Abstract
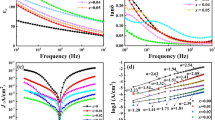
(LaBa)Co2O5+δ (LBCO) thin films were successfully fabricated on Si (001) substrates by polymer-assisted deposition method. Microstructures were examined by X-ray diffraction technique, which confirmed the films were a single phase, pseudo cubic structure. The electrical transport properties of the films were investigated by the temperature dependence of films resistance, which suggested that LBCO films have typical semiconductor properties. After circle tests, the oxygen–hydrogen response rate did not show obvious variation in the specific temperature environment of 580 °C. This demonstrates that the LBCO thin films have a superior stability in both oxygen and hydrogen (6 % H2, 94 % N2) environment. Simultaneously, the drastic changes of films resistance (from ~106 to ~102 Ω) with the switch of redox (O2–H2) environment within such a short time (~2.2 s) indicated that LBCO films have an excellent oxygen sensitive property and extraordinary fast surface exchange rate.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kawada T, Suzuki J, Sase M, Kaimai A, Nigara Y (2002) J ElectrochemSoc 149:252–259
Yamamoto. ElectrochimActa 45, 2423–2435 (2000)
Fergus JW (2003) J Mat Sci 38:4259–4263
Xu YL, Zhou XH, Sorensen OT (2000) Sens Actuat B-Chem 65:2–4
Liu J, Liu M, Collins G, Chen CL et al (2010) Chem Mat 22:799–802
He J, Jiang JC, Liu J, Liu M, Collins G, Ma CR, Chen CL (2011) Thin Solid Films 519:4371–4376
Yuan Z, Liu J, Weaver J, Chen CL, Jiang JC, Lin B et al (2007) Appl Phys Lett 90:202901–202905
Jia QX, Cleskey TM, Burrell AK, Lin Y, Collis GE, Wang H et al (2004) Nat Mater 3:529–533
Lin Y, Lee J-S, Wang H, Li Y, Foltyn SR, Jia QX (2004) Appl Phys Lett 85:5007–6001
Burrell AK, McCleskey TM, Jia QX (2008) Chem Commun 11:1271–1275
Dawley JT, Clem PG (2002) Appl Phys Lett 81:3028–3030
Dechakupt T, Yang GY, Randall CA (2008) J Am Ceram Soc 91:1845–1850
Bretos I, Schneller T, Waser R, Hennings DF, Halder S, Thomas F (2010) J Am Ceram Soc 93:506–515
Jiang JC, Meletis EI, Yuan Z, Liu J, Weaver J, Chen CL et al (2008) J Nano Res 1:59–63
Bao LJ, Ryley J, Li ZG, Wilker C, Zhang L, Reardon D et al (2009) Appl Phys Lett 106:114114–114119
Shin J, Goyal A, Jesse S, Kim DH (2009) Appl Phys Lett 94:252903
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (Nos. ZYGX2011J028 and ZYGX2012J037), the Guangdong Innovative Research Team Program (No. 201001D0104713329) and the Cooperation Project in Industry, Education and Research of Guangdong Province and Ministry of Education of PR China (No. 2012B091100097).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, D., Pan, T., Feng, D. et al. The oxygen sensitive properties of (LaBa)Co2O5+δ thin films fabricated by polymer-assisted deposition technique. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 71, 464–469 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-014-3395-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-014-3395-4