Abstract
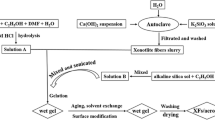
This work introduces a new synthesis procedure for obtaining homogeneous silica hybrid aerogels with carbon nanotube contents up to 2.50 wt.%. The inclusion of nanotubes in the highly porous silica matrix was performed by a two-step sol–gel process, resulting in samples with densities below 80 mg/cm3. The structural analyses (N2 physisorption and SEM) revealed the hierarchical structure of the porous matrix formed by nanoparticles arranged in clusters of 100 and 300 nm in size, specific surface areas around 600 m2/g and porous volumes above 4.0 cm3/g. In addition, a relevant increase on the mechanical performance was found, and an increment of 50% for the compressive strength and 90% for the maximum deformation were measured by uniaxial compression. This reinforcement was possible thanks to the outstanding dispersion of the CNT within the silica matrix and the formation of Si–O–C bridges between nanotubes and silica matrix, as suggested by FTIR. Therefore, the original synthesis procedure introduced in this work allows the fabrication of highly porous hybrid materials loaded with carbon nanotubes homogeneously distributed in the space, which remain available for a variety of technological applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morris C (1999) Silica sol as a nanoglue: flexible synthesis of composite aerogels. Science 284:622–624. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.284.5414.622
Anderson M, Stroud R, Rolison D (2002) Enhancing the activity of fuel-cell reactions by designing three-dimensional nanostructured architectures: catalyst-modified carbon−silica composite aerogels. Nano Lett 2:235–240. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl015707d
Warren S, Perkins M, Adams A et al. (2012) A silica sol–gel design strategy for nanostructured metallic materials. Nat Mater 11:460–467. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat3274
Brinker C, Scherer G (1990) Sol-gel science, the physics and chemistry of sol-gel processing. Academic Press, San Diego
Aegerter M, Leventis N, Koebel M (2011) Aerogels handbook. Springer, New York
Leventis N, Sotiriou-Leventis C, Zhang G, Rawashdeh A (2002) Nanoengineering strong silica aerogels. Nano Lett 2:957–960. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl025690e
de la Rosa-Fox N, Morales-Flórez V, Toledo-Fernández J et al. (2007) Nanoindentation on hybrid organic/inorganic silica aerogels. J Eur Ceram Soc 27:3311–3316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2007.02.209
Maleki H, Durães L, Portugal A (2014) An overview on silica aerogels synthesis and different mechanical reinforcing strategies. J Non Cryst Solids 385:55–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2013.10.017
Ślosarczyk A, Wojciech S, Piotr Z, Paulina J (2015) Synthesis and characterization of carbon fiber/silica aerogel nanocomposites. J Non Cryst Solids 416:1–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2015.02.013
Zhao S, Zhang Z, Sèbe G et al. (2015) Multiscale assembly of superinsulating silica aerogels within silylated nanocellulosic scaffolds: improved mechanical properties promoted by nanoscale chemical compatibilization. Adv Funct Mater 25:2326–2334. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201404368
Tang X, Sun A, Chu C et al. (2017) A novel silica nanowire-silica composite aerogels dried at ambient pressure. Mater Des 115:415–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.11.080
Hou X, Zhang R, Fang D (2018) An ultralight silica-modified ZrO 2 –SiO 2 aerogel composite with ultra-low thermal conductivity and enhanced mechanical strength. Scr Mater 143:113–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2017.09.028
Coleman J, Khan U, Blau W, Gun’ko Y (2006) Small but strong: a review of the mechanical properties of carbon nanotube–polymer composites. Carbon 44:1624–1652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2006.02.038
Esawi A, Farag M (2007) Carbon nanotube reinforced composites: potential and current challenges. Mater Des 28:2394–2401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2006.09.022
Liu Y, Ramirez C, Zhang L et al. (2017) In situ direct observation of toughening in isotropic nanocomposites of alumina ceramic and multiwall carbon nanotubes. Acta Mater 127:203–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2017.01.024
Esquivias L, Piñero M, Morales-Flórez V, de la Rosa-Fox N (2011). In: Aegerter M, Leventis N, Koebel M (eds) Aerogels Handbook, Springer, New York
Berguiga L, Bellessa J, Vocanson F et al. (2006) Carbon nanotube silica glass composites in thin films by the sol–gel technique. Opt Mater 28:167–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2005.03.002
Eder D (2010) Carbon nanotube−inorganic hybrids. Chem Rev 110:1348–1385. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr800433k
López A, Ureña A, Rams J (2011) Wear resistant coatings: silica sol–gel reinforced with carbon nanotubes. Thin Solid Films 519:7904–7910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2011.05.076
Yusof Y, Johan M (2014) Concentration-dependent properties of amorphous carbon nanotube/silica composites via the sol–gel technique. CrystEngComm 16:8570–8575. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ce01083c
Loo S, Idapalapati S, Wang S et al. (2007) Effect of surfactants on MWCNT-reinforced sol–gel silica dielectric composites. Scr Mater 57:1157–1160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2007.07.040
OH t, Choi C (2010) Comparison between SiOC thin film by plasma enhance chemical vapor deposition and SiO2 thin film by fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. J Korean Phys Soc 56:1150–1155. https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.56.1150
Hassan M, Takahashi T, Koyama K (2013) Preparation and characterisation of SiOC ceramics made from a preceramic polymer and rice bran. J Eur Ceram Soc 33:1207–1217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2012.11.027
Esquivias L, Rodriguez-Ortega J, Barrera-Solano C, De La Rosa-Fox N (1998) Structural models of dense aerogels. J Non Cryst Solids 225:239–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-3093(98)00123-9
Morales-Flórez V, Piñero M, de la Rosa-Fox N et al. (2008) The cluster model: a hierarchically-ordered assemblage of random-packing spheres for modelling microstructure of porous materials. J Non Cryst Solids 354:193–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2007.07.061
Amonette J, Matyáš J (2017) Functionalized silica aerogels for gas-phase purification, sensing, and catalysis: a review. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 250:100–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.04.055
Zamora-Ledezma C, Añez L, Primera J et al. (2008) Photoluminescent single wall carbon nanotube–silica composite gels. Carbon 46:1253–1255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2008.04.020
Vila M, Hueso J, Manzano M et al. (2009) Carbon nanotubes—mesoporous silica composites as controllable biomaterials. J Mater Chem 19:7745. https://doi.org/10.1039/b909628k
Bargozin H, Amrikhani L, Moghaddas JS, Ahadian MM (2010) Synthesis and applications of silica aerogel-MWCNT nanocomposites for adsorption of organic pollutants. Trans F 17:122–132
Duque J, Gupta G, Cognet L et al. (2011) New route to fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube/silica nanocomposites: balancing fluorescence intensity and environmental sensitivity. J Phys Chem C 115:15147–15153. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp2012107
Shearer C, Cherevan A, Eder D (2014) Application and future challenges of functional nanocarbon hybrids. Adv Mater 26:2295–2318. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201305254
Sivakumar R, Guo S, Nishimura T, Kagawa Y (2007) Thermal conductivity in multi-wall carbon nanotube/silica-based nanocomposites. Scr Mater 56:265–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2006.10.025
Ślosarczyk A (2017) Synthesis and characterization of silica aerogel-based nanocomposites with carbon fibers and carbon nanotubes in hybrid system. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 84:16–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4470-4
Hamilton C, Chavez M, Duque J et al. (2010) Carbon nanomaterials in silica aerogel matrices. MRS Proceedings 1258. https://doi.org/10.1557/proc-1258-r05-11
Duque J, Hamilton C, Gupta G et al. (2011) Fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube aerogels in surfactant-free environments. ACS Nano 5:6686–6694. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn202225k
Chernov A, Predein A, Danilyuk A et al. (2016) Optical properties of silica aerogels with embedded multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Phys Status Solidi (b) 253:2440–2445. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.201600326
Menshutina N, Ivanov S, Tsygankov P, Khudeev I (2017) Synthesis and characterization of composite materials “aerogel-MWCNT”. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 84:382–390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4474-0
ASTM D7012-14e1 (2014) Standard test methods for compressive strength and elastic moduli of intact rock core specimens under varying states of stress and temperatures. ASTM International, West Conshohocken PA USA
Dervin S, Lang Y, Perova T et al. (2017) Graphene oxide reinforced high surface area silica aerogels. J Non Cryst Solids 465:31–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2017.03.030
Acknowledgements
Dr. Miguel Castillo is acknowledged for their wise advises and original ideas. Mr. Alejandro Jurado-Jiménez is acknowledged for his contributions to the starting of this work during his stage at our laboratory. Dr. Alberto Santos and Mr. José Francisco Hidalgo Ramírez are acknowledged for their help in the experimental setup. The technical staff of the characterisation services of the CITIUS (Universidad de Sevilla) is also acknowledged. J.A.D.F. thanks the grant from VI Plan Propio de la Universidad de Sevilla for 'starting researchers', M.V.R.P. thanks the 'Programa de contratación de personal técnico de apoyo a la I+D+I 2017' from the Junta de Andalucía (Spain) and V.M.F thanks the postdoctoral grant from the 'V Plan Propio de la Universidad de Sevilla'. This work has been financed by the support of the Junta de Andalucía (Spain) to the research group TEP-115 (Spain) and by the 'Plan Propio de Investigación (I.5 Ayudas uso SGI)' of the Universidad de Sevilla.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Highlights
-
Homogeneous SiO2–carbon nanotube monolithic aerogels were obtained by rapid controlled gelation.
-
The carbon nanotubes were homogeneously dispersed in the highly porous silica matrix.
-
The hybrid aerogels kept outstanding structural features and densities below 80 mg/cm3 in all cases.
-
The Si–O–C covalent bonding between carbon nanotubes and silica matrix was prompted by FTIR.
-
The carbon nanotubes turned the aerogels into 100% stiffer and 60% more deformable materials.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piñero, M., Mesa-Díaz, M.d.M., de los Santos, D. et al. Reinforced silica-carbon nanotube monolithic aerogels synthesised by rapid controlled gelation. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 86, 391–399 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-018-4645-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-018-4645-7