightfoot PD, Fouchard RC, Turcotte AM, Kwok QSM, Jones DEG. Thermal techniques used in the hazard evaluation of pyrotechnics. J Pyrotech. 2000;14:15.
Smith WD. Introductory chemistry for pyrotechnics. Atoms, molecules and their interactions. J Pyrotech. 1994;1:12–25.
Hou HY, Duh YS, Lee WL, Shu CM. Hazard evaluation for redox system of cumene hydroperoxide mixed with inorganic alkaline solutions. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;95(2):541–5.
Roy M, Dave P, Barbar SK, Jangid S, Phase DM, Awasthi AM. X-ray, SEM and DSC studies of ferroelectric Pb1−x Ba x TiO3 ceramics. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2010;101:833–7.
Simoes RD, Rodriguez Perez MA, De Saja JA, Constantino CJL. Thermomechanical characterization of PVDF and P(VDF- TrFE) blends containing corn starch and natural rubber. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2010;99:621–9.
Townsend DI, Tou JC. Thermal hazard evaluation by an accelerating rate calorimetry. Thermochem. Acta. 1980;37:1–30.
Boonchom B. Kinetic and thermodynamic studies of MgHPO4·3H2O by non-isothermal decomposition data. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;98:863–71.
Chen JR, SH Wu, Lin SY, Hou HY, Shu CM. Utilization of microcalorimetry for an assessment of the potential for a runaway decomposition of cumene hydroperoxide at low temperatures. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2008;93:127–33.
Hofelich TC, Thomas RC. The use/misuse of the 100 degree rule in the interpretation of thermal hazard tests. In Proceedings of the international symposium on runaway reactions, Ichem; AIChe; CCPS; 1989, pp. 74–85.
Surianarayanan M, Vijayaraghavan R, Swaminathan G, Rao PG. Microcalorimetry and its role in thermal hazard quantification. Curr Sci. 2001;6:738–47.
Badeen CM, Kwok OSM, Vachon MCR, Turcotte R, Jones DEG. Hazard characterization of mixtures of ammonium nitrate with the sodium salt of dichloroisocyanuric acid. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2005;81:225–233.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Prof NR Rajagopal for his encouragement. One of the authors SVP thanks CSIR, New Delhi for SRF fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pakkirisamy, S.V., Mahadevan, S., Paramashivan, S.S. et al. Adiabatic thermokinetics and process safety of pyrotechnic mixtures. J Therm Anal Calorim 109, 1387–1395 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-011-1824-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-011-1824-y