Abstract
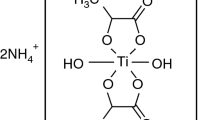
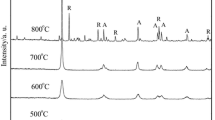
A new study of the preparation of nanocrystalline titanium dioxide (TiO2) fibers is reported in the paper, which were prepared by sol–gel process with titanium acetate [Ti(CH3COO)4] as precursor. After that, centrifugal spinning and steam atmosphere heat-treatment were used to obtain final fibers. Here, the molecule structure of precursor was analyzed and the TiO2 fibers obtained were characterized. Additionally, the effects of the silica (SiO2) doping were discussed in this paper. By the Fourier transformation infrared spectrum analysis, the chain structure of –O–Ti–O–Ti–O– was confirmed in the Ti(CH3COO)4 precursor, as a result the precursor spinning solution showed a good spinning performance. And the pyrolysis process of precursor fibers was analyzed with the help of DSC–TG method. The phase of TiO2 fibers obtained after heat-treatment with steam atmosphere was characterized mainly by the X-ray diffractometer (XRD), from the XRD curves, the result that the SiO2 doping can efficiently inhibit the grain growth of TiO2 fibers could also be verified. The microstructure of the TiO2 fibers was observed by scanning electron microscope, which showed that diameter of TiO2 fibers obtained with excellent continuity are from 5 to 10 μm. At last, the photocatalytic property of TiO2 fibers was also tested.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fujishima A, Honda K (1972) Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature 238(5358):37–38
Sato S, Kunimatsu K (1984) Infrared spectroscopic study of platinized titania photocatalysts. J Phys Chem 88(2):175–177
Baiju KV, Shukla S, Sandhya KS et al (2007) Photocatalytic activity of sol–gel-derived nanocrystalline titania. J Phys Chem C 111(21):7612–7622
Chen YL, Chang YH, Huang JL et al (2012) Light scattering and enhanced photoactivities of electrospun titania nanofibers. J Phys Chem C 116(5):3857–3865
Mor GK, Shankar K, Paulose M et al (2005) Enhanced photocleavage of water using titania nanotube arrays. Nano Lett 5(1):191–195
Kisch H, Sakthivel S, Janczarek M et al (2007) A low-band gap, nitrogen-modified titania visible-light photocatalyst. J Phys Chem C 111(30):11445–11449
Chen HS, Huang SH, Perng TP (2012) Preparation and characterization of molecularly homogeneous silica–titania film by sol–gel process with different synthetic strategies. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4(10):5188–5195
Hüsing N, Launay B, Doshi D et al (2002) Mesostructured silica–titania mixed oxide thin films. Chem Mater 14(6):2429–2432
Chi B, Jin T (2007) Synthesis of titania nanostructure films via TiCl4 evaporation–deposition route. Cryst Growth Des 7(4):815–819
Yue L, Gao W, Zhang D et al (2006) Colloids seeded deposition: growth of titania nanotubes in solution. J Am Chem Soc 128(34):11042–11043
Tachikawa T, Tojo S, Fujitsuka M et al (2006) Photoinduced charge separation in titania nanotubes. J Phys Chem B 110(29):14055–14059
Khan MA, Yang OB (2009) Optimization of silica content in initial sol–gel grain particles for the low temperature hydrothermal synthesis of titania nanotubes. Cryst Growth Des 9(4):1767–1774
Li D, Xia Y (2003) Fabrication of titania nanofibers by electrospinning. Nano Lett 3(4):555–560
Chae WS, Lee SW, Kim YR (2005) Templating route to mesoporous nanocrystalline titania nanofibers. Chem Mater 17(12):3072–3074
Retuert J, Quijada R, Arias V (1998) Porous titania obtained through polymer incorporated composites. Chem Mater 10(12):3923–3927
Parker A, Marszewski M, Jaroniec M (2013) Microwave-assisted synthesis of porous carbon–titania and highly crystalline titania nanostructures. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5(6):1948–1954
Torma V, Peterlik H, Bauer U et al (2005) Mixed silica titania materials prepared from a single-source sol–gel precursor: a time-resolved SAXS study of the gelation, aging, supercritical drying, and calcination processes. Chem Mater 17(12):3146–3153
Yi DK, Yoo SJ, Kim DY (2002) Spin-on-based fabrication of titania nanowires using a sol–gel process. Nano Lett 2(10):1101–1104
Padmanabhan SC, Pillai SC, Colreavy J et al (2007) A simple sol–gel processing for the development of high-temperature stable photoactive anatase titania. Chem Mater 19(18):4474–4481
Liu H, Yang W, Ma Y et al (2003) Synthesis and characterization of titania prepared by using a photoassisted sol–gel method. Langmuir 19(7):3001–3005
Kaewsaenee J, Visal-athaphand P, Supaphol P et al (2011) Effects of magnesium and zirconium dopants on characteristics of titanium(IV) oxide fibers prepared by combined sol–gel and electrospinning techniques. Ind Eng Chem Res 50(13):8042–8049
Liu G, Liu Y, Yang G et al (2009) Preparation of titania–silica mixed oxides by a sol–gel route in the presence of citric acid. J Phys Chem C 113(21):9345–9351
Shafi KVPM, Ulman A, Yan X et al (2001) Sonochemical preparation of silane-coated titania particles. Langmuir 17(5):1726–1730
Seriani N, Pinilla C, Cereda S et al (2012) Titania–silica Interfaces. J Phys Chem C 116(20):11062–11067
Chen HS, Huang SH, Perng TP (2012) Preparation and characterization of molecularly homogeneous silica–titania film by sol–gel process with different synthetic strategies. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4(10):5188–5195
Simons WW (1978) Sadtler handbook of infrared spectra. Sadtler research laboratories
Heyi L, Yan C, Shiguang P, Guishuang L, Jinqiang L (2013) Preparation of nanocrystalline titaniumdioxide fibers using sol–gel method and centrifugal spinning. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 65:443–451
Licun M, Jianjun Y, Hongxi D, Zhijun Z (2003) Preparation of nano-crystal TiO2 porous thin films and their photocatalytic performance. Chin J Catal 24(7):553–557
Ligun M, Jianjun Y et al (2011) Studies on photochemical and photocatalytic synergistic decoloration of brilliant red X-3B solution. Chin J CataI 22(2):181–184
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Zhou, X., Chen, Y. et al. Titanium dioxide fibers prepared by sol–gel process and centrifugal spinning. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 71, 102–108 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-014-3332-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-014-3332-6