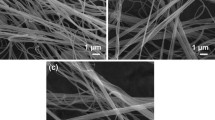
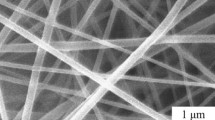
Abstract
Fast and large-scale production of mesoporous titania nanofibers was achieved by solution blow spinning. The blow spinning setup provides a method to prepare titania nanofibers in a safe and scalable way without using a high-voltage electric field. Titania microstructure and porosity can be modified by adding a suitable template, such as pluronic polymers. The blow spun titania nanofibers had a good performance on the photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline and could be easily removed from the tetracycline aqueous solution due to their large aspect ratio. Solution blow spinning method has a great potential for the large-scale production of titania nanofibers with good photocatalytic properties.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang W, Zhu R, Ke L, Liu X, Liu B, Ramakrishna S (2010) Small 6:2176–2182
Chuangchote S, Jitputti J, Sagawa T, Yoshikawa S (2009) ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 1:1140–1143
Zheng Z, Liu H, Ye J, Zhao J, Waclawik ER, Zhu H (2010) J Mol Catal A-Chem 316:75–82
Li D, McCann JT, Gratt M, Xia YN (2004) Chem Phys Lett 394:387–391
Caruso RA, Schattka JH, Greiner A (2001) Adv Mater 13:1577–1579
Kim S-W, Han TH, Kim J, Gwon H, Moon H-S, Kang S-W, Kim SO, Kang K (2009) Acs Nano 3:1085–1090
Li D, Xia YN (2003) Nano Lett 3:555–560
Li D, Xia YN (2004) Nano Lett 4:933–938
Yang G, Chang W, Yan W (2014) J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 69:473–479
Qin D, Liang G, Gu A, Yuan L (2013) J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 67:451–457
Luo CJ, Stoyanov SD, Stride E, Pelan E, Edirisinghe M (2012) Chem Soc Rev 41:4708–4735
Vasquez H, Gutierrez H, Lozano K, Leal G (2015) J Eng Fiber Fabr 10:129–136
Bao N, Wei Z, Ma Z, Liu F, Yin GJ (2010) J Hazar Mater 174:129–136
Liu H, Zhou X, Chen Y, Li T, Pei S (2014) J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 71:102–108
Medeiros ES, Glenn GM, Klamczynski AP, Orts WJ, Mattoso LHC (2009) J Appl Polym Sci 113:2322–2330
Cheng B, Tao X, Shi L, Yan G, Zhuang X (2014) Ceram Int 40:15013–15018
Li L, Kang W, Zhuang X, Shi J, Zhao Y, Cheng B (2015) Mater Lett 160:533–536
Chattopadhyay S, Saha J, De G (2014) J Mater Chem A 2:19029–19035
Abdal-hay A, Hamdy AS, Lim JH (2014) Ceram Int 40:15403–15409
Lisboa Costa D, Santos Leite R, Araujo Neves G, Navarro de Lima Santana L, Souto Medeiros E, Rodrigues Menezes R (2016) Mat Lett 183:109–113
Abdal-hay A, Hamdy MAS, Khalil KA (2015) ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:13329–13341
Costa RGF, Brichi GS, Ribeiro C, Mattoso LHC (2016) Polym Bull. doi:10.1007/s00289-016-1635-1
Li H, Zhang W, Pan W (2011) J Am Ceram Soc 94:3184–3187
Kartini I, Meredith P, Da Costa JCD, Lu GQ (2004) J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 31:185–189
Lopez R, Gomez R (2012) J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 61:1–7
Zhang QH, Gao L, Guo JK (2000) Appl Catal B-Environ 26:207–215
Jang HD, Kim SK, Kim SJ (2001) J Nanopart Res 3:141–147
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank CONACYT-Mexico for its support through CB-239354 project and Mario Hernandez for his 3D model of the spinneret. R. Cruz-Silva thanks the support of the Center of Innovation Program from Japan Science and Technology Agency, JST.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gonzalez-Abrego, M., Hernandez-Granados, A., Guerrero-Bermea, C. et al. Mesoporous titania nanofibers by solution blow spinning. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 81, 468–474 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-016-4210-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-016-4210-1