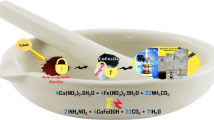
Abstract
Iron-tungsten oxide nanospinel have been prepared by two methods: microwave combustion method and Pechini method. The W-Fe bimetallic ferberite was successfully synthesized by microwave-assisted techniques. The resultant magnetic nanocomposites were characterized by thermal analysis, X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray, transmission electron microscopy, nitrogen adsorption, and magnetic properties measurement system. The prepared ferberite nanoparticles (50–65 nm) using microwave combustion method were pure monoclinic ferberite. The ferberite nanoparticles showed ferrimagnetic hysteresis loop with values of saturation magnetization and coercivity of 4.829 A.m2/Kg and 0.0312 T, successively.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cm-Dresdner H, Escobar C (1968) Zeitschrift für Kristallographie. Crystalline Materials 127:61–72
Hu W, Zhao Y, Liu Z, Dunnill CW, Gregory DH, Zhu Y (2008) Nanostructural evolution: from one-dimensional tungsten oxide nanowires to three-dimensional ferberite flowers. Chem Mater 20:5657–5665
Sakharkar MV, Sharma J, Ray RK, Biswas AK (1997) Characterization of synthesized wolframite minerals and their leach residues. Hydrometallurgy 44:65–69
Buhl J-C, Willgallis A (1984) Kinetics and mechanism of Hübnerite (MnWO4) and Ferberite (FeWO4) crystallization under hydrothermal conditions. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung A - A Journal of Physical Sciences 39:963–965
Buhl J-C, Willgallis A (1985) On the hydrothermal synthesis of wolframite. Chem Geol 48:93–102
Buhl J-C, Willgallis A (1986) The low-temperature crystallization of (Fe,Mn)WO4 (wolframite), (Zn,Fe)WO4 (sanmartinite) and (Zn,Mn)WO4 solid solutions under hydrothermal conditions. Chem Geol 56:271–279
Kloprogge JT, Weier ML, Duong LV, Frost RL (2004) Microwave-assisted synthesis and characterisation of divalent metal tungstate nanocrystalline minerals: ferberite, hübnerite, sanmartinite, scheelite and stolzite. Mater Chem Phys 88:438–443
Yu S, Liu B, Mo M, Huang J, Liu X, Qian Y (2003) General synthesis of single-crystal tungstate nanorods/nanowires: a facile, low-temperature solution approach. Adv Funct Mater 13:639–647
Zhang J, Wang Y, Li S, Wang X, Huang F, Xie A, Shen Y (2011) Controlled synthesis, growth mechanism and optical properties of FeWO4 hierarchical microstructures. CrystEngComm 13:5744–5750
Cao X, Chen Y, Jiao S, Fang Z, Xu M, Liu X, Li L, Pang G, Feng S (2014) Magnetic photocatalysts with a p–n junction: Fe3O4 nanoparticle and FeWO4 nanowire heterostructures. Nanoscale 6:12366–12370
He G-L, Chen M-J, Liu Y-Q, Li X, Liu Y-J, Xu Y-H (2015) Hydrothermal synthesis of FeWO4-graphene composites and their photocatalytic activities under visible light. Appl Surf Sci 351:474–479
Laishram K, Mann R, Malhan N (2012) A novel microwave combustion approach for single step synthesis of α-Al2O3 nanopowders. Ceramics International 38:1703–1706
Zaki T, Kabel KI, Hassan H (2012) Preparation of high pure α-Al2O3 nanoparticles at low temperatures using Pechini method. Ceram Int 38:2021–2026
Zaki T, Kabel KI, Hassan H (2012) Using modified Pechini method to synthesize α-Al2O3 nanoparticles of high surface area. Ceram Int 38:4861–4866
Yu S-H, Liu B, Mo M-S, Huang J-H, Liu X-M, Qian Y-T (2003) General synthesis of single-crystal tungstate nanorods/nanowires: a facile, low-temperature solution approach. Adv Funct Mater 13:639–647
Yu F, Schanz U, Schmidbauer E (1993) Single crystal growth of FeWO4 and CuWO4. J Cryst Growth 132:606–605
Zhou Y-X, Yan H-B, Zang Q, Gong J-Y, Liu S-J, Yu S-H (2009) Hierarchical FeWO4 microcrystals: solvothermal synthesis and their photocatalytic and magnetic properties. Inorg Chem 48:1082–1090
Almeida MAP, Cavalcante LS, Morilla-Santos C, Lisboa Filho PN, Beltrán A, Andrés J, Gracia L, Longo E (2012) Electronic structure and magnetic properties of FeWO4 nanocrystals synthesized by the microwave-hydrothermal method. Mater Charact 73:124–129
Salamanca M, Licea YE, Echavarría A, Faro Jr. AC, Palacio LA (2009) Hydrothermal synthesis of new wolframite type trimetallic materials and their use in oxidative dehydrogenation of propane. Phys Chem Chem Phys 11:9583–9591
Miller, FA (2003) Infrared Spectra of Inorganic Materials, Chapter 11, course notes on the interpretation of infrared and Raman spectra. In: Mayo, DW, Miller, FA, Hannah, RW (eds.), John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, New Jersey, USA, pp 297–354.
Thommes M (2010) Physical adsorption characterization of nanoporous materials. Chemie Ingenieur Technik 82:1059–1073
Guillen R, Regnard JR (1985) Magnetic properties of natural and synthetic wolframites FexMn1-xWO4. Phys Chem Miner 12:246–254
Rajagopal S, Bekenev VL, Nataraj D, Mangalaraj D, Yu. Khyzhun O (2010) Electronic structure of FeWO4 and CoWO4 tungstates: first-principles FP-LAPW calculations and X-ray spectroscopy studies. J Alloys Compd 496:61–68
Angadi VJ, Rudraswamy B, Sadhana K, Praveena K (2016) Structural and magnetic properties of manganese zinc ferrite nanoparticles prepared by solution combustion method using mixture of fuels. J Magn Magn Mater 409:111–115
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Maghrabi, H.H., Zaki, T. A facile synthesis for magnetic ferberite nanostructured material. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 81, 436–441 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-016-4195-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-016-4195-9