Abstract
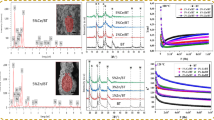
The paper presents the complex studies of adsorption and porosity of pure and modified–aluminium oxides samples. The presence of Mn2+ and Ni2+ modifiers on the aluminium oxide surface causes increase in water adsorption capacity and its decrease in the case of benzene and n-octane. This is due to decrease of specific surface area, volume and radius of pores as a result of surface impregnation and microcrystals formation during modification with manganese and nickel chlorides. Microcrystals formation on the surface and porosity decrease where confirmed by the AFM and SEM studies.
From the Q-TG and Q-DTG data, the energies of liquid desorption from the surface of the samples and the functions of desorption, energy distribution were calculated. High degree of nonlinearity of the run of the functions resulting from great heterogeneity of the studied surface was found. Adsorption of cations creates more homogeneous surface of aluminium oxide, and it is responsible for the change in adsorbate molecule interaction energy and changes mechanism of adsorption and desorption as well as thickness and structure of the adsorbed film. From the experimental data some parameters characterizing adsorption properties and porosity of the studied samples were determined using the measuring methods (thermal analysis, sorptomate, porosimetry, AFM).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
SJ Teichner (1974) Bul. Soc. Chim. Fr. 7-8 1226
J Deng Z Cao B Zhou (1995) Appl. Catal. A: General 132 9 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXpsV2ntr4%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/0926-860X(95)00172-7
MN Ramsis ChA Philip M Abd El Khlik ER Souaya (1996) J. Thermal Anal. 46 1775 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XlsVOktbk%3D Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01980782
E Kis R Marinkovic-Neducin G Lomic G Boskovic DZ Obadovic J Kiurski P Putanov (1998) Polyhedron 17 27 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXotVyqu7c%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0277-5387(97)00263-5
D Franquin S Monteverdi S Molina MM Betahar Y Fort (1999) J. Mater. Sci. 34 4481 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXmsFWmu7c%3D Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1004637221636
B Grzybowska-Owierkosz et al. (1993) Elementy katalizy heterogenicznej (Elements of heterogeneity catalysis) PWN Warszawa
BB Popowski (1976) Nauka (Novosibirsk) 61 16
D Sternik P Staszczuk G Grodzicka J Pekalska K Skrzypiec (2004) J. Therm. Anal. Cal. 77 171 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXlt1yntrw%3D Occurrence Handle10.1023/B:JTAN.0000033201.86803.fa
AK Khattak M Afzal M Saleem G Yasmeen R Ahmad (2000) Colloids Surf., A: Physicochem. Engin. Aspects 162 99 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXhtFeltLg%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0927-7757(99)00218-6
J Deng Z Cao B Zhou (1995) Appl. Catal., A: General 132 9 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXpsV2ntr4%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/0926-860X(95)00172-7
A Braithwaite M Cooper (1996) Chromatographia 429 77 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02271059
AL McClellan HF Harnsberger (1967) J. Coll. Int. Sci. 23 577 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF2sXktlKlsLs%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/0021-9797(67)90204-4
P Staszczuk VV Kutarov M Planda (2003) J. Therm. Anal. Cal. 71 445 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXitVygurc%3D Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1022839406755
P Staszczuk D Sternik VV Kutarov (2003) J. Therm. Anal. Cal. 69 23 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1019973303894
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Staszczuk, P., Planda-Czyz, M., Sternik, D. et al. The influence of Mn2+ and Ni2+ ions on the surface properties of the aluminium oxide samples using Q-TG and Q-DTG data. J Therm Anal Calorim 85, 339–349 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-005-7015-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-005-7015-y