Abstract
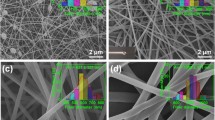
Among the inorganic nanofibers, silica nanofibers are of great interest due to high reactivity and availability of silicon compounds in nature. Sol–gel process is required for electrospinning of silica nanofibers, in which a metal alkoxide is hydrolyzed and the viscosity increased. In this study, silica nanofibrous yarn containing silver nanoparticles were synthesized and electrospun from a mixture of silica sol with an easy spinnable polymer (PVA) as an additive. The silica sol contains tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS), silver nitrate, distilled water, nitric acid and ethanol. Nanofiber yarn was formed through two opposite nozzle methods with the same voltage and diverse polarization. The nanofiber yarn was calcinated to remove the solvent and additive polymer. Consequently, pure silica nanofibrous yarn was produced. FTIR analysis showed entire removal of polyvinyl alcohol from the yarn structure and formation of silan groups. The presence of silver, silica and oxygen was confirmed by EDX and XRD patterns also revealed the presence of silver nanoparticles with a mean crystal size of 18 nm. FESEM images of nanofiber yarn showed the fracture surface on the yarn. Adding silver nitrate into the sol–gel resulted in decrease in nanofiber diameter from 286 to 136 nm. Tensile strength results showed higher strength and modulus of elasticity for the glass nanofiber yarn produced with PVA/sol–gel = 1:4 at 2000 turns per meter (TPM) comparing with other samples by different twist levels and sol–gel ratios. Furthermore, the electrospun glass yarn showed more resistance in acidic media than alkaline media.

Preparation of silica sol contains TEOS, silver nitrate, distilled water, nitric acid and ethanol for synthesize of silica nanofibrous yarn containing silver nanoparticles through electrospun. The presence of silver nitrate into the sol–gel resulted in finer nanofiber with 136 nm.
Highlights
-
Synthesis of silica nanofibrous yarn containing silver nanoparticles through electrospun.
-
The prepared sol-gel resulting in complete separated and finer nanofibers with 136 nm.
-
A higher strength and modulus of elasticity obtained for the PVA: sol-gel=1:4 at 2000 TPM.
-
The prepared yarn showed more resistance in acidic than alkaline media.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shao C, Kim HY, Gong J, Ding B, Lee DR, Park SJ (2003) Fiber mats of poly(vinyl alcohol)/silica composite via electrospinning. Mater Lett 57:1579–1584
Choi SS, Lee SG, Im SS, Kim SH (2003) Silica nanofibers from electrospinning/sol-gel process. J Mater Sci Lett 22: 891–893
Li D, Xia Y (2003) Fabrication of titania nanofibers by electrospinning. Nano Lett 3:555–560
Qiu Y et al. (2014) High-rate, ultralong cycle-life lithium/sulfur batteries enabled by nitrogen-doped graphene. Nano Lett 14:4821–4827
Ramaseshan R et al. (2007) Nanostructured ceramics by electrospinning. J Appl Phys 102:7
Bhuvenesh C Goswami, Rajesh D. Anandjiwala, David M Hall (2004) Textil sizing. CRC Press, Bosa Roca, p 1–19.
Patel AC, Li S, Wang C, Zhang W, Wei Y (2007) Electrospinning of porous silica nanofibers containing silver nanoparticles for catalytic applications. Chem Mater 19:1231–1238
Peltola T, Jokinen M, Veittola S, Rahiala H, Yli-Urpo A (2001) Influence of sol and stage of spinnability on in vitro bioactivity and dissolution of sol–gel-derived SiO2 fibers. Biomaterials 22:589–598
Pirzada T, Arvidson SA, Saquing CD, Shah SS, Khan SA (2012) Hybrid silica-PVA nanofibers via sol-gel electrospinning. Langmuir 28:5834–5844
Shao CL, Kim H, Gong J, Lee D (2002) A novel method for making silica nanofibres by using electrospun fibres of polyvinylalcohol/silica composite as precursor. Nanotechnology 13:635–637
Min KD, Park WH, Youk JH, Kwark YJ (2008) Controlling size and distribution of silver nanoparticles generated in inorganic silica nanofibers using poly(vinyl pyrrolidone). Macromol Res 16:626–630
Kameoka J, Verbridge SS, Liu H, Czaplewski DA, Craighead HG (2004) Fabrication of suspended silica glass nanofibers from polymeric materials using a scanned electrospinning source. Nano Lett 4:2105–2108
Quintero F, Dieste Ó, Penide J, Lusquiños F, Riveiro A, Pou J (2014) Nonconventional production of glass nanofibers by laser spinning J Am Ceram Soc 97:3116–3121
Praeger M, Saleh E, Vaughan A, Stewart WJ, Loh WH (2012) Fabrication of nanoscale glass fibers by electrospinning. Appl Phys Lett 100:2–4
Smit E, Buttner U, Sanderson RD (2005) Continuous yarns from electrospun fibers. Polym (Guildf) 46:2419–2423
Wang X et al. (2008) Continuous polymer nanofiber yarns prepared by self-bundling electrospinning method. Polym (Guildf) 49:2755–2761
Teo WE, Gopal R, Ramaseshan R, Fujihara K, Ramakrishna S (2007) A dynamic liquid support system for continuous electrospun yarn fabrication. Polym (Guildf) 48:3400–3405
Liu CK, Sun RJ, Lai K, Sun CQ, Wang YW (2008) Preparation of short submicron-fiber yarn by an annular collector through electrospinning. Mater Lett 62:4467–4469
Memarian F, Latifi M, Amani-Tehran M (2014) Innovative method for electrospinning of continuous TiO2 nanofiber yarns: Importance of auxiliary polymer and solvent selection. J Ind Eng Chem 20:1886–1891
Ali U, Zhou Y, Wang X, Lin T (2012) Direct electrospinning of highly twisted, continuous nanofiber yarns. J Text Inst 103:80–88
Nakamura R, Goda K (2014) Effect of yarn structure on mechanical properties of twisted yarn composites. MATER SCI Forum 783-786:1554–1559
Hajiani F, Jeddi AAA, Gharehaghaji AA (2012) An investigation on the effects of twist on geometry of the electrospinning triangle and polyamide 66 nanofiber yarn strength. Fibers Polym 13:244–245
Niederberger M, Pinna N (2009) Metal oxide nanoparticles in organic solvents: synthesis, formation, assembly and application. Springer, London
Moazami A, Montazer M, Dolatabadi MK (2016) Tunable functional properties on polyester fabric using simultaneous green reduction of graphene oxide and silver nitrate. Fibers Polym 17:1359–1370
Guin J, Wiederhorn SM (2004) Fracture of silicate glasses: Ductile or brittle? Phys Rev Lett 92:21–24
Yuan Fenglin, Huang Liping (2014) Brittle to ductile transition in densified silica glass. Scientific reports 1:5035
Luo J et al. (2016) Size-dependent brittle-to-ductile transition in silica glass nanofibers. Nano Lett 16:105–113
Matos JC, Avelar I, Martins MBF, Gonalves MC (2017) Green silica vectors for smart textiles. Carbohydr Polym 156:268–275
Hosseinkhani M, Montazer M, Harifi T (2017) Protein and silver nitrate interaction during finer wool production: Enhancing tensile properties along with synthesis of nano silver. J Text Inst 108:78–83
Abdelrahim K, Younis S, Mohamed A, Salmeen K, Mustafa AEMA, Moussa S (2017) Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Rhizopus stolonifer. Saudi J Biol Sci 24:208–216
Misran H, Salim MA, Ramesh S (2018) Effect of Ag nanoparticles seeding on the properties of silica spheres. Ceram Int 44:5901–5908
Chien C, Lin C, Ko C, Tseng S, Shih C (2018) Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles (AgNP) confined to mesostructured silica against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). J Alloy Compd 747:1–7
Babita Devi T, Ahmaruzzaman M (2017) Bio-inspired facile and green fabrication of Au@Ag@AgCl Core–double shells nanoparticles and their potential applications for elimination of toxic emerging pollutants: A green and efficient approach for wastewater treatment. Chem Eng J 317:726–741
Kinsella Michael, Murray Dennis, Crane David, Mancinelli John, Kranjc Mark (2001) Mechanical properties of polymeric composites reinforced with high strength glass fibers. Int SAMPE Tech Conf 33:1644–1657
Siddiqui NA, Sham ML, Tang BZ, Munir A, Kim JK (2009) Tensile strength of glass fibres with carbon nanotube-epoxy nanocomposite coating. COMPOS PART A-APPL S 40:1606–1614
Emery NM, Edward RH (1942) High silica glass. US Patent 2,303,756, December 1, 1942
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kangazian Kangazi, M., Gharehaghaji, A.A. & Montazer, M. Glass nanofibrous yarn through electrospinning along with in situ synthesis of silver nanoparticles. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 88, 528–540 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-018-4848-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-018-4848-y