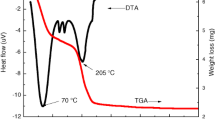
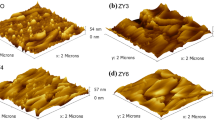
Abstract
Yttrium-doped ZnO gel was spin-coated on the SiO2/Si substrate. The as-prepared ZnO:Y (YZO) thin films then underwent a rapid thermal annealing (RTA) process conducted at various temperatures. The structural and photoluminescence characteristics of the YZO films were discussed thereafter. Our results indicated that the grain size of YZO thin films being treated with various annealing temperatures became smaller as compared to the ones without being doped with yttrium. Furthermore, unlike other ZnO films, the grains of YZO thin films appeared to separate from one another rather than aggregating together as both types of the films were annealed under the same environment. The photoluminescence characteristic measured showed that the UV emission was the only radiation obtained. However, the UV emission intensity of YZO thin film was much stronger than that of the ZnO thin film after annealing them with the same condition. It was also found that the intensity increased with an increase in the annealing temperature, which was caused by the exciton generated and the texture surface of the YZO thin film.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nakamura S, Fasol G (1997) The blue laser diode. Springer, Berlin
Sheu JK, Chang SJ, Kuo CH, Su YK, Wu LW, Lin YC, Lai WC, Tsai JM, Chi GC, Wu RK (2003) IEEE Photonics Technol Lett 15:18–20
Rodrigues SCP, d’Eurydice MN, Sipahi GM, da Silva EF Jr (2005) Microelectronics 36:1002
Ramanachalam MS, Rohatgi A, Carter WB, Schaffer JP, Gupta TK (1995) J Electron Mater 24:413–419
Martin SJ, Schwartz SS, Gunshor RL, Pieret RF (1983) J Appl Phys 54:561–569
Tsukazaki A, Ohtomo A, Onuma T, Ohtani M, Makino T, Sumiya M, Ohtani K, Chichinbu SF, Fuke S, Segawa Y, Ohno H, Koinuma H, Kawasaki M (2005) Nature Mater 1:42–46
Hoffman RL, Norris BJ, Wagera JF (2003) Appl Phys Lett 82:733–735
Yoon KH, Cho JY (2000) Mater Res Bull 35:39–46
Fu Z, Lin B, Zu J (2002) Thin Solid Films 402:302–306
Nakanishi Y, Miyake A, Kominami H, Aoki T, Hatanaka Y, Shimaoka G (1999) Appl Surf Sci 142:233–236
Bae SH, Lee SY, Kim HY, Im S (2001) Opt Mater 17:327–330
Wang YG, Lau SP, Zhang XH, Lee HW, Yu SF, Tay BK, Hng HH (2003) Chem Phys Lett 375:113–118
Sakurai K, Kanehiro M, Nakahara K, Tanabe T, Fujita S (2000) J Cryst Growth 209:522–525
Lim J, Shin K, Kim HW, Lee C (2004) J Lumin 109:181–185
Bethke S, Pan H, Wessels BW (1998) Appl Phys Lett 52:138–140
Minami T, Nanto H, Takata S (1983) Thin Solid Films 109:379–384
Zhang Y, Lin B, Fu Z, Liu C, Han W (2006) Opt Mater 28:1192–1196
Chatterjee A, Shen CH, Ganguly A, Chen LC, Hsu CW, Hwang JY, Chen KH (2004) Chem Phys Lett 391:278–282
Yang Y, Yan H, Fu Z, Yang B, Xia L, Xu Y, Zuo J, Li F (2006) Solid State Commun 138:521–525
Agyeman O, Xu CN, Shi W, Zheng XG, Suzuki M (2002) Jpn J Appl Phys 41:666–669
Kuo SY, Chen WC, Cheng CP (2006) Superlattices Microstruct 39:162–170
Abou-Helal MO, Seeber WT (1997) J Non Cryst Solids 218:139–145
Wu GS, Zhuang YL, Lin ZQ, Yuan XY, Xie T, Zhang LD (2006) Physica E 31:5–8
Minami T, Yamamoto T, Miyata T (2000) Thin Solid Films 366:63–68
Kaur R, Singh AV, Sehrawat K, Mehra NC, Mehra RM (2006) J Non Cryst Solids 352:2565–2568
Kaur R, Singh AV, Mehra RM (2005) Physica Status Solidi A 202:1053–1059
Yu Q, Fu W, Yu C, Yang H, Wei R, Sui Y, Liu S, Liu Z, Li M, Wang G, Shao C, Liu Y, Zou G (2007) J Phys D Appl Phys 40:5592–5597
Hsieh PT, Chen YC, Kao KS, Lee MS, Cheng CC (2007) J Eur Ceram Soc 27:3815–3818
Futsuhara M, Yoshioka K, Takai O (1998) Thin Solid Films 322:274–281
Islam MN, Ghosh TB, Chopra KL, Acharya HN (1996) Thin Solid Films 280:20–25
Kim YS, Tai WP, Shu SJ (2005) Thin Solid Films 491:153–160
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsieh, PT., Chuang, R.WK., Chang, CQ. et al. Optical and structural characteristics of yttrium doped ZnO films using sol–gel technology. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 58, 42–47 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-010-2352-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-010-2352-0