Abstract
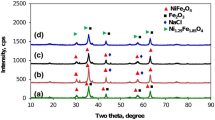
Magnetic nickel ferrite (NiFe2O4) was prepared by sol–gel process and calcined in the 2.45 GHz singlemode microwave furnace to synthesize nickel nanopowder. The sol–gel method was used for the processing of the NiFe2O4 powder because of its potential for making fine, pure and homogeneous powders. Sol–gel is a chemical method that has the possibility of synthesizing a reproducible material. Microwave energy is used for the calcining of this powder and the sintering of the NiFe2O4 samples. Its use for calcination has the advantage of reducing the total processing time and the soak temperature. In addition to the above combination of sol–gel and microwave processing yields to nanoscale particles and a more uniform distribution of their sizes. X-ray diffraction, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy and vibrating sample magnetometer were carried out to investigate structural, elemental, morphological and magnetic aspects of NiFe2O4. The results showed that the mean size and the saturation magnetization of the NiFe2O4 nanoparticles are about 30 nm and 55.27 emu/g, respectively. This method could be used as an alternative to other chemical methods in order to obtain NiFe2O4 nanoparticles.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xu Q , Wei Y, Liu Y, Ji X, Yang L , Gu M (2009) Solid State Sci 11(2) 472
Tian MB (2001) Magnetic material. Tsinghua University Press, Beijing
Pileni MP (2001) Adv Funct Mater 5:323
Cheng FY, Su CH, Yang YS, Yeh CS, Tsa CY, Wu CL (2005) Biomaterial 26:729
Song Q, Zhang ZJ (2004) J Am Chem Soc 126:6164
Kodama RH, Berkowitz AE, Niff EJ Mc, Foner S (1996) Phys Rev Lett 77:394
Shafi KVPM, Koltypin Y, Gedanken A, Prozorov R, Balogh J, Lendvai J, Felner I (1997) J Phys Chem B 101:6409
Calvin S, Carpenter EE, Harris VG, Morrison SA (2002) Phys Rev B 66:224405
Jonsson T, Svedlindh P, Hansen MF (1998) Phys Rev Lett 81:3976
Otero JG, Porto M, Rivas J, Bunde A (2000) Phys Rev Lett 84:167
Kodama RH, Berkowitz AE, McNiff EJ, Foner S (1996) Phys Rev Lett 77:394
Nabiyouni G, Fesharaki MJ, Zolotovsky AA (2012) Task Quart 15:107
Gabal MA, Reda ME, Angari YMA (2012) J Magn Magn Mater 324:2258
Phadatare MR, Khot VM, Salunkhe AB, Thorat ND, Pawar SH (2012) J Magn Magn Mater 324:770
Ramakrishna K, Ravinder D, Vijaya Kumar K, Abraham Lincon Ch (2012) World J Condens Mater Phys 2:153
Zabotto FL, Gualdi AJ, Eiras JA, de Oliveira AJA, Garcia D (2012) Mater Res 5(3):428
Sivakumar P, Ramesh R, Ramanand A, Ponnusamy S, Muthamizhchelvan C (2012) Mater Lett 66:314
Chen D, Liu H (2012) Mater Lett 72:95
Ilmars Z, Gundega H, Maris K, Janis G, Mikhail M (2012) Mater Sci 18:1392
Chen DH, He X (2001) Mater Res Bull 36:1369
Sankaranarayanan VK, Sreekumar C (2003) Curr Appl Phys 3:205
Shahmirzaei M, Ebrahimi AS, Dehghan R (2011) Mod Phys Lett B 25:855
Bhavikatti AM, Kulkarni S, Lagashetty A (2011) Int J Eng Sci Tech 3:687
Gedye R, Smith F, Westaway K, Ali H, Baldisera L, Laberge L, Rousell J (1986) Tetra Lett 27:279
Giguere RJ, Bray TL, Duncan SM, Majetich G (1986) Tetra Lett 27:4945
Nathani H, Gubbala S, Misra RDK (2005) Mater Sci Eng B 121(1–2):126
Kodama RH, Berkowitz AE, McNiff JEJ, Foner S (1996) Phys Rev Lett 77(2):394
Manova E, Tsoncheva T, Estournes C, Paneva D, Tenchev K, Mitov I, Petrov L (2006) Appl Catal A 300(2):170
Li GY, Jiang YR, Huang KL, Ding P, Chen J (2008) J Alloys Compd 466(1–2):451
Pazik R, Piaseck E, Małecka M, Kessler VG, Idzikowski B, Sniadeckid Z, Wiglusz RJ (2013) RSC Adv 3:12230
Sivakumar P, Ramesh R, Ramanand A, Ponnusamy S, Muthamizhchelvan C (2011) Mater Lett 65:1438
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Brain Korea 21 Program of South Korean Research Foundation and Changwon National University, South Korea. One of the authors Ramakrishna Reddy Rajuru thanks University Grants Commission (UGC), New Delhi for providing Basic Science Research (BSR) faculty fellowship during this time when part of the work has been carried out.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Penchal Reddy, M., Madhuri, W., Sadhana, K. et al. Microwave sintering of nickel ferrite nanoparticles processed via sol–gel method. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 70, 400–404 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-014-3295-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-014-3295-7